The past tense of bite, which is bit, is an essential part of English grammar for students, language learners, writers, and grammar enthusiasts.
Understanding how to use bit correctly can make your sentences clear and engaging.
The verb bite is irregular, meaning it doesn’t follow the standard “-ed” ending for past tense like regular verbs.
This article will guide you through the definition, formation, and usage of bit, with verb tense examples, conjugation tips, and practical exercises.
If you’re describing a dog that bit a bone or a moment you bit into an apple, this beginner-friendly guide offers skimmable sections, real-life examples, and actionable tips to master the past tense of bite.
Let’s dive into the world of bit and make grammar fun and accessible!
What Is the Past Tense of “Bite”?
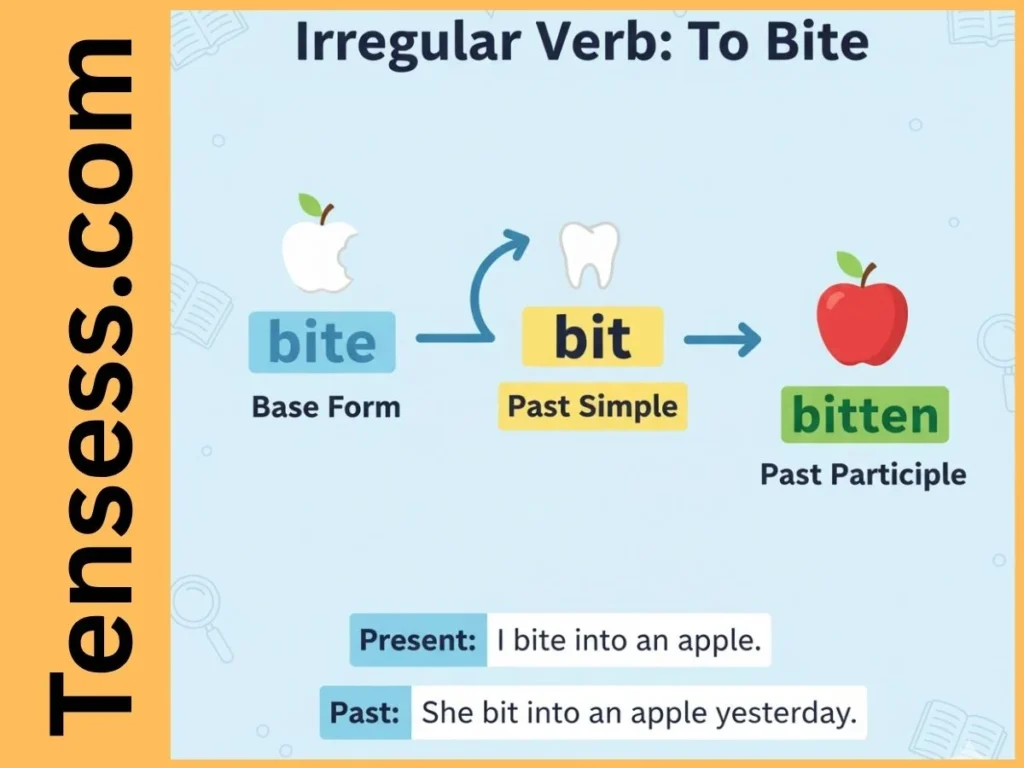
The past tense of bite is bit. It’s used to describe actions that happened in the past, such as when someone or something used their teeth to cut, pierce, or grip. For example, “The dog bit the toy yesterday.” Unlike regular verbs like “walk” (walked), bite is an irregular verb, so it changes form in the past tense. The past participle of bite is bitten, used with helping verbs like “has” or “had” (e.g., “She has bitten into the apple”). Understanding bit helps you communicate past actions clearly, whether in storytelling, academic writing, or casual conversation.
How to Recognize the Past Tense of “Bite”?
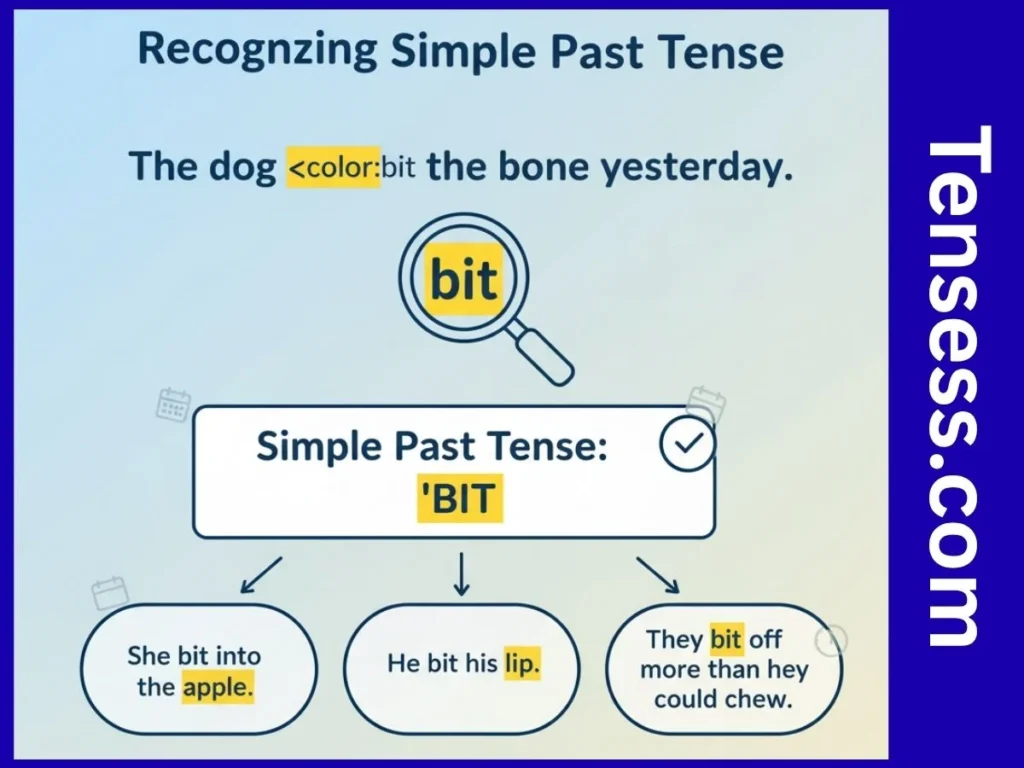
To recognize bit as the past tense of bite, look for actions completed in the past involving biting. The verb bit stands alone in simple past tense sentences without auxiliary verbs. For example:
- “I bit into a sandwich.” (Simple past)
- Not: “I have bit” (Incorrect; use bitten for perfect tenses).
Check the context: if the sentence describes a completed biting action without “has,” “had,” or “will,” it’s likely bit. Also, bit is used for all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), making it easy to spot.
Structure of a Sentence Using “Bit”
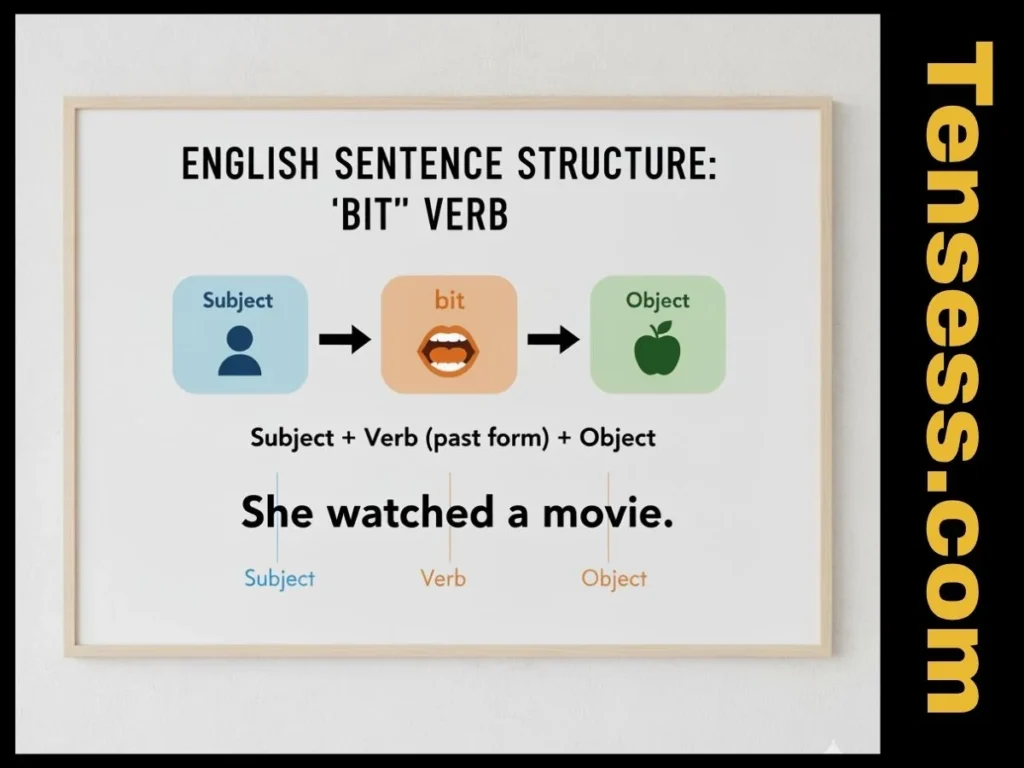
The sentence structure for bit in the simple past tense follows this pattern:
- Subject + bit + object (optional) + additional information (optional).
- Example: “She bit the apple quickly.”
For negative sentences:
- Subject + did not + bite + object (optional).
- Example: “She did not bite the apple.”
For interrogative sentences:
- Did + subject + bite + object (optional)?
- Example: “Did she bite the apple?”
Formation of “Bit”
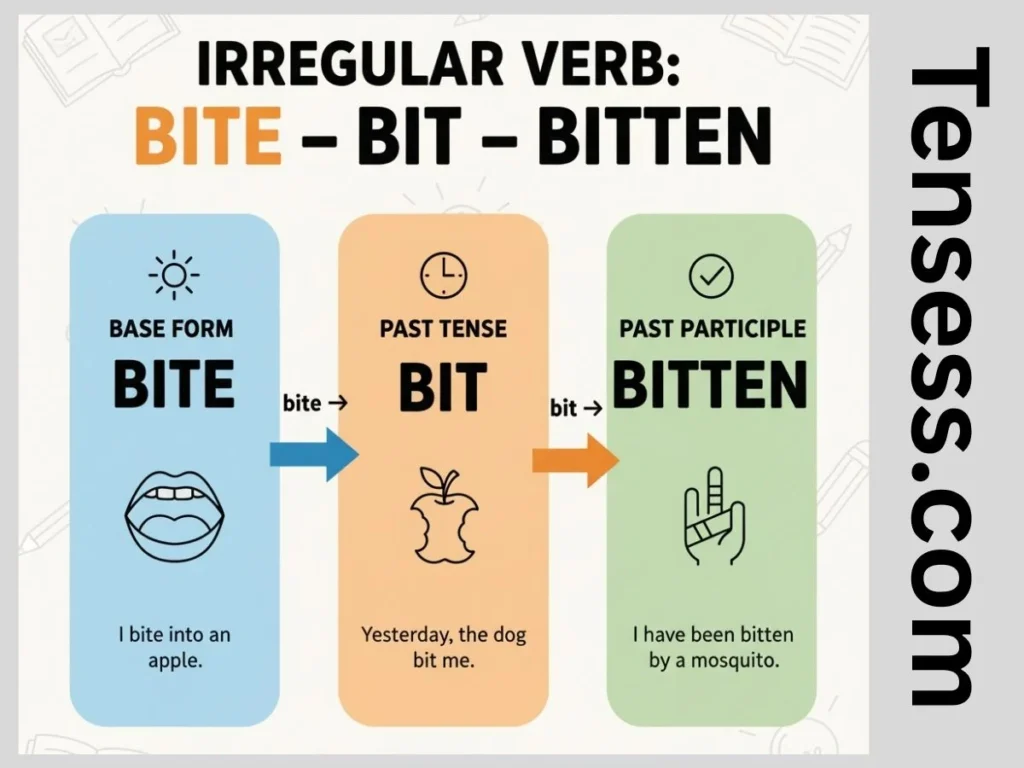
The past tense of bite, bit, is formed by changing the base verb bite to bit for simple past tense. No auxiliary verbs are needed for affirmative simple past sentences. For negatives and questions, use “did” as a helping verb and revert to the base form bite:
- Affirmative: “He bit the rope.”
- Negative: “He did not bite the rope.”
- Question: “Did he bite the rope?”
Verbs Related to “Bite”
The verb bite is irregular, with these forms:
- Base: Bite
- Past Simple: Bit
- Past Participle: Bitten
- Present Participle: Biting
Other verbs like bite include irregular verbs with unique past tense forms, such as:
- Write → Wrote (past)
- Eat → Ate (past)
Helping Verbs with “Bit”
In the simple past tense, bit doesn’t require helping verbs for affirmative sentences. However, for negatives and questions, did is the helping verb:
- Negative: “They did not bite the food.”
- Question: “Did they bite the food?”
For past perfect (had bitten), “had” is the helping verb (e.g., “She had bitten the cookie before dinner”).
Explanation of Verbs with Reference to “Bit”
Some irregular verbs follow patterns similar to bite. For example:
- Bite → Bit → Bitten (base, past, past participle)
- Write → Wrote → Written
- Break → Broke → Broken
These verbs change vowels or forms unpredictably in the past tense, unlike regular verbs (e.g., talk → talked). Recognizing bit as the past of bite helps you understand similar irregular verbs.
Table of Regular and Irregular Verbs in Past Tense
| Base Verb | Past Tense | Type |
| Bite | Bit | Irregular |
| Write | Wrote | Irregular |
| Eat | Ate | Irregular |
| Walk | Walked | Regular |
| Talk | Talked | Regular |
| Run | Ran | Irregular |
| See | Saw | Irregular |
| Drink | Drank | Irregular |
| Play | Played | Regular |
| Sing | Sang | Irregular |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I bit into a juicy peach.
- She bit her lip nervously.
- He bit the sandwich hungrily.
- We bit into the pizza together.
- They bit the candy with joy.
- The dog bit the bone fiercely.
- You bit the apple loudly.
- It bit the toy aggressively.
- The child bit the cookie softly.
- The horse bit the carrot quickly.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I did not bite the sandwich.
- She did not bite her nails.
- He did not bite the rope.
- We did not bite into the cake.
- They did not bite the fruit.
- The dog did not bite the stranger.
- You did not bite the bread.
- It did not bite the toy.
- The child did not bite the apple.
- The cat did not bite the string.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Did I bite the cookie?
- Did she bite the fruit?
- Did he bite the sandwich?
- Did we bite into the pizza?
- Did they bite the candy?
- Did the dog bite the bone?
- Did you bite the apple?
- Did it bite the toy?
- Did the child bite the bread?
- Did the horse bite the carrot?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Did I not bite the sandwich?
- Did she not bite her lip?
- Did he not bite the rope?
- Did we not bite the pizza?
- Did they not bite the candy?
- Did the dog not bite the bone?
- Did you not bite the apple?
- Did it not bite the toy?
- Did the child not bite the cookie?
- Did the horse not bite the carrot?
How to Conjugate “Bit” Tense
The past tense of bite, bit, is the same for all subjects in the simple past tense. Here’s how to conjugate it:
- I bit: I bit the apple.
- You bit: You bit the sandwich.
- He/She/It bit: She bit her lip.
- We bit: We bit into the cake.
- They bit: They bit the candy.
- Use did + bite for negatives: “I did not bite.”
- Use did + subject + bite for questions: “Did you bite?”
- For past perfect, use had + bitten: “She had bitten the fruit.”
- No spelling changes occur with bit.
- Practice with different subjects to master conjugation.
Conjugation Table for “Bite” in Past Tense
| Subject | Simple Past | Negative Form | Interrogative Form |
| I | Bit | Did not bite | Did I bite? |
| You | Bit | Did not bite | Did you bite? |
| He/She/It | Bit | Did not bite | Did he/she/it bite? |
| We | Bit | Did not bite | Did we bite? |
| They | Bit | Did not bite | Did they bite? |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
The verb bite is irregular, so it doesn’t follow the “-ed” rule for past tense. Key points:
- Base form: Bite
- Past tense: Bit (vowel change from “i” to “i”).
- Past participle: Bitten (adds “-en”).
- No spelling changes occur within bit itself.
- Confusion often arises with bitten, which is only used with helping verbs like “has” or “had” (e.g., “She has bitten the apple”).
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I bit into a crisp apple yesterday.
- You bit the sandwich with enthusiasm.
- He bit the rope to free himself.
- She bit her lip during the movie.
- It bit the toy and shook it.
- We bit into the pizza hungrily.
- They bit the candy bars eagerly.
- The dog bit the bone fiercely.
- The child bit the cookie softly.
- The horse bit the carrot quickly.
- I didn’t bite the fruit because it was sour.
- You bit into the bread cautiously.
- She had bitten the apple before noticing a worm.
- We bit the chocolates with delight.
- They didn’t bite the spicy food.
Common Mistakes with “Bit” Tense
- Using bitten instead of bit in simple past: “She bitten the apple” (Incorrect). Use bit.
- Adding “-ed”: “He bited the rope” (Incorrect). Use bit.
- Forgetting “did” in negatives: “I not bite” (Incorrect). Use “I did not bite.”
- Using bit in perfect tenses: “I have bit” (Incorrect). Use bitten.
- Confusing bit with beat: “He bit the drum” (Incorrect for hitting).
- Omitting the object: “She bit” (Unclear without context).
- Incorrect question form: “Bit she the apple?” (Incorrect). Use “Did she bite?”
- Mixing tenses: “She bit yesterday and bites now” (Avoid unless intentional).
- Misusing bit as a noun: “The bit hurt” (Use “bite” for the noun).
- Overusing bit in formal writing: Vary with synonyms like “nibbled.”
How to Avoid These Mistakes
- Memorize bite, bit, bitten as the correct forms.
- Use bit for simple past, bitten for perfect tenses.
- Always use did for negatives and questions.
- Check if bit fits the context (e.g., biting, not hitting).
- Practice with varied subjects and sentence types.
- Read examples to internalize correct usage.
- Use a grammar checker for feedback.
- Compare with similar verbs like eat (ate, eaten).
- Write sentences and review them.
- Ask a teacher or peer to correct your work.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for “Bit”
Synonyms for bite in the past tense include:
- Nibbled: “She nibbled the cookie” (gentler than bit).
- Chomped: “He chomped the carrot” (more forceful).
- Gnawed: “The dog gnawed the bone” (continuous biting).
Verbs often confused with bite:
- Beat (hit): “He beat the drum” (not biting).
- Eat (consume): “She ate the apple” (includes chewing).
Sentence Comparisons
- Bit vs. Nibbled: “She bit the apple” (quick action) vs. “She nibbled the apple” (small bites).
- Bit vs. Chomped: “He bit the sandwich” (normal) vs. “He chomped the sandwich” (vigorous).
- Bit vs. Gnawed: “The dog bit the toy” (single action) vs. “The dog gnawed the toy” (repeated).
Tips to Practice Using “Bit” Tense
- Write 10 sentences using bit with different subjects.
- Create a story about a dog that bit something.
- Practice negative sentences with “did not bite.”
- Form questions like “Did you bite the apple?”
- Use bit in a conversation about food or animals.
- Read books and highlight bit in past tense.
- Record yourself saying sentences with bit.
- Play a game: Describe past actions using bit.
- Teach a friend how to use bit correctly.
- Use flashcards to memorize bite, bit, bitten.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past tense of bite?
It’s bit for simple past, bitten for past participle. - Is “bited” a word?
No, “bited” is incorrect; use bit. - When do I use “bitten”?
Use bitten with “has,” “had,” or “have” (e.g., “She has bitten”). - Is “bit” used for all subjects?
Yes, bit is the same for I, you, he, she, it, we, they. - Can “bit” be a noun?
No, use “bite” for the noun (e.g., “The bite hurt”). - How do I form a question with “bit”?
Use “Did + subject + bite” (e.g., “Did you bite?”). - What’s the difference between “bit” and “beat”?
Bit is for biting; beat is for hitting. - Can I say “I bit yesterday”?
It’s correct but needs context, like “I bit an apple yesterday.” - Is “bit” formal or informal?
It’s neutral but can be replaced with synonyms in formal writing. - How do I practice “bit”?
Write sentences, read examples, and use grammar exercises.
Exercises
- Write 5 sentences using bit with different subjects.
- Convert: “I bite the apple” to past tense.
- Make a negative sentence with bit.
- Form a question using bite in past tense.
- Rewrite: “She has bitten the cookie” in simple past.
- Use bit in a sentence about a dog.
- Create a dialogue using bit twice.
- Replace bit with a synonym in “He bit the bread.”
- Write a sentence with bit and an adverb.
- Correct: “They bited the candy.”
Quizzes
- What is the past tense of bite? (Answer: Bit)
- Is “bited” correct? (Answer: No)
- What is the past participle of bite? (Answer: Bitten)
- Which is correct: “She bit” or “She bitten”? (Answer: She bit)
- What helping verb is used in negative sentences? (Answer: Did)
- Complete: “Did he ___ the apple?” (Answer: Bite)
- Is bit used for all subjects? (Answer: Yes)
- Correct or incorrect: “I bit the sandwich yesterday”? (Answer: Correct)
- Synonym for bit? (Answer: Nibbled, chomped, etc.)
- Form a question with bit. (Answer: e.g., Did you bite?)
True or False
- “Bited” is the past tense of bite. (False)
- Bit is used for all subjects. (True)
- “She has bit” is correct. (False)
- Bitten is used in simple past tense. (False)
- “Did you bite?” is a correct question. (True)
- Bit can mean hitting. (False)
- “The dog bit the bone” is correct. (True)
- Bite is a regular verb. (False)
- “They didn’t bite” uses the base form. (True)
- Bit requires a helping verb in affirmative sentences. (False)
Conclusion
Mastering the past tense of bite, bit, is a simple yet powerful step for students, language learners, and writers.
By understanding its formation, conjugation, and common pitfalls, you can confidently use bit in everyday communication.
From crafting vivid stories to acing grammar tests, the verb tense examples and tips in this guide make it easy to grasp.
Practice with the provided exercises, quizzes, and sentence examples to solidify your skills.
Try writing your own sentences or use a grammar checker to polish your work. Keep exploring verb conjugation to enhance your English fluency.
Ready to bite into grammar success? Start practicing bit today and share your sentences in the comments or with a study buddy!



