The future tense is a cornerstone of English grammar, allowing us to express actions or states that will happen later.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering the future tense helps you communicate plans, predictions, and intentions clearly.
This guide breaks down the future tense conjugation, offering simple explanations, real-life verb tense examples, and practical tips to make learning engaging and beginner-friendly.
By the end, you’ll confidently know how to use the future tense correctly, avoid common mistakes, and practice effectively.
Let’s dive into the world of future tense verbs and explore how to form sentences, recognize patterns, and conjugate verbs like a pro!
What Is the Future Tense?

. It’s used for predictions (e.g., “It will rain tomorrow”), intentions (e.g., “I will study tonight”), or scheduled events (e.g., “The train will leave at 6 PM”). This tense helps convey plans, expectations, or possibilities, making it essential for clear communication. Unlike the past or present tense, the future tense relies on helping verbs like will or shall combined with the base verb. Understanding its structure is key to mastering verb conjugation in English.
How to Recognize the Future Tense?
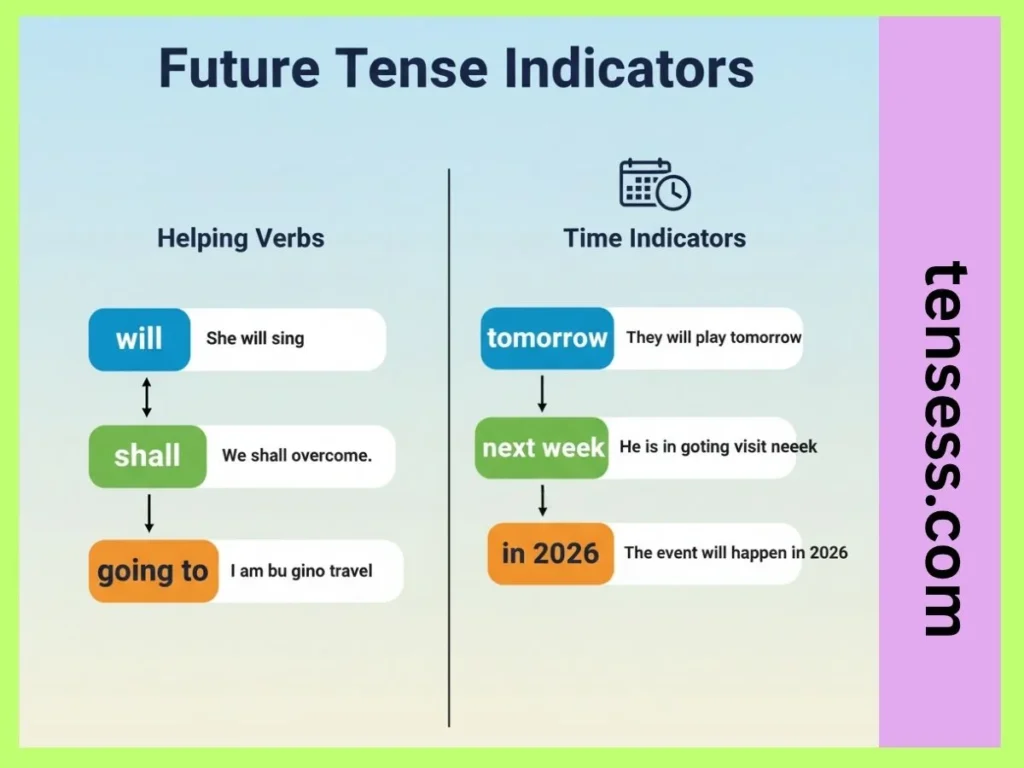
You can spot the future tense by looking for helping verbs like will or shall followed by a base verb. For example, in “She will sing,” will signals the future, and sing is the main verb. Other indicators include phrases like “going to” (e.g., “I am going to travel”) or time expressions like “tomorrow,” “next week,” or “in 2026.” Recognizing these clues helps you identify future tense conjugation in sentences.
Structure of a Sentence in Future Tense
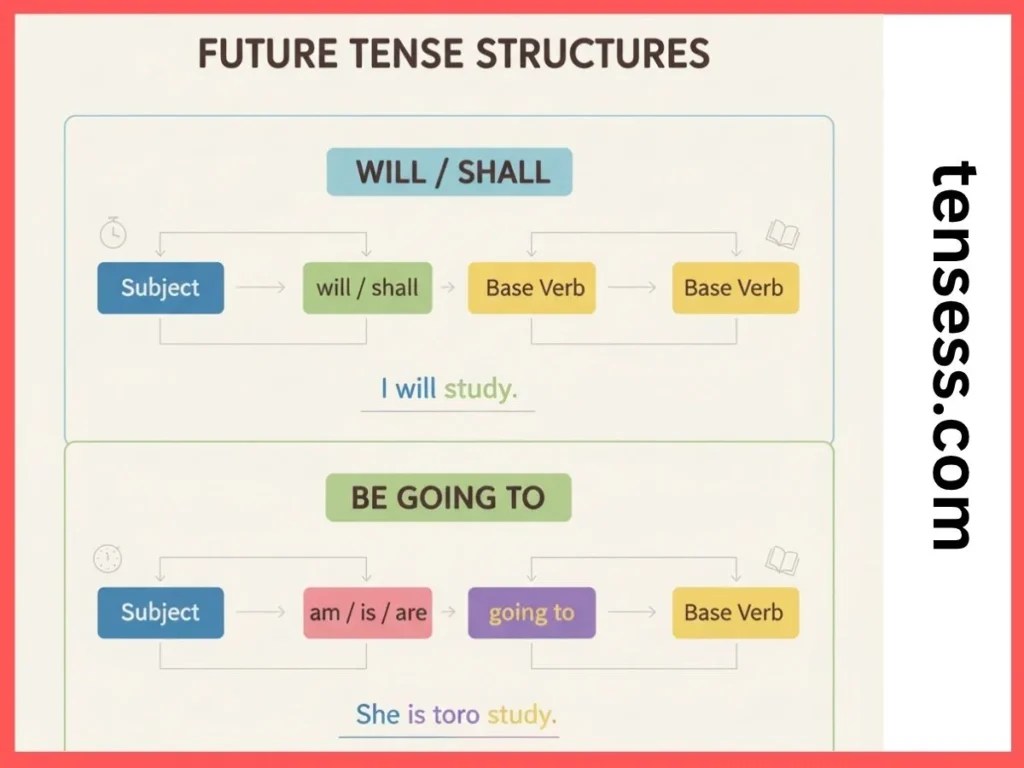
The future tense follows a simple structure:
- Subject + will/shall + base verb (e.g., “I will eat dinner.”)
- Subject + am/is/are + going to + base verb (e.g., “They are going to play soccer.”)
This structure applies to all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they). The choice between will and going to often depends on context, with will used for spontaneous decisions or predictions and going to for planned actions.
Formation of the Future Tense
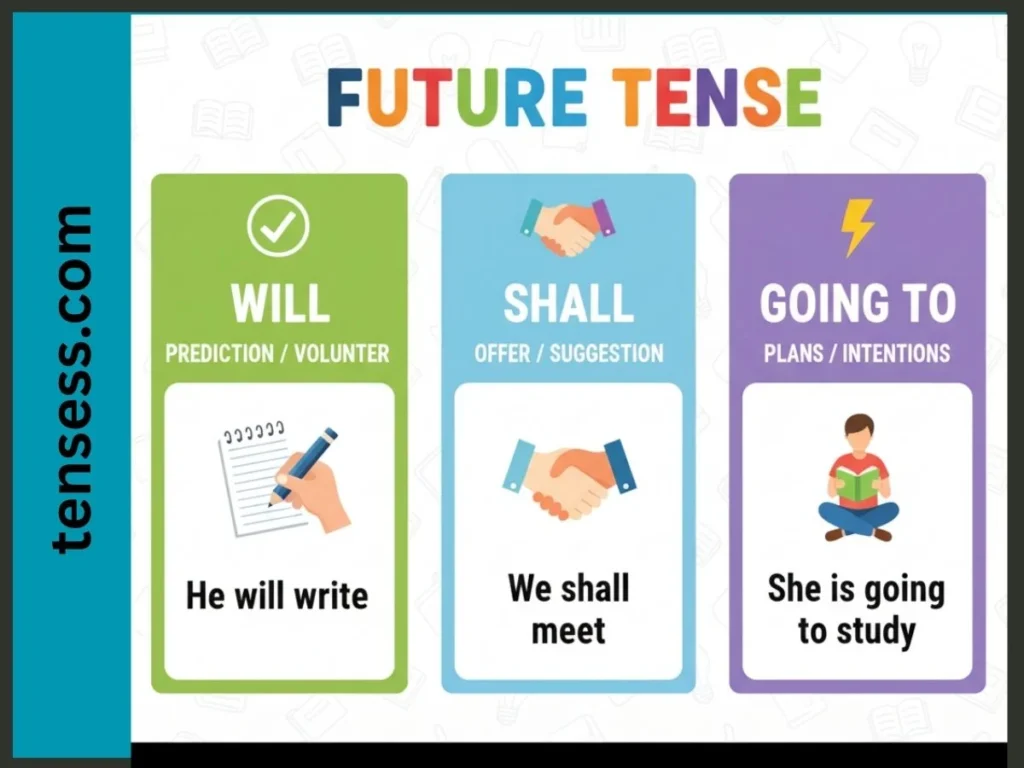
To form the future tense, combine a helping verb with the base form of the main verb. Here’s how it works:
- Using “will”: Subject + will + base verb (e.g., “He will write a letter.”)
- Using “shall”: Traditionally used with “I” or “we” for formal writing (e.g., “We shall meet at noon.”)
- Using “going to”: Subject + am/is/are + going to + base verb (e.g., “She is going to learn coding.”)
The base verb remains unchanged regardless of the subject, making future tense conjugation straightforward.
Verbs in the Future Tense
Any verb can be used in the future tense by pairing it with will, shall, or going to. Regular verbs (e.g., walk, talk) and irregular verbs (e.g., go, eat) follow the same pattern. The base form of the verb is used without alterations. For example:
- Regular: “I will walk to school.”
- Irregular: “They will go to the party.”
Helping Verbs in the Future Tense
The future tense relies on these helping verbs:
- Will: Most common, used for predictions, decisions, or promises (e.g., “I will help you.”)
- Shall: Formal, often used with “I” or “we” (e.g., “We shall overcome.”)
- Am/Is/Are + going to: Indicates planned actions or likely events (e.g., “It is going to rain.”)
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Future Tense
Let’s explore how common verbs behave in the future tense:
- Go: “I will go to the store.” (Irregular verb, base form used.)
- Eat: “She is going to eat sushi.” (Irregular, no change in base form.)
- Study: “We will study for the exam.” (Regular verb, simple to conjugate.)
- Write: “He will write a novel.” (Regular, follows the standard pattern.)
Each verb follows the same future tense conjugation rules, making it easy to apply across contexts.
Table of Some Regular and Irregular Verbs in Future Tense
| Verb | Type | Future Tense Example |
| Walk | Regular | I will walk to school. |
| Talk | Regular | She will talk to him. |
| Go | Irregular | They will go to Paris. |
| Eat | Irregular | He will eat pizza. |
| Write | Regular | We will write a story. |
| Run | Regular | You will run tomorrow. |
| See | Irregular | I will see a movie. |
| Sing | Regular | She will sing a song. |
| Take | Irregular | They will take a bus. |
| Play | Regular | We will play soccer. |
Simple Sentence Examples
Here are 10 future tense examples with different subjects:
- I will visit my grandparents tomorrow.
- You will learn Spanish next month.
- He will buy a new car soon.
- She will dance at the recital.
- It will rain this afternoon.
- We will travel to Japan in 2026.
- They will finish the project by Friday.
- John will call you later.
- The dog will bark at strangers.
- The team will win the championship.
Negative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 negative future tense examples:
- I won’t attend the meeting tomorrow.
- You won’t forget the deadline.
- He won’t play soccer this weekend.
- She won’t travel abroad this year.
- It won’t snow tonight.
- We won’t buy a new house soon.
- They won’t finish the assignment on time.
- Mary won’t join the club.
- The cat won’t eat that food.
- The kids won’t watch TV tonight.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 future tense question examples:
- Will I need a jacket tomorrow?
- Will you come to the party?
- Will he finish his homework?
- Will she sing at the event?
- Will it rain this evening?
- Will we meet at 5 PM?
- Will they travel to Europe?
- Will John call me back?
- Will the dog behave well?
- Will the team win the game?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 combined negative and interrogative future tense examples:
- Won’t I be late for the meeting?
- Won’t you join us for dinner?
- Won’t he forget the appointment?
- Won’t she miss the flight?
- Won’t it stop raining soon?
- Won’t we finish the project early?
- Won’t they cancel the trip?
- Won’t Mary attend the class?
- Won’t the kids behave at the party?
- Won’t the car break down again?
How to Conjugate Future Tense
Conjugating the future tense is simple. Follow these steps:
- Choose the subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- Add will or shall before the base verb.
- Use the base form of the verb (e.g., go, eat, write).
- For “going to,” use am/is/are + going to + base verb.
- Ensure time expressions (e.g., tomorrow) match the future context.
- Keep the verb unchanged regardless of the subject.
- Use will for predictions or spontaneous decisions.
- Use going to for plans or likely events.
- Check for correct helping verb agreement with the subject.
- Practice with different verbs to build confidence.
Conjugation Table for Future Tense
| Subject | Will Structure | Going to Structure |
| I | I will go | I am going to go |
| You | You will go | You are going to go |
| He | He will go | He is going to go |
| She | She will go | She is going to go |
| It | It will go | It is going to go |
| We | We will go | We are going to go |
| They | They will go | They are going to go |
| John | John will go | John is going to go |
| The dog | The dog will go | The dog is going to go |
| The team | The team will go | The team is going to go |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
The future tense is straightforward because it uses the base verb without changes. Unlike past tense (e.g., “go” becomes “went”), the future tense doesn’t alter verb spellings. For example:
- Regular verbs: walk → “I will walk” (no change).
- Irregular verbs: go → “I will go” (base form used).
There are no spelling changes or irregularities in future tense conjugation, making it one of the easiest tenses to learn.
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
Here are 15 future tense examples:
- I will read a book tonight.
- You will meet your friends tomorrow.
- He is going to paint the house.
- She will bake a cake for the party.
- It will snow this weekend.
- We will visit the museum next week.
- They are going to start a business.
- John will call his parents later.
- The cat will sleep all day.
- The team will practice this evening.
- I am going to learn coding.
- You will win the competition.
- She will travel to Paris.
- We will celebrate New Year together.
- They will study abroad next year.
Common Mistakes with Future Tense
Avoid these 10 frequent errors in future tense conjugation:
- Using present tense instead: “I go tomorrow” → Correct: “I will go tomorrow.”
- Omitting will: “She sing at the concert” → Correct: “She will sing.”
- Wrong helping verb agreement: “He are going to run” → Correct: “He is going to run.”
- Changing the base verb: “They will walked” → Correct: “They will walk.”
- Mixing tenses: “I will go yesterday” → Correct: “I will go tomorrow.”
- Overusing shall: “He shall come” (too formal) → Use “He will come.”
- Forgetting “going to” structure: “She going study” → Correct: “She is going to study.”
- Incorrect negative form: “I not will go” → Correct: “I won’t go.”
- Misplacing time expressions: “Tomorrow I will” → Correct: “I will tomorrow.”
- Confusing will vs. going to: Use going to for plans, will for predictions.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Future Tense
Some verbs or expressions are similar to future tense structures:
- Predict (synonym for will in predictions): “I predict rain” vs. “It will rain.”
- Plan (similar to going to): “I plan to study” vs. “I am going to study.”
- Intend: “She intends to travel” vs. “She will travel.”
- Expect: “We expect to win” vs. “We will win.”
- Hope: “I hope to learn” vs. “I will learn.”
- Be about to: “He is about to leave” (near future) vs. “He will leave.”
- Decide: “They decided to go” vs. “They will go.”
- Aim: “I aim to finish” vs. “I will finish.”
- Propose: “We propose to meet” vs. “We will meet.”
- Anticipate: “She anticipates success” vs. “She will succeed.”
Example comparison: “I plan to visit Paris” (implies intention) vs. “I will visit Paris” (definite future action).
Tips to Practice Using Future Tense
Here are 10 ways to master the future tense:
- Write daily plans using will or going to.
- Predict the weather for the week in future tense.
- Create a list of goals for next year.
- Practice negative sentences (e.g., “I won’t forget”).
- Ask questions in future tense (e.g., ” Will you come?”).
- Read books and highlight future tense examples.
- Use flashcards to memorize helping verbs.
- Speak about your plans with friends in English.
- Watch movies and note future tense usage.
- Complete online future tense quizzes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the future tense? It describes actions that will happen later, using will or going to.
- When to use “will” vs. “going to”? Use will for predictions, going to for plans.
- Is “shall” still used? Yes, but it’s formal and less common.
- Can all verbs be used in future tense? Yes, all verbs use their base form.
- How do I make negative sentences? Use won’t or not going to (e.g., “I won’t go”).
- What are common time expressions? Tomorrow, next week, in 2026, etc.
- Are there irregular verbs in future tense? No, the base form is used.
- Can I combine tenses? Avoid mixing; keep future context clear.
- How do I ask questions? Start with will or am/is/are (e.g., ” Will she come?”).
- Where can I practice? Try online exercises or grammar apps.
Exercises
Try these 10 future tense exercises:
- Write 5 sentences about your plans for next weekend.
- Convert “I eat dinner” to future tense.
- Make a negative sentence with “travel.”
- Ask a question using “study” in future tense.
- Write a prediction about tomorrow’s weather.
- Use “going to” with “learn” in a sentence.
- Create a sentence with “we” and “visit.”
- Form a negative question with “attend.”
- Write a sentence with “shall” and “I.”
- Combine “they” and “play” in a future tense sentence.
Quizzes
Test your knowledge with these 10 future tense questions:
- What is the correct form: “She __ (go) to school”?
- Is “I will tomorrow” correct? Why or why not?
- Convert “He runs” to future tense.
- Make “We study” negative in future tense.
- Ask a question with “they” and “win.”
- What’s wrong with “I will goes“?
- Use “going to” with “she” and “sing.”
- Is “shall” used with “he”? Explain.
- Write a sentence with “it” and “rain.”
- Correct: “They not will come.”
True or False
Answer these 10 future tense statements:
- “Will” is a helping verb. (True)
- The base verb changes in future tense. (False)
- “Going to” is used for plans. (True)
- “Shall” is common in modern English. (False)
- “I will yesterday” is correct. (False)
- All subjects use the same verb form. (True)
- Negative sentences use won’t. (True)
- “He are going to” is correct. (False)
- Time expressions like “tomorrow” signal future tense. (True)
- Irregular verbs change spelling in future tense. (False)
Conclusion
Mastering the future tense is a game-changer for clear communication.
By understanding how to conjugate the future tense, recognizing its structure, and practicing with real-life verb tense examples, you can confidently express plans, predictions, and intentions.
Avoid common mistakes, use helping verbs like will or going to correctly, and practice regularly with exercises and quizzes.
Whether you’re a student or writer, the future tense is a powerful tool to enhance your English skills.
Try writing 10 sentences today using the future tense, or use a grammar checker to polish your work.
Share your sentences in the comments or explore more grammar tips to keep learning!