The past tense of lend is an essential concept for students, language learners, writers, and grammar enthusiasts looking to master English verb conjugation.
Understanding how to use lent, the past tense form of lend, helps you communicate clearly about actions like loaning money or items in the past.
This article breaks down the definition, structure, and usage of lent in a beginner-friendly way.
With real-life verb tense examples, conjugation tables, and practical tips, you’ll gain confidence in using lend past tense correctly.
If you’re writing a story, preparing for an English test, or improving your grammar, this guide offers a clear path to mastering lent with skimmable sections and actionable advice.
What Is the Past Tense of Lend?

The verb lend means to give something temporarily with the expectation of its return. Its past tense and past participle form is lent. Unlike regular verbs that add “-ed” (e.g., walk → walked), lend is an irregular verb, so its past tense doesn’t follow the standard pattern. For example, “I lend you my book today” becomes “I lent you my book yesterday.” Recognizing lent as the correct form is key to avoiding common grammar mistakes.
How to Recognize the Past Tense of Lend?

To identify lent as the past tense of lend, look for actions that occurred in the past where something was loaned. For instance, in the sentence “She lent me her car last week,” lent indicates a completed action. Pay attention to time markers like “yesterday,” “last month,” or “in 2024” that signal past tense usage. Lent is used in both simple past and past participle forms, such as in perfect tenses (e.g., “I have lent”).
Structure of Sentences with Lent
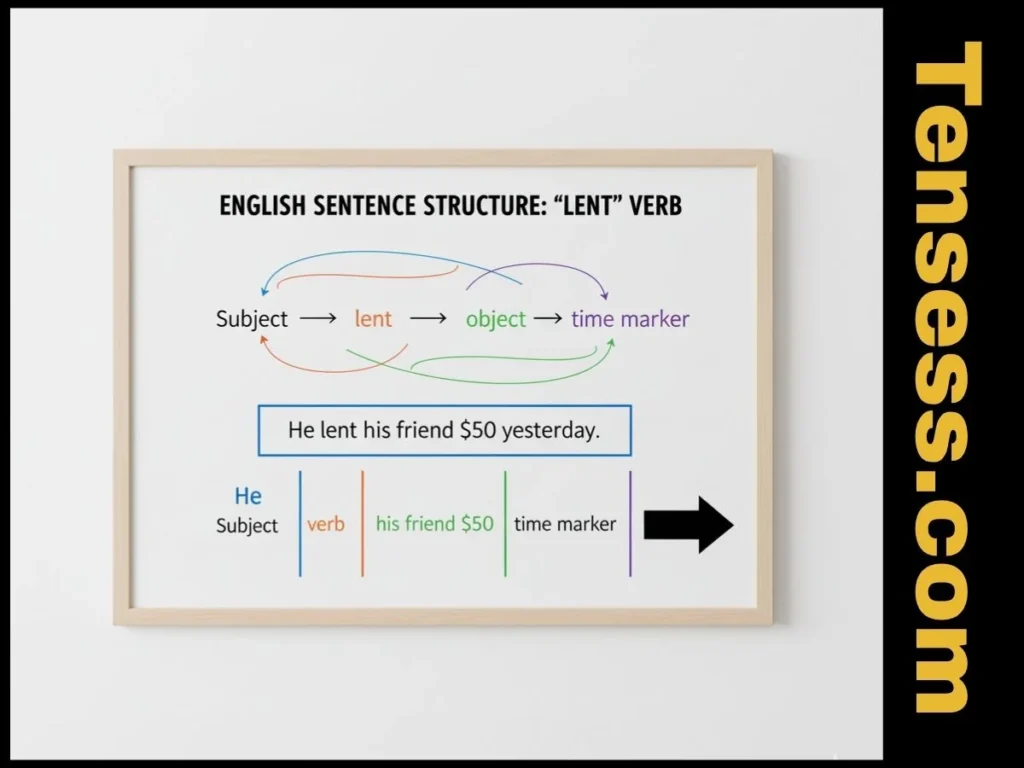
Sentences using lent typically follow this structure:
- Subject + lent + object + (optional time marker).
- Example: “He lent his friend $50 yesterday.”
In negative sentences, use “didn’t lend” (more on this later). For questions, the structure is “Did + subject + lend + object?” (e.g., “Did you lend her the book?”). This structure applies to all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
Formation of Lent
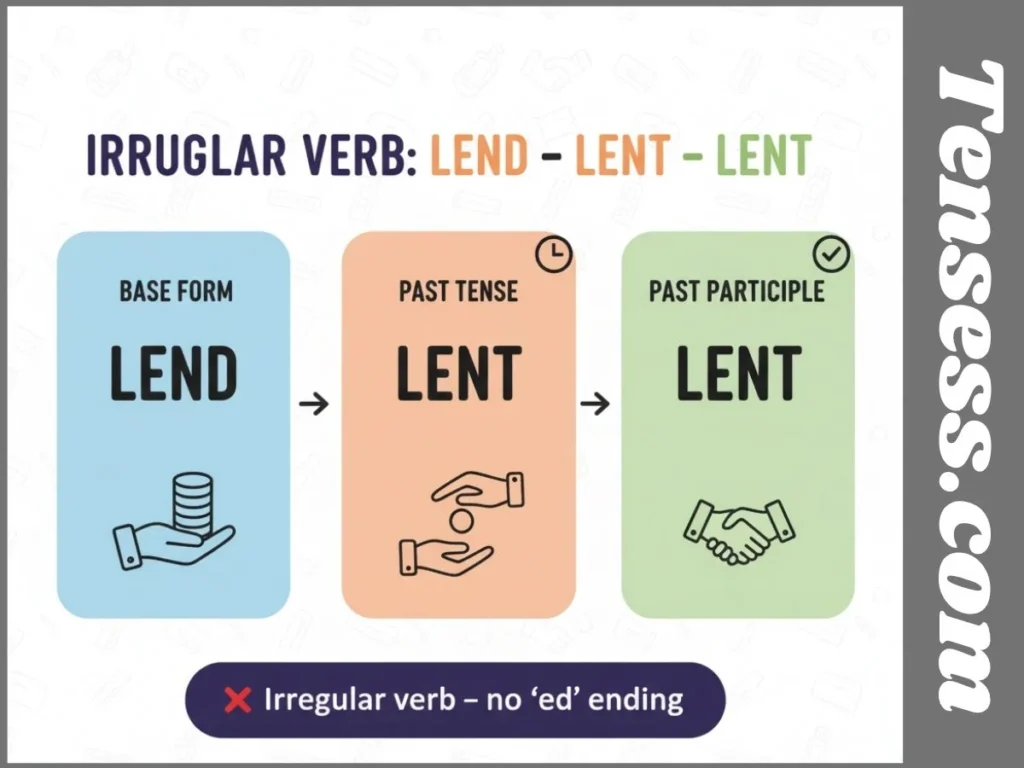
Since lend is irregular, its past tense lent doesn’t require suffixes like “-ed.” It’s formed directly:
- Present: I lend
- Past: I lent
- Past Participle: I have lent
No helping verbs are needed in simple past tense sentences. However, in perfect tenses, have/has/had are used (e.g., “She has lent me her notes”).
Verbs and Helping Verbs
The verb lend doesn’t require helping verbs in the simple past tense. However, in negative or interrogative sentences, did is used:
- Negative: “I didn’t lend the money.”
- Question: “Did you lend the money?”
In perfect tenses, have/has/had act as helping verbs (e.g., “They had lent their tools before the project started”).
Explanation of Verbs Related to Lent
Some verbs related to lend include borrow (to take temporarily) and loan (often used interchangeably with lend). For example:
- Lend: “I lent her my jacket.” (Giving)
- Borrow: “She borrowed my jacket.” (Taking)
- Loan: “The bank loaned me $500.” (Formal, often financial)
Understanding these distinctions prevents confusion when using lent in sentences.
Table of Regular and Irregular Verbs in Past Tense
| Verb | Present | Past | Irregular? |
| Lend | Lend | Lent | Yes |
| Borrow | Borrow | Borrowed | No |
| Give | Give | Gave | Yes |
| Take | Take | Took | Yes |
| Loan | Loan | Loaned | No |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I lent my friend $20 yesterday.
- She lent her bike to her brother.
- He lent his notes to the class.
- We lent our neighbor a ladder.
- They lent their car to a colleague.
- You lent me your pen last week.
- The bank lent her money for a house.
- It lent charm to the old library.
- John lent his jacket to a stranger.
- The teacher lent books to students.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I didn’t lend my phone to anyone.
- She didn’t lend her dress to her friend.
- He didn’t lend his tools last weekend.
- We didn’t lend our camera to them.
- They didn’t lend their books to the library.
- You didn’t lend me your charger.
- The bank didn’t lend him any money.
- It didn’t lend itself to easy repairs.
- John didn’t lend his car to his cousin.
- The teacher didn’t lend her notes.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Did you lend her your book?
- Did she lend her phone to him?
- Did he lend his laptop to a friend?
- Did we lend them our tent?
- Did they lend their house keys?
- Did you lend me your jacket?
- Did the bank lend her money?
- Did it lend itself to the project?
- Did John lend his bike to anyone?
- Did the teacher lend her books?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Didn’t you lend her your pen?
- Didn’t she lend her car to him?
- Didn’t he lend his phone to anyone?
- Didn’t we lend them our tools?
- Didn’t they lend their books?
- Didn’t you lend me your notes?
- Didn’t the bank lend him money?
- Didn’t it lend itself to repairs?
- Didn’t John lend his laptop?
- Didn’t the teacher lend her notes?
How to Conjugate Lend in Past Tense
The past tense of lend is lent for all subjects. Here’s how it’s used:
- I lent my book.
- You lent your phone.
- He lent his car.
- She lent her dress.
- It lent charm to the room.
- We lent our tools.
- They lent their notes.
- John lent his bike.
- The bank lent money.
- The teacher lent books.
Conjugation Table for Lend in Past Tense
| Subject | Conjugation |
| I | Lent |
| You | Lent |
| He/She/It | Lent |
| We | Lent |
| They | Lent |
| John | Lent |
| The bank | Lent |
| The teacher | Lent |
| You (plural) | Lent |
| Anyone | Lent |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
As an irregular verb, lend changes to lent in the past tense without following the “-ed” rule. There are no spelling changes based on the subject, making it straightforward. However, confusion often arises with lend vs. loan or borrow. Always use lent for the past tense of lend, not “loaned” (unless referring to the verb loan).
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I lent my sister my headphones yesterday.
- You lent your friend a book last month.
- He lent his neighbor a lawnmower.
- She lent her colleague her laptop.
- It lent a cozy vibe to the room.
- We lent our camping gear to friends.
- They lent their car to a relative.
- John lent his jacket to a stranger.
- The bank lent her $10,000 for a car.
- The teacher lent her notes to the class.
- You (plural) lent us your tent.
- Sarah lent her phone to her brother.
- The library lent books to students.
- My parents lent me money for rent.
- The company lent equipment to the team.
Common Mistakes with Lend Past Tense
- Using loaned instead of lent: “I loaned her my book” is incorrect for the verb lend. Use lent.
- Confusing lend and borrow: “I borrowed her my pen” is wrong; use “I lent her my pen.”
- Omitting did in negatives: “I not lent her money” should be “I didn’t lend her money.”
- Incorrect question structure: “Lent you her book?” should be “Did you lend her book?”
- Using lent in present tense: “I lent you my phone today” should be “I lend you my phone today.”
- Adding “-ed” to lend: “I lended her money” is incorrect; use lent.
- Mixing up subjects: “They lent me their book” is correct, not “They lent I their book.”
- Forgetting time markers: “I lent her money” is vague without context like “yesterday.”
- Using lent in future tense: “I will lent you my car” should be “I will lend you my car.”
- Overusing loan: Reserve loan for formal or financial contexts, not casual lending.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Always use lent for the past tense of lend, not loaned.
- Clarify lend (give) vs. borrow (take) in context.
- Use didn’t lend for negatives and Did…lend for questions.
- Double-check question structure: Did + subject + lend.
- Use lend for present and lent for past.
- Avoid “lended”; it’s not a word.
- Ensure subject-verb agreement (e.g., “She lent,” not “She lent’s”).
- Add time markers like “yesterday” for clarity.
- Reserve loan for formal contexts like banking.
- Practice with examples to internalize correct usage.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Lend
- Borrow: To take something temporarily (opposite of lend).
- Loan: A synonym for lend, often used in financial contexts.
- Give: To provide without expecting return.
- Advance: To lend money or resources in specific contexts.
- Provide: To supply something, often less temporary than lend.
- Share: To let someone use something jointly.
- Grant: To give formally, often money or rights.
- Offer: To propose giving something.
- Bestow: To give something as a gift (formal).
- Supply: To provide resources.
Sentence Comparisons
- Lend: “I lent her my book.” (Temporary, expecting return)
- Loan: “The bank loaned her $500.” (Formal, financial)
- Borrow: “She borrowed my book.” (Taking, not giving)
- Give: “I gave her my book.” (Permanent, no return expected)
Tips to Practice Using Lend Past Tense
- Write 5 sentences using lent with different subjects.
- Create a dialogue where characters use lent and borrow.
- Practice negative sentences with “didn’t lend.”
- Form 5 interrogative sentences using “Did…lend?”
- Use lent in a short story about lending items.
- Quiz yourself on lend vs. borrow in sentences.
- Read books and highlight instances of lent.
- Practice with flashcards: present (lend) vs. past (lent).
- Record yourself using lent in sentences and review.
- Use a grammar app to check your lent sentences.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past tense of lend?
It’s lent, used for both simple past and past participle. - Is ‘lended’ a word?
No, “lended” is incorrect; use lent. - How is lent different from loaned?
Lent is the past tense of lend; loaned is for loan, often financial. - Can I say ‘I lent her my book yesterday’?
Yes, that’s correct for past tense. - What’s the difference between lend and borrow?
Lend means to give; borrow means to take. - How do I form a negative sentence with lent?
Use “didn’t lend,” e.g., “I didn’t lend her money.” - Is lent used with all subjects?
Yes, lent is the same for I, you, he, she, it, we, they. - Can lent be used in perfect tenses?
Yes, e.g., “I have lent her my notes.” - What’s a synonym for lend?
Loan or advance in specific contexts. - How do I avoid confusing lend and borrow?
Focus on the action: lend is giving, borrow is taking.
Exercises
- Fill in: I ___ my friend my phone yesterday. (Answer: lent)
- Rewrite: She lent her car. (Negative)
- Form a question: You lent him money.
- Correct: I lended her my book.
- Write a sentence using lent with “they.”
- Identify the error: He lent me his pen today.
- Complete: Did she ___ her notes?
- Rewrite: We didn’t lend our tools. (Question)
- Use lent in a sentence with “the bank.”
- Combine: She lent / her friend / a dress / last week.
Quizzes
- The past tense of lend is lent. (True/False: True)
- “I lended her money” is correct. (True/False: False)
- Lent is used in negative sentences without “did.” (True/False: False)
- Loan and lend are always interchangeable. (True/False: False)
- “Did you lend her your book?” is correct. (True/False: True)
- Lent changes based on the subject. (True/False: False)
- “She has lent me her notes” uses past participle. (True/False: True)
- “I borrowed her my book” is correct. (True/False: False)
- Lent is an irregular verb form. (True/False: True)
- “The bank lent her money” is correct. (True/False: True)
True/False
- Lent is the past tense of lend. (True)
- “I lended my book” is correct. (False)
- Lent is used for all subjects. (True)
- “Didn’t she lent her car?” is correct. (False)
- Loan is a synonym for lend. (True)
- “I lent her money tomorrow” is correct. (False)
- Lent requires helping verbs in simple past. (False)
- “She lent her friend a pen” is correct. (True)
- Lend and borrow mean the same thing. (False)
- “Have you lent him your notes?” is correct. (True)
Conclusion
Mastering the past tense of lend—lent—is a small but powerful step toward better English grammar.
By understanding its formation, recognizing common mistakes, and practicing with real-life examples, you can use lent confidently in writing and conversation.
This guide has provided clear explanations, conjugation tables, and practical exercises to help you internalize lend past tense.
Keep practicing by writing sentences, engaging in dialogues, or using grammar tools to reinforce your skills.
For further improvement, try a grammar checker or share your sentences in the comments below to get feedback.
Start using lent today to make your English more precise and natural!



