The present progressive tense, also known as the present continuous tense, is a key part of English grammar.
It’s used to describe actions happening right now or around the current moment.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, understanding this tense can boost your communication skills.
This article explains the present progressive tense in a beginner-friendly way, with real-life examples, clear explanations, and practical tips.
By the end, you’ll know how to form, use, and avoid common mistakes with this versatile tense.
Let’s dive into the present progressive tense and explore its structure, conjugation, and more!
What Is the Present Progressive Tense?

The present progressive tense describes actions that are ongoing at the moment of speaking or temporary actions happening around now. For example, “I am writing this article” shows an action in progress. It’s also used for future plans or changing situations, like “She is moving next week.” This tense combines the verb “to be” (am, is, are) with a verb ending in -ing. It’s dynamic and emphasizes action over completion, making it perfect for vivid descriptions.
How to Recognize the Present Progressive Tense?

To spot the present progressive tense, look for:
- A form of “to be” (am, is, are) as a helping verb.
- A main verb ending in -ing (e.g., running, singing).
- Sentences describing actions happening now or temporarily (e.g., “They are studying for exams”).
- Contexts like ongoing actions, future plans, or temporary situations.
Structure of a Sentence
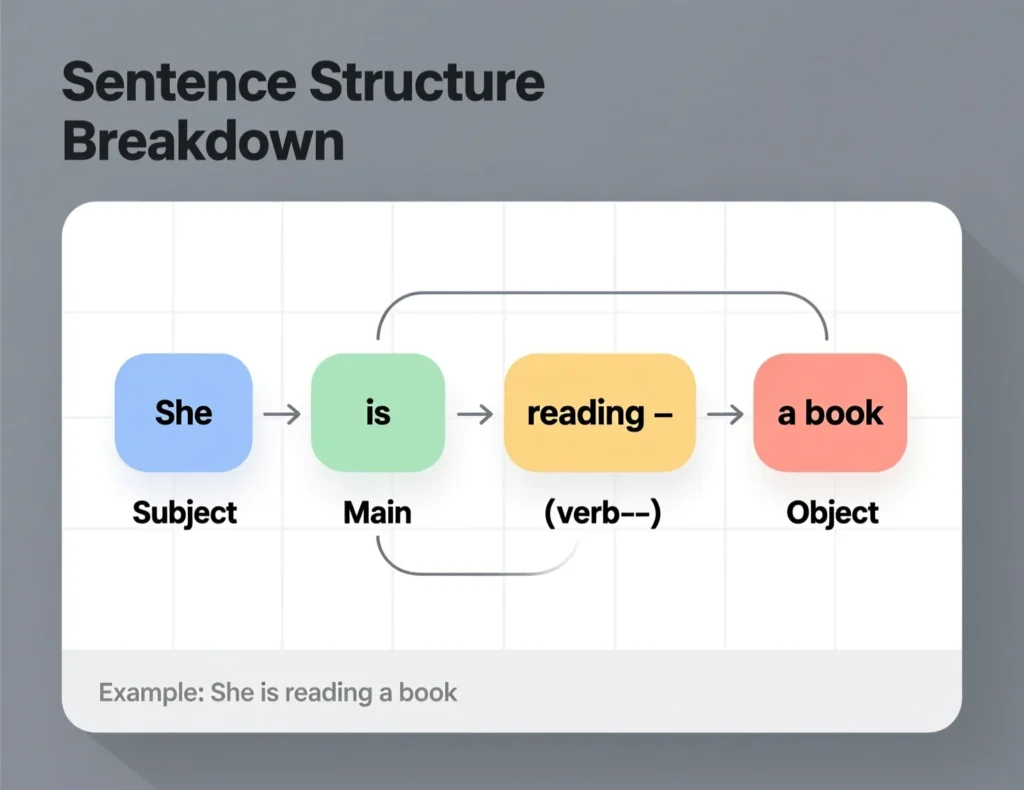
The present progressive tense follows this structure:
Subject + am/is/are + verb(-ing) + object/complement (optional).
- Example: “She is reading a book.”
- Subject: She
- Helping verb: is
- Main verb: reading
- Object: a book
Formation

To form the present progressive tense:
- Choose the correct form of “to be” based on the subject (am for I, is for he/she/it, are for you/we/they).
- Add the main verb with an -ing ending.
- Include any additional details (e.g., time, place).
Example: “We are playing soccer in the park.”
Verbs
Most verbs can be used in the present progressive tense by adding -ing. These include:
- Action verbs (e.g., run, sing, write).
- Verbs describing temporary states (e.g., stay, wait).
However, some verbs, like know or love (stative verbs), are rarely used in this tense because they describe permanent states.
Helping Verbs
The present progressive tense relies on the helping verb “to be”:
- Am: Used with “I” (e.g., I am learning).
- Is: Used with “he/she/it” (e.g., He is cooking).
- Are: Used with “you/we/they” (e.g., They are dancing).
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Present Progressive Tense
Some verbs behave uniquely in the present progressive tense:
- Run: Becomes “running” (e.g., She is running fast).
- Swim: Becomes “swimming” (e.g., They are swimming in the pool).
- Write: Becomes “writing” (e.g., I am writing a letter).
Stative verbs like believe or own are rarely used, as they describe fixed states, not ongoing actions.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Present Progressive Tense
| Base Verb | Present Progressive Form |
| Run | Running |
| Swim | Swimming |
| Write | Writing |
| Sing | Singing |
| Take | Taking |
| Sit | Sitting |
| Get | Getting |
| Come | Coming |
| Eat | Eating |
| Sleep | Sleeping |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I am reading a novel.
- She is dancing in the studio.
- He is playing soccer.
- We are studying for the test.
- They are watching a movie.
- You are cooking dinner.
- It is raining outside.
- John is painting the house.
- The kids are jumping on the bed.
- Maria is singing a song.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I am not reading a novel.
- She is not dancing in the studio.
- He is not playing soccer.
- We are not studying for the test.
- They are not watching a movie.
- You are not cooking dinner.
- It is not raining outside.
- John is not painting the house.
- The kids are not jumping on the bed.
- Maria is not singing a song.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Am I reading a novel?
- Is she dancing in the studio?
- Is he playing soccer?
- Are we studying for the test?
- Are they watching a movie?
- Are you cooking dinner?
- Is it raining outside?
- Is John painting the house?
- Are the kids jumping on the bed?
- Is Maria singing a song?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Am I not reading a novel?
- Is she not dancing in the studio?
- Is he not playing soccer?
- Are we not studying for the test?
- Are they not watching a movie?
- Are you not cooking dinner?
- Is it not raining outside?
- Is John not painting the house?
- Are the kids not jumping on the bed?
- Is Maria not singing a song?
How to Conjugate Present Progressive Tense
To conjugate the present progressive tense:
- Use am for “I.”
- Use is for “he/she/it.”
- Use are for “you/we/they.”
- Add -ing to the base verb.
- For negative sentences, add “not” after the helping verb.
- For questions, invert the subject and helping verb.
- Ensure the verb agrees with the subject.
- Use for ongoing or temporary actions.
- Avoid stative verbs.
- Practice with different subjects.
Conjugation Table for All Subjects
| Subject | Positive Example | Negative Example | Interrogative Example |
| I | I am running | I am not running | Am I running? |
| You | You are singing | You are not singing | Are you singing? |
| He | He is eating | He is not eating | Is he eating? |
| She | She is writing | She is not writing | Is she writing? |
| It | It is raining | It is not raining | Is it raining? |
| We | We are dancing | We are not dancing | Are we dancing? |
| They | They are studying | They are not studying | Are they studying? |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
When adding -ing:
- For verbs ending in -e, drop the “e” (e.g., write → writing).
- For verbs ending in consonant-vowel-consonant, double the last consonant (e.g., run → running).
- For verbs ending in -ie, change to -y (e.g., lie → lying).
- Regular verbs simply add -ing (e.g., talk → talking).
- No changes for most irregular verbs (e.g., see → seeing).
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I am learning English.
- You are playing the guitar.
- He is swimming in the lake.
- She is painting a picture.
- It is snowing heavily.
- We are traveling to Paris.
- They are laughing at the joke.
- John is fixing the car.
- The dog is barking loudly.
- The students are presenting their project.
- Maria is cooking dinner.
- I am exercising at the gym.
- You are reading a magazine.
- She is shopping online.
- They are hiking in the mountains.
Common Mistakes with Present Progressive Tense
- Using stative verbs (e.g., “I am knowing” → incorrect; use “I know”).
- Forgetting the helping verb (e.g., “She singing” → incorrect; use “She is singing”).
- Wrong form of “to be” (e.g., “I is running” → incorrect; use “I am running”).
- Misplacing “not” in negatives (e.g., “She not is dancing” → incorrect; use “She is not dancing”).
- Using for permanent states (e.g., “I am living forever” → incorrect).
- Incorrect subject-verb agreement (e.g., “They is studying” → incorrect).
- Forgetting -ing (e.g., “He is run” → incorrect).
- Overusing for habitual actions (e.g., “I am going to school every day” → use simple present).
- Incorrect spelling changes (e.g., “writeing” → incorrect; use writing).
- Confusing with simple present (e.g., “She is singing every day” → use “She sings”).
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Avoid stative verbs; use simple present for states like know or love.
- Always include am/is/are before the -ing verb.
- Match the helping verb to the subject.
- Place “not” after am/is/are for negatives.
- Use present progressive for temporary or ongoing actions only.
- Double-check subject-verb agreement.
- Ensure -ing is added to the verb.
- Use simple present for habitual actions.
- Follow spelling rules for -ing verbs.
- Practice with examples to clarify tense usage.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Present Progressive Tense
Verbs often confused with present progressive:
- Run (synonym: jog) → “She is running” vs. “She is jogging.”
- Talk (synonym: speak) → “They are talking” vs. “They are speaking.”
- Write (synonym: compose) → “I am writing” vs. “I am composing.”
- Eat (synonym: consume) → “He is eating” vs. “He is consuming.”
- Sleep (synonym: rest) → “It is sleeping” vs. “It is resting.”
- Sing (synonym: hum) → “She is singing” vs. “She is humming.”
- Walk (synonym: stroll) → “We are walking” vs. “We are strolling.”
- Work (synonym: labor) → “They are working” vs. “They are laboring.”
- Read (synonym: study) → “I am reading” vs. “I am studying.”
- Dance (synonym: sway) → “She is dancing” vs. “She is swaying.”
Sentence Comparisons
- She is running fast. / She is jogging slowly.
- They are talking loudly. / They are speaking softly.
- I am writing a letter. / I am composing an email.
- He is eating breakfast. / He is consuming a snack.
- The cat is sleeping on the mat. / The cat is resting quietly.
- She is singing a song. / She is humming a tune.
- We are walking to school. / We are strolling in the park.
- They are working on a project. / They are laboring in the garden.
- I am reading a book. / I am studying for a test.
- She is dancing gracefully. / She is swaying to the music.
Tips to Practice Using Present Progressive Tense
- Write 10 sentences daily using different subjects and verbs.
- Describe what people around you are doing right now.
- Use a grammar app to check your sentences.
- Practice speaking with a friend about ongoing actions.
- Watch movies and note present progressive examples.
- Create a journal of daily activities using this tense.
- Play a game: Describe what everyone is doing in a photo.
- Use flashcards with -ing verbs for practice.
- Read news articles and highlight present progressive sentences.
- Practice forming negatives and questions.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the present progressive tense? It describes ongoing actions (e.g., I am writing).
- When do we use it? For actions happening now or temporarily.
- Can stative verbs be used? Rarely, as they describe fixed states.
- How do I form negatives? Add “not” after am/is/are.
- How do I form questions? Invert subject and am/is/are.
- What are common verbs? Run, sing, write, etc.
- Are there spelling rules? Yes, like dropping -e or doubling consonants.
- Can it describe future plans? Yes, e.g., “I am traveling tomorrow.”
- What’s the difference from simple present? It’s for ongoing, not habitual, actions.
- How do I practice? Write, speak, and read examples daily.
Exercises
- Convert “She sings” to present progressive.
- Make “I read a book” negative.
- Turn “They play soccer” into a question.
- Write a sentence with “run” and “he.”
- Use “dance” in a negative sentence.
- Form a question with “you” and “study.”
- Create a sentence with “we” and “cook.”
- Make “It rains” negative and interrogative.
- Use “swim” with “they” in a sentence.
- Write a question with “she” and “write.”
Quizzes
- What is the correct form: I am run / I am running?
- Is “She is knowing” correct? Why?
- Form a negative: He is playing.
- Form a question: They are studying.
- Which verb is stative: run or know?
- Correct the error: We is dancing.
- Add -ing to “write.”
- Is “I am loving it” correct? Why?
- Form a sentence with “you” and “sing.”
- Turn “It is raining” into negative.
True or False
- Present progressive uses am/is/are. (True)
- “I am knowing” is correct. (False)
- It describes permanent states. (False)
- “She is dancing” is present progressive. (True)
- Stative verbs are common in this tense. (False)
- “They are not studying” is negative. (True)
- Questions start with am/is/are. (True)
- “Write” becomes “writeing.” (False)
- It can describe future plans. (True)
- “He is run” is correct. (False)
Conclusion
The present progressive tense is a powerful tool for describing actions happening now, temporary situations, or future plans.
By mastering its structure (am/is/are + verb-ing), you can make your writing and speaking more dynamic.
Practice with the examples, exercises, and tips provided to build confidence. Avoid common mistakes like using stative verbs or incorrect helping verbs.
If you’re a student or writer, this tense will enhance your English skills.
Try writing 10 sentences today using the present progressive tense, or use a grammar checker to refine your work. Keep practicing, and you’ll master this tense in no time!



