The past progressive tense, also known as the past continuous tense, is a vital tool for describing actions that were ongoing in the past.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, understanding this tense can enhance your communication skills.
It helps paint vivid pictures of events happening at a specific moment in the past, like “I was studying when the phone rang.”
This beginner-friendly guide will break down the past progressive tense, its structure, usage, and common pitfalls.
With real-life verb tense examples, conjugation tables, and practice tips, you’ll master this tense in no time.
Let’s dive into how to use the past progressive tense correctly and confidently!
What Is the Past Progressive Tense?
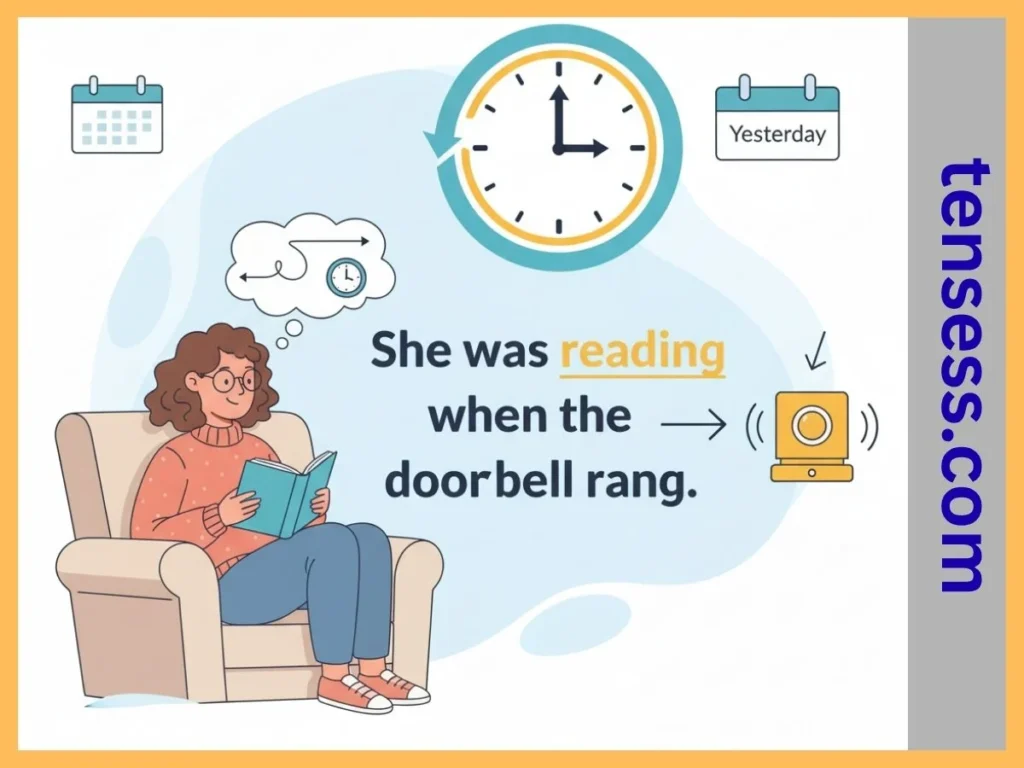
The past progressive tense describes actions that were in progress at a specific point in the past. It emphasizes the duration or continuity of an action, often setting the scene for another event. For example, “She was reading a book when the doorbell rang.” This tense is perfect for storytelling, describing simultaneous actions, or highlighting temporary past activities. It’s formed using the helping verb “was” or “were” plus the present participle (verb + -ing).
How to Recognize the Past Progressive Tense?
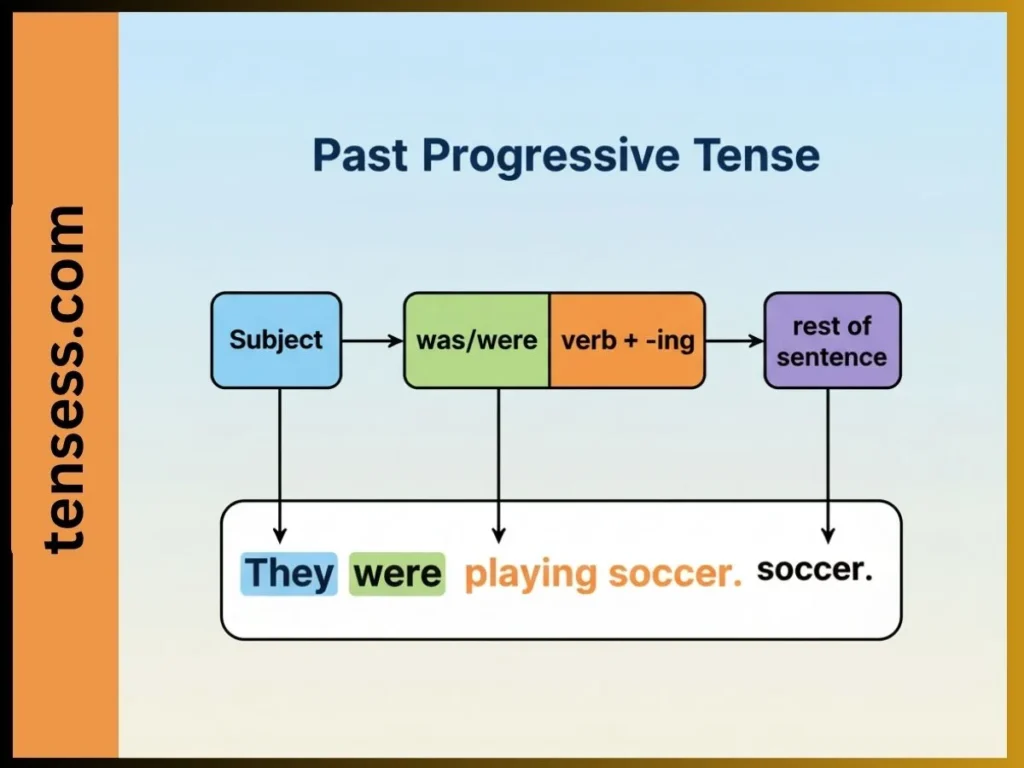
You can spot the past progressive tense by looking for:
- Was/Were: The helping verbs indicate the subject and past tense.
- Verb + -ing: The main verb ends in -ing, showing ongoing action.
- Time markers: Words like “when,” “while,” or “at that moment” often signal this tense.
For example, in “They were playing soccer,” “were” pairs with “playing” to show an ongoing past action.
Structure of a Sentence

The past progressive tense follows this structure:
- Subject + was/were + verb + -ing
- Example: “I was running.”
- For negative sentences: Subject + was/were + not + verb + -ing (e.g., “I was not running”).
- For interrogative sentences: Was/Were + subject + verb + -ing? (e.g., “Was I running?”).
Formation
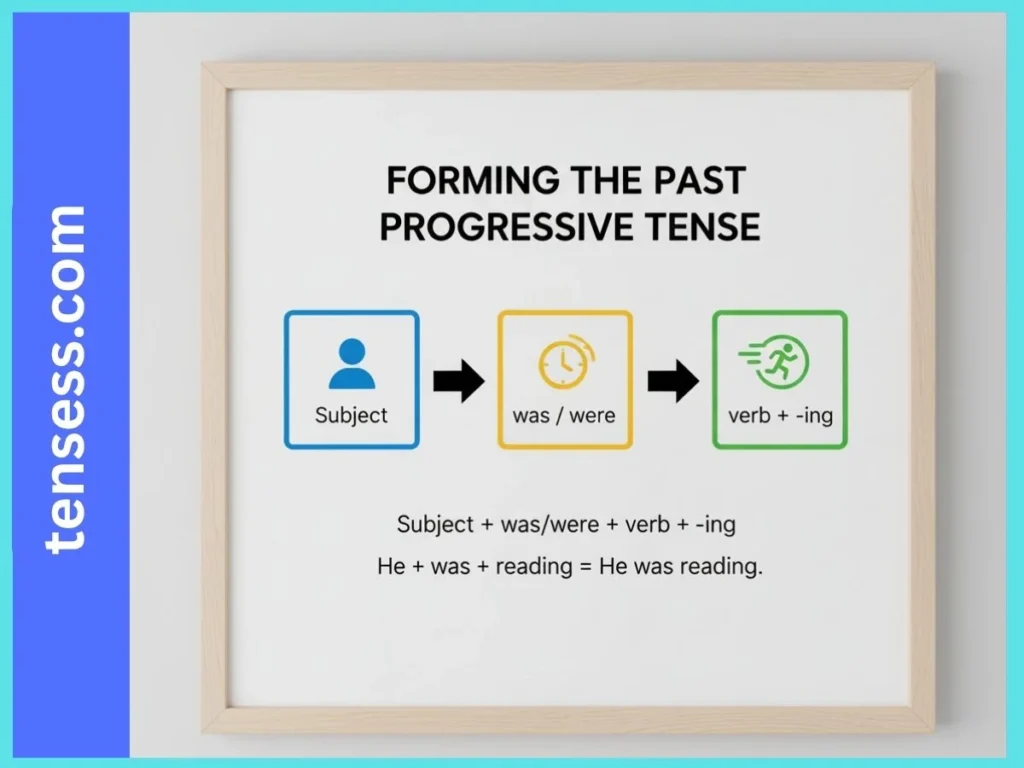
To form the past progressive tense:
- Identify the subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- Choose was (for singular subjects: I, he, she, it) or were (for plural subjects: you, we, they).
- Add the present participle of the main verb (verb + -ing).
Example: “She was singing.”
Verbs
The past progressive tense works with most verbs, both regular and irregular. The main verb transforms into its present participle form by adding -ing. For example:
- Regular verb: walk → walking
- Irregular verb: run → running
The key is the helping verb (was/were) paired with the participle.
Helping Verbs
The helping verbs in the past progressive tense are:
- Was: Used with singular subjects (I, he, she, it).
- Were: Used with plural subjects (you, we, they).
Example: “He was studying” vs. “They were studying.”
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Past Progressive Tense
Certain verbs shine in the past progressive tense:
- Dynamic verbs: Actions like “run,” “dance,” or “write” work well because they describe ongoing activities (e.g., “She was dancing”).
- Stative verbs: Verbs like “know” or “love” are rarely used in this tense since they describe states, not actions. Instead, use the past simple (e.g., “She knew” not “She was knowing”).
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Past Progressive Tense
| Base Verb | Regular/Irregular | Past Progressive Form |
| Walk | Regular | was/were walking |
| Write | Regular | was/were writing |
| Sing | Regular | was/were singing |
| Run | Irregular | was/were running |
| Swim | Irregular | was/were swimming |
| Eat | Irregular | was/were eating |
| Drink | Irregular | was/were drinking |
| Go | Irregular | was/were going |
| See | Irregular | was/were seeing |
| Come | Irregular | was/were coming |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I was reading a novel last night.
- She was cooking dinner at 6 PM.
- He was playing guitar in the park.
- We were watching a movie yesterday.
- They were running in the rain.
- You were studying for the exam.
- It was raining all afternoon.
- John was writing a letter.
- The kids were laughing loudly.
- Sarah was painting the house.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I was not reading during the meeting.
- She wasn’t cooking when I arrived.
- He wasn’t playing soccer yesterday.
- We weren’t watching TV last night.
- They weren’t running in the park.
- You weren’t studying at 8 PM.
- It wasn’t raining this morning.
- John wasn’t writing emails.
- The kids weren’t laughing quietly.
- Sarah wasn’t painting the walls.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Was I reading too slowly?
- Was she cooking dinner earlier?
- Was he playing the piano?
- Were we watching the right show?
- Were they running in the race?
- Were you studying last night?
- Was it raining all day?
- Was John writing a book?
- Were the kids laughing at the joke?
- Was Sarah painting the room?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Wasn’t I reading the instructions correctly?
- Wasn’t she cooking when you called?
- Wasn’t he playing with the team?
- Weren’t we watching the sunset?
- Weren’t they running too fast?
- Weren’t you studying for the test?
- Wasn’t it raining earlier today?
- Wasn’t John writing a report?
- Weren’t the kids laughing at the show?
- Wasn’t Sarah painting the fence?
How to Conjugate Past Progressive Tense
To conjugate the past progressive tense:
- Use was for singular subjects (I, he, she, it).
- Use were for plural subjects (you, we, they).
- Add the present participle (verb + -ing).
- Ensure subject-verb agreement.
- For negatives, add “not” after was/were.
- For questions, invert was/were and the subject.
- Use time markers like “while” for clarity.
- Avoid stative verbs like “know.”
- Check for spelling changes in verbs.
- Practice with varied subjects and verbs.
Conjugation Table (for All Subjects)
| Subject | Positive Form | Negative Form | Interrogative Form |
| I | was running | was not running | Was I running? |
| You | were running | were not running | Were you running? |
| He/She/It | was running | was not running | Was he/she/it running? |
| We | were running | were not running | Were we running? |
| They | were running | were not running | Were they running? |
| John | was running | was not running | Was John running? |
| The kids | were running | were not running | Were the kids running? |
| You (pl) | were running | were not running | Were you running? |
| It | was raining | was not raining | Was it raining? |
| Sarah | was painting | was not painting | Was Sarah painting? |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- Verbs ending in -e: Drop the -e before adding -ing (e.g., write → writing).
- Consonant + vowel + consonant: Double the final consonant (e.g., run → running).
- Verbs ending in -ie: Change to -y + ing (e.g., lie → lying).
- Irregular verbs: The base verb may be irregular, but the -ing form follows standard rules (e.g., swim → swimming).
- No major irregularities in the past progressive tense itself, as the helping verb (was/were) remains consistent.
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I was walking to school yesterday.
- You were singing beautifully last night.
- He was fixing the car all morning.
- She was reading a thriller novel.
- It was snowing heavily last week.
- We were dancing at the party.
- They were playing chess for hours.
- John was writing a poem.
- The dogs were barking loudly.
- Sarah was painting the kitchen.
- You (plural) were studying together.
- The kids were laughing at the clown.
- Anna was cooking a delicious meal.
- The team was practicing for the game.
- I was jogging in the park.
Common Mistakes with Past Progressive Tense
- Using stative verbs (e.g., “I was knowing” instead of “I knew”).
- Forgetting subject-verb agreement (e.g., “She were” instead of “She was”).
- Omitting the -ing form (e.g., “He was play” instead of “He was playing”).
- Overusing the tense for completed actions (e.g., “I was finishing” vs. “I finished”).
- Incorrect negation (e.g., “She not was running” instead of “She wasn’t running”).
- Misplacing time markers (e.g., “When she was cooking, she burns” vs. “burned”).
- Confusing with past simple (e.g., “I was studying” for a completed action).
- Incorrect question structure (e.g., “She was running?” vs. “Was she running?”).
- Spelling errors in -ing forms (e.g., “runing” vs. “running”).
- Using wrong helping verbs (e.g., “They was” vs. “They were”).
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Avoid stative verbs; use past simple for states like “know” or “love.”
- Double-check was/were agreement with the subject.
- Always include the -ing form of the main verb.
- Reserve past progressive for ongoing actions, not completed ones.
- Use “wasn’t” or “weren’t” for negatives, not “not was.”
- Pair with time markers like “while” or “when” correctly.
- Practice past progressive vs. past simple to clarify usage.
- Structure questions by inverting was/were and the subject.
- Review spelling rules for -ing forms (e.g., doubling consonants).
- Memorize that “I/he/she/it” uses was, and “you/we/they” uses were.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Past Progressive Tense
The past progressive tense doesn’t have synonyms, but it’s often confused with:
- Past simple: Describes completed actions (e.g., “She cooked” vs. “She was cooking”).
- Present progressive: Ongoing actions now (e.g., “She is cooking”).
- Common verbs in this tense: run, walk, write, sing, play.
- Confused verbs: Stative verbs like “seem,” “belong,” or “own” (use past simple instead).
Sentence Comparisons
- Past Progressive: She was cooking when I arrived.
Past Simple: She cooked dinner last night. - Past Progressive: They were playing outside.
Past Simple: They played soccer yesterday. - Past Progressive: I was writing a letter.
Past Simple: I wrote a letter. - Past Progressive: He was reading a book.
Past Simple: He read a book. - Past Progressive: We were dancing at the party.
Past Simple: We danced all night.
Tips to Practice Using Past Progressive Tense
- Write a short story using past progressive to describe ongoing actions.
- Pair with past simple to show interruptions (e.g., “I was reading when…”).
- Use time markers like “while” or “when” in sentences.
- Practice with different subjects (I, you, he, etc.).
- Create negative and interrogative sentences.
- Read books and identify past progressive examples.
- Speak sentences aloud to practice fluency.
- Use flashcards for was/were and -ing forms.
- Try online grammar quizzes for past progressive.
- Journal about past events using this tense.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past progressive tense? It describes ongoing past actions.
- When do we use it? For actions in progress at a specific past moment.
- What’s the difference between past simple and past progressive? Past simple is for completed actions; past progressive is for ongoing ones.
- Can stative verbs be used? No, use past simple for states like “know.”
- How do I form negatives? Add “not” after was/were.
- How do I form questions? Invert was/were and the subject.
- What are common time markers? “When,” “while,” “at that moment.”
- Are there spelling changes? Yes, like dropping -e or doubling consonants.
- Can I use irregular verbs? Yes, just add -ing (e.g., run → running).
- How do I practice? Write stories, use quizzes, or speak sentences.
Exercises
- Write 5 sentences using past progressive with different subjects.
- Convert 5 past simple sentences to past progressive.
- Create 5 negative past progressive sentences.
- Form 5 interrogative past progressive sentences.
- Combine past progressive and past simple in 5 sentences.
- Identify past progressive in a paragraph from a book.
- Write a dialogue using past progressive.
- Correct 5 incorrect past progressive sentences.
- Use time markers in 5 past progressive sentences.
- Describe a past event using 5 past progressive sentences.
Quizzes
- What is the correct form: “She ___ (run) yesterday”?
a) was running b) runs c) ran
Answer: a) was running - Which is correct?
a) They was playing b) They were playing c) They is playing
Answer: b) They were playing - Negative form of “He was singing”?
a) He wasn’t singing b) He not was singing c) He didn’t sing
Answer: a) He wasn’t singing - Interrogative form of “We were studying”?
a) Were we studying? b) We were studying? c) Did we study?
Answer: a) Were we studying? - Which verb can’t be used?
a) was running b) was knowing c) was writing
Answer: b) was knowing - Correct the error: “I were reading.”
Answer: I was reading. - Spell the -ing form of “write.”
Answer: writing - What’s the helping verb for “they”?
a) was b) were c) is
Answer: b) were - Combine: “She was cooking. He arrived.”
Answer: She was cooking when he arrived. - Identify the tense: “They were dancing.”
Answer: Past progressive
True/False
- The past progressive uses “was” for “they.” False (uses “were”).
- Stative verbs like “love” work in this tense. False.
- “Was she running?” is correct. True.
- “I was write” is correct. False (should be “writing”).
- Time markers like “while” are common. True.
- Irregular verbs don’t use -ing. False.
- “They were not singing” is correct. True.
- The tense shows completed actions. False.
- “Was” is used for plural subjects. False.
- Spelling changes occur for some verbs. True.
Conclusion
Mastering the past progressive tense opens doors to clearer, more dynamic communication.
By understanding its structure—was/were + verb + -ing—and practicing with real-life examples, you can describe past actions with confidence.
Avoid common mistakes like using stative verbs or incorrect helping verbs, and use tools like quizzes and exercises to reinforce your skills.
If you’re a student, writer, or language learner, the past progressive tense is a powerful tool for storytelling and clarity.
Try writing a short story or journaling about a past event using this tense. For extra help, consider using a grammar checker to polish your sentences.
Start practicing today and watch your grammar skills soar!



