The present tense is one of the most fundamental aspects of English grammar, used to describe actions, habits, facts, and current states.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering the present tense is essential for clear communication.
This article, we’ll break down what the present tense is, how to use it correctly, and common mistakes to avoid.
With real-life verb tense examples, conjugation tables, and practice tips, this guide is designed to be skimmable and beginner-friendly.
By the end, you’ll feel confident using the present tense in your writing and conversations.
Let’s dive into the world of present tense verbs and explore how they shape our everyday language!
What Is the Present Tense?

The present tense describes actions happening now, general truths, habits, routines, or states that are currently true. It’s used to express what someone does regularly, what’s happening at the moment, or facts that remain constant. For example, “The sun rises in the east” (a fact) or “I walk to school every day” (a habit). The present tense includes four forms: simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and present perfect continuous. This article focuses on the simple present tense, the most common form for stating facts, routines, and general truths.
How to Recognize the Present Tense?
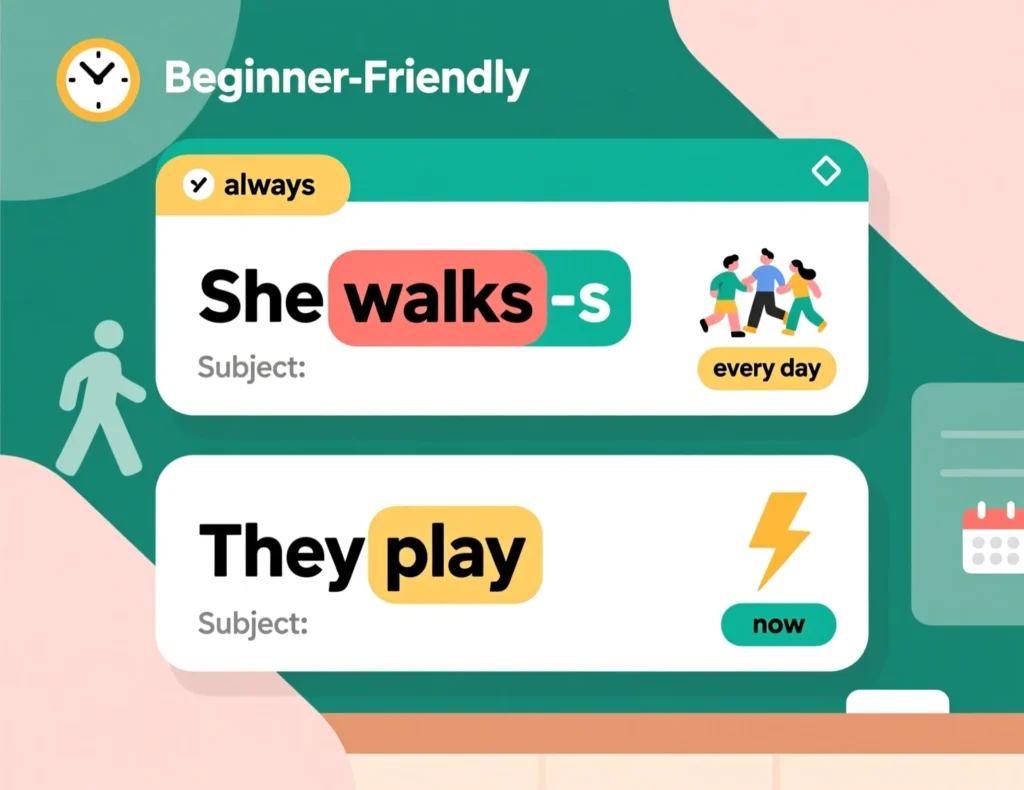
You can recognize the present tense by looking at the verb form and context. In the simple present, verbs typically end in -s or -es for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), like “She walks” or “He watches.” For other subjects (I, you, we, they), the base verb is used, like “They walk.” The present tense often appears with time expressions like always, usually, every day, or now. If the sentence describes a routine, fact, or current action, it’s likely in the present tense.
Structure of a Sentence
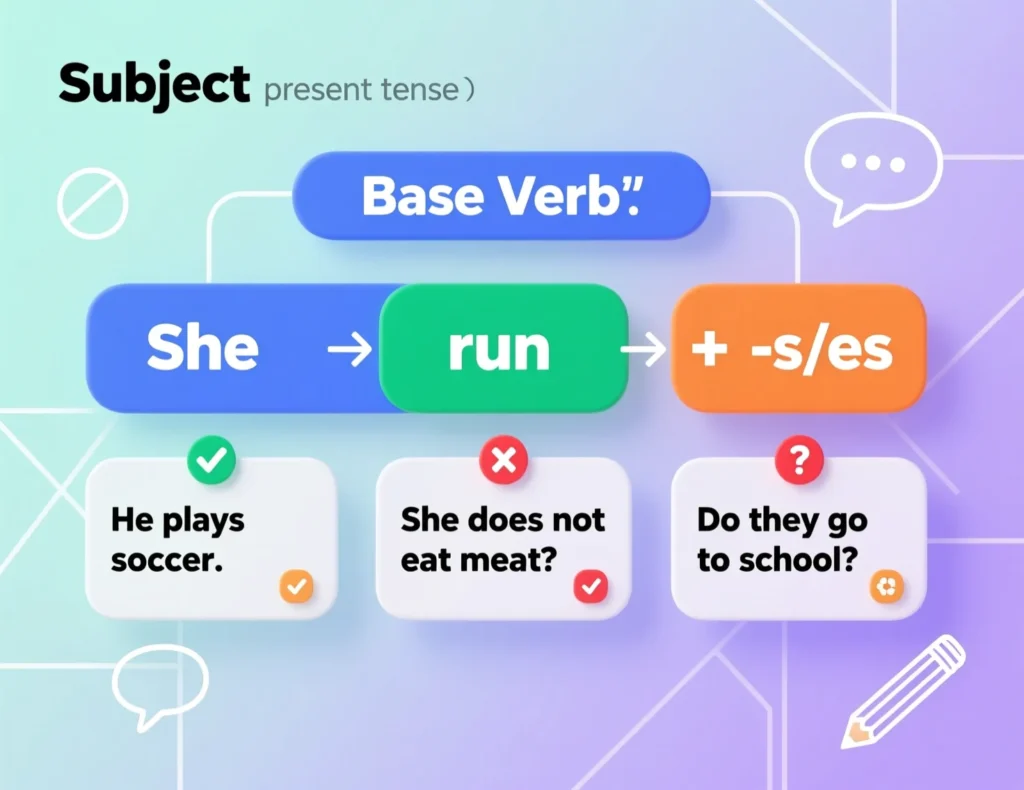
The simple present tense follows a straightforward structure:
- Subject + Base Verb (add -s or -es for he, she, it)
- Example: I read books. She reads books.
- Use do/does + not + base verb for negatives.
- Example: I don’t read books. She doesn’t read books.
- Use do/does + subject + base verb for questions.
- Example: Do I read books? Does she read books?
Formation
To form the simple present tense, use the base verb for most subjects (I, you, we, they). For third-person singular (he, she, it), add -s or -es to regular verbs. For negatives, use do not (or don’t) or does not (or doesn’t) before the base verb. For questions, start with do or does, followed by the subject and base verb. Time expressions like every day or often often accompany the present tense to clarify the context.
Verbs
The present tense uses both regular verbs (follow a predictable pattern, like walk, talk) and irregular verbs (like have, go). Regular verbs typically add -s or -es for third-person singular subjects. Irregular verbs may change entirely (e.g., have becomes has). The choice of verb depends on the subject and whether the action is habitual or a fact.
Helping Verbs
In the simple present tense, the main helping verbs are do and does. They’re used in:
- Negative sentences: I don’t like coffee. She doesn’t play soccer.
- Questions: Do you like coffee? Does she play soccer?
These helping verbs ensure proper sentence structure for negatives and interrogatives.
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Present Tense
Here’s how common verbs behave in the simple present tense:
- Walk (regular): I walk, she walks.
- Study (regular, ends in -y): I study, he studies (change y to -ies after a consonant).
- Have (irregular): I have, she has.
- Go (irregular): I go, he goes (add -es).
These examples show how verb endings change based on the subject and verb type.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Present Tense
| Verb | I/You/We/They | He/She/It |
| Walk | walk | walks |
| Run | run | runs |
| Study | study | studies |
| Have | have | has |
| Go | go | goes |
| Watch | watch | watches |
| Do | do | does |
| Play | play | plays |
| Eat | eat | eats |
| Write | write | writes |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I eat breakfast every morning.
- She walks to school daily.
- They play soccer on weekends.
- He reads novels in his free time.
- We watch movies every Friday.
- You write emails quickly.
- The dog barks at strangers.
- John studies math every evening.
- The kids run in the park.
- It rains often in spring.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I don’t eat spicy food.
- She doesn’t walk to work.
- They don’t play video games.
- He doesn’t read newspapers.
- We don’t watch horror movies.
- You don’t write letters often.
- The cat doesn’t like water.
- Mary doesn’t study on weekends.
- The kids don’t run in the house.
- It doesn’t snow here in summer.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Do I look tired?
- Does she walk to school?
- Do they play basketball?
- Does he read books?
- Do we need more time?
- Do you write poems?
- Does the dog bark at night?
- Does John study hard?
- Do the kids run fast?
- Does it rain often?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Don’t I look okay?
- Doesn’t she walk home daily?
- Don’t they play soccer?
- Doesn’t he read novels?
- Don’t we watch TV enough?
- Don’t you write emails?
- Doesn’t the cat like milk?
- Doesn’t Mary study math?
- Don’t the kids run outside?
- Doesn’t it snow in winter?
How to Conjugate Present Tense
Conjugating verbs in the simple present tense depends on the subject:
- Use the base verb for I, you, we, they (e.g., I walk).
- Add -s for he, she, it with most verbs (e.g., She walks).
- Add -es for verbs ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, or -z (e.g., He watches).
- For verbs ending in a consonant + -y, change -y to -ies (e.g., She studies).
- For verbs ending in a vowel + -y, just add -s (e.g., He plays).
- Irregular verbs like have become has for he, she, it.
- Use do for questions/negatives with I, you, we, they.
- Use does for questions/negatives with he, she, it.
- Ensure subject-verb agreement in all sentences.
- Practice with different verbs to master conjugation.
Conjugation Table for All Subjects
| Subject | Walk | Have | Study | Go |
| I | walk | have | study | go |
| You | walk | have | study | go |
| He/She/It | walks | has | studies | goes |
| We | walk | have | study | go |
| They | walk | have | study | go |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- Verbs ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z: Add -es (e.g., watch → watches).
- Consonant + -y: Change -y to -ies (e.g., study → studies).
- Vowel + -y: Add -s (e.g., play → plays).
- Irregular verbs: Have → has, go → goes, do → does.
- Verbs like be are highly irregular (e.g., I am, she is, they are).
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I love to sing.
- You dance beautifully.
- He works at a bank.
- She cooks dinner daily.
- It rains every afternoon.
- We study English together.
- They play chess often.
- John writes stories.
- The dog chases cats.
- The children laugh loudly.
- You (plural) travel every summer.
- Mary reads novels.
- I exercise every morning.
- He drives to work.
- We watch TV at night.
Common Mistakes with Present Tense
- Forgetting -s for he/she/it: Incorrect: She walk. Correct: She walks.
- Using does with I/you/we/they: Incorrect: I does go. Correct: I do go.
- Omitting do/does in questions: Incorrect: She like it? Correct: Does she like it?
- Adding -s to irregular verbs incorrectly: Incorrect: He haves. Correct: He has.
- Using -ies with vowel + -y: Incorrect: She plaies. Correct: She plays.
- Mixing tenses: Incorrect: I go yesterday. Correct: I go every day.
- Incorrect negative form: Incorrect: She not like it. Correct: She doesn’t like it.
- Forgetting subject-verb agreement: Incorrect: They walks. Correct: They walk.
- Using do instead of does: Incorrect: He do like it. Correct: He does like it.
- Overusing -es: Incorrect: He walkes. Correct: He walks.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Always check if the subject is he/she/it for -s or -es.
- Use does only for he/she/it in questions and negatives.
- Practice forming questions with do/does + base verb.
- Memorize irregular verbs like have/has, go/goes.
- Double-check verbs ending in -y for correct spelling (e.g., studies vs. plays).
- Avoid mixing past and present tenses in the same sentence.
- Use a grammar checker to catch errors in real-time.
- Read sentences aloud to ensure they sound natural.
- Practice with varied subjects to reinforce agreement.
- Review conjugation tables for clarity.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Present Tense
Some verbs and synonyms are often confused with present tense verbs:
- Walk – Synonyms: stroll, stride.
- Run – Synonyms: jog, sprint.
- Have – Synonym: possess.
- Go – Synonyms: travel, move.
- Study – Synonyms: learn, review.
- Play – Synonyms: perform, engage.
- Eat – Synonyms: consume, dine.
- Write – Synonyms: compose, jot.
- Watch – Synonyms: view, observe.
- Do – Synonyms: perform, execute.
Sentence Comparisons:
- Walk vs. Stroll: She walks quickly. She strolls leisurely.
- Run vs. Jog: He runs fast. He jogs slowly.
- Have vs. Possess: I have a car. I possess a car.
Tips to Practice Using Present Tense
- Write 5 sentences daily using different subjects and verbs.
- Read books and highlight present tense verbs.
- Practice speaking with a friend about daily routines.
- Use apps like Duolingo for grammar exercises.
- Create flashcards for irregular verbs (e.g., have/has).
- Watch English shows and note present tense usage.
- Keep a journal to describe your day in present tense.
- Play grammar games online for fun practice.
- Join a language learning group to practice speaking.
- Use a grammar checker to review your writing.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the present tense used for? It describes habits, facts, and current actions.
- How do I know if a verb is in the present tense? Look for -s or -es for he/she/it or base verbs for other subjects.
- What’s the difference between do and does? Do is for I/you/we/they; does is for he/she/it.
- Are there irregular verbs in the present tense? Yes, like have/has, go/goes.
- How do I form negative sentences? Use don’t or doesn’t + base verb.
- How do I ask questions in present tense? Use do/does + subject + base verb.
- Why do some verbs end in -ies? For verbs ending in consonant + -y, like study.
- Can I use present tense for future events? Yes, for scheduled events (e.g., The train leaves tomorrow).
- How do I practice present tense? Write, speak, and use grammar apps.
- What’s a common mistake with present tense? Forgetting -s for he/she/it.
Exercises
- Write 5 present tense sentences about your day.
- Convert 5 sentences to negative form.
- Create 5 interrogative present tense sentences.
- Identify the verb in 5 sentences and check for -s or -es.
- Write 3 sentences with irregular verbs (e.g., have, go).
- Practice conjugating study for all subjects.
- Change 5 past tense sentences to present tense.
- Write a short paragraph about your routine in present tense.
- Correct 5 incorrect present tense sentences.
- Use a grammar app to practice present tense verbs.
Quizzes
- What is the correct form: She walk or She walks? (Answer: She walks)
- Which is correct: I does or I do? (Answer: I do)
- Fill in: He ___ (study) every night. (Answer: studies)
- Is this correct: They goes to school? (Answer: No, They go)
- What’s the negative of “She runs”? (Answer: She doesn’t run)
- What’s the question form of “You play”? (Answer: Do you play?)
- Correct: He have a dog. (Answer: He has a dog)
- Fill in: We ___ (watch) TV. (Answer: watch)
- Is “It rains” in present tense? (Answer: Yes)
- Change to negative: They eat pizza. (Answer: They don’t eat pizza)
True or False
- The present tense is only for actions happening now. (False, it’s also for habits and facts)
- Does is used for I and you. (False, do is used)
- Verbs ending in -ch add -es for he/she/it. (True)
- Have becomes has for she. (True)
- Questions need do or does. (True)
- Play becomes plaies for he. (False, it’s plays)
- Present tense can describe routines. (True)
- Irregular verbs follow the same rules. (False)
- Negative sentences use don’t or doesn’t. (True)
- You can’t use present tense for facts. (False)
Conclusion
Mastering the present tense is a key step for students, language learners, and writers to communicate clearly.
By understanding its structure, conjugation rules, and common pitfalls, you can use the present tense confidently in everyday conversations and writing.
Practice with the exercises, quizzes, and tips provided to reinforce your skills. Try writing a few sentences daily or use a grammar checker to polish your work.
The present tense is your gateway to expressing habits, facts, and current actions with ease. Start practicing today, and share your present tense sentences in the comments below to keep improving!