The past tense is a fundamental part of English grammar, used to describe actions, events, or states that have already happened.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering the past tense is essential for clear communication.
From recounting a childhood memory to crafting a compelling story, this tense helps you express completed actions with confidence.
In this article, we’ll explore the past tense, its structure, formation, and common uses, with plenty of verb tense examples to make it beginner-friendly.
You’ll also find tables, sentence examples, and practice tips to help you use the past tense correctly.
Let’s dive into the world of past tense conjugation and learn how to make your sentences shine!
What Is the Past Tense?

The past tense describes actions or events that occurred at a specific time in the past. It’s used to talk about things that are finished, like “I walked to school yesterday” or “She read a book last night.” There are four main types: simple past, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous. Each serves a unique purpose, but this article focuses on the simple past tense, which is the most common for describing completed actions.
How to Recognize the Past Tense?
You can spot the past tense by looking for specific verb forms or time indicators. Words like “yesterday,” “last week,” or “ago” often signal the past tense. For regular verbs, the past tense typically ends in -ed (e.g., “walked,” “played”). Irregular verbs, however, have unique forms, like “went” (from “go”) or “saw” (from “see”). Pay attention to the verb’s form and context to identify the past tense.
Structure of Sentence
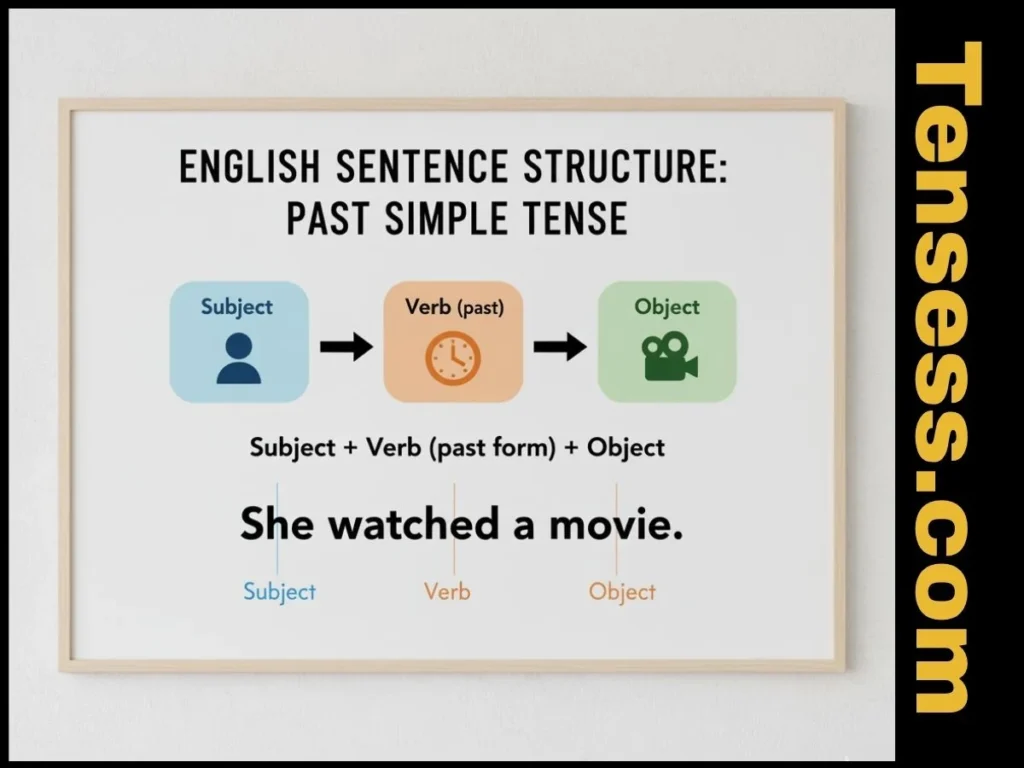
The simple past tense follows a straightforward structure:
- Subject + Verb (past form) + Object/Complement
- Example: “She watched a movie.”
For negative sentences: - Subject + did not + Base Verb + Object/Complement
- Example: “She did not watch a movie.”
For interrogative sentences: - Did + Subject + Base Verb + Object/Complement?
- Example: “Did she watch a movie?”
Formation
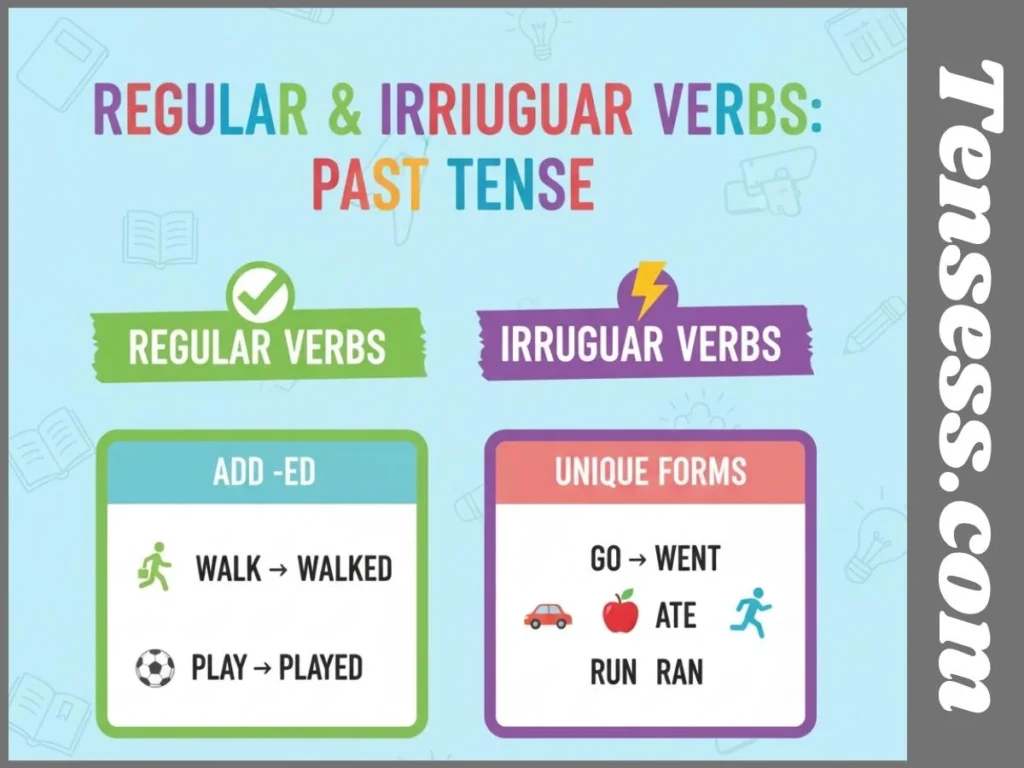
To form the simple past tense:
- Regular verbs: Add -ed to the base verb (e.g., “walk” → “walked”).
- Irregular verbs: Use the unique past form (e.g., “go” → “went”).
- Use did for negatives and questions with the base verb (e.g., “did not go,” “Did you go?”).
The formation depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular, which we’ll explore further.
Verbs
In the past tense, verbs are either regular or irregular. Regular verbs follow a predictable pattern by adding -ed, while irregular verbs change unpredictably. Knowing the difference is key to mastering past tense conjugation.
Helping Verbs
The simple past tense primarily uses did as a helping verb for negative and interrogative sentences. For example:
- Negative: “I did not play soccer.”
- Interrogative: “Did you play soccer?”
Other helping verbs like “was” or “had” appear in other past tenses (e.g., past continuous or past perfect), but did is central to the simple past.
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Past Tense
Let’s look at how common verbs behave in the past tense:
- Walk (regular): Add -ed → “walked.”
- Go (irregular): Changes to “went.”
- Eat (irregular): Changes to “ate.”
- Read (irregular): Changes to “read” (pronounced /rɛd/).
These examples show how past tense verbs vary based on their regularity.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Past Tense
| Base Verb | Past Tense | Regular/Irregular |
| Walk | Walked | Regular |
| Play | Played | Regular |
| Study | Studied | Regular |
| Go | Went | Irregular |
| Eat | Ate | Irregular |
| See | Saw | Irregular |
| Write | Wrote | Irregular |
| Sing | Sang | Irregular |
| Run | Ran | Irregular |
| Read | Read | Irregular |
Simple Sentence Examples
Here are 10 simple past tense examples with different subjects:
- I walked to the park.
- You played soccer yesterday.
- He read a novel last night.
- She wrote a letter.
- It rained all day.
- We visited the museum.
- They sang beautifully.
- John ran a marathon.
- The dog barked loudly.
- Mary studied for hours.
Negative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 negative past tense examples:
- I did not walk to the park.
- You did not play soccer yesterday.
- He did not read a novel.
- She did not write a letter.
- It did not rain today.
- We did not visit the museum.
- They did not sing at the event.
- John did not run a marathon.
- The dog did not bark last night.
- Mary did not study for the test.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 interrogative past tense examples:
- Did I walk to the park?
- Did you play soccer yesterday?
- Did he read a novel?
- Did she write a letter?
- Did it rain yesterday?
- Did we visit the museum?
- Did they sing at the event?
- Did John run a marathon?
- Did the dog bark last night?
- Did Mary study for the test?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
Here are 10 negative interrogative past tense examples:
- Didn’t I walk to the park?
- Didn’t you play soccer yesterday?
- Didn’t he read a novel?
- Didn’t she write a letter?
- Didn’t it rain yesterday?
- Didn’t we visit the museum?
- Didn’t they sing at the event?
- Didn’t John run a marathon?
- Didn’t the dog bark last night?
- Didn’t Mary study for the test?
How to Conjugate Past Tense
To conjugate verbs in the simple past tense:
- Identify if the verb is regular or irregular.
- For regular verbs, add -ed (e.g., “talk” → “talked”).
- For irregular verbs, use the unique past form (e.g., “go” → “went”).
- Use did for negative sentences (e.g., “did not go”).
- Use did for questions (e.g., “Did you go?”).
- Ensure subject-verb agreement (e.g., “He walked,” not “He walk”).
- Watch for spelling changes (e.g., “study” → “studied”).
- Memorize common irregular verbs like “eat” (ate) or “see” (saw).
- Practice with different subjects (I, you, he, etc.).
- Check context for time indicators like “yesterday.”
Conjugation Table (for All Subjects)
Here’s a conjugation table for the verb “walk” in the simple past tense:
| Subject | Conjugation |
| I | Walked |
| You | Walked |
| He/She/It | Walked |
| We | Walked |
| They | Walked |
| John | Walked |
| Mary | Walked |
| The dog | Walked |
| You (pl) | Walked |
| I (formal) | Walked |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- Regular verbs: Add -ed (e.g., “play” → “played”). For verbs ending in -e, add -d (e.g., “love” → “loved”). For verbs ending in consonant + y, change y to i and add -ed (e.g., “study” → “studied”).
- Irregular verbs: No consistent rule; memorize forms like “go” → “went,” “read” → “read” (/rɛd/), or “write” → “wrote.”
- Doubling consonants: For verbs like “stop” (ending in consonant-vowel-consonant), double the final consonant and add -ed (e.g., “stopped”).
Sentence Examples
Here are 15 past tense examples with various subjects:
- I ate a delicious pizza.
- You saw a movie last weekend.
- He wrote a poem for her.
- She danced at the party.
- It snowed heavily yesterday.
- We traveled to Paris.
- They played chess all night.
- John bought a new car.
- Mary sang a beautiful song.
- The cat slept on the couch.
- You studied for the exam.
- He ran to catch the bus.
- She read a book in one day.
- We laughed at the joke.
- They visited their grandparents.
Common Mistakes with Past Tense
Here are 10 frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Using -ed on irregular verbs (e.g., “I goed” → Correct: “I went”).
- Forgetting did in negatives (e.g., “I not went” → Correct: “I did not go”).
- Omitting did in questions (e.g., “You went?” → Correct: “Did you go?”).
- Misspelling regular verbs (e.g., “studied” as “studyed”).
- Using present tense verbs (e.g., “I walk yesterday” → Correct: “I walked yesterday”).
- Mixing tenses (e.g., “I walked and see a dog” → Correct: “I walked and saw a dog”).
- Incorrect irregular forms (e.g., “I eated” → Correct: “I ate”).
- Overusing -ed (e.g., “I runned” → Correct: “I ran”).
- Ignoring spelling rules (e.g., “stop” → “stoped” instead of “stopped”).
- Forgetting time indicators (e.g., “I walked” → Better: “I walked yesterday”).
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Past Tense
Some verbs are often confused with past tense forms:
- Go (went) vs. Come (came): “I went to the store” vs. “I came home.”
- See (saw) vs. Look (looked): “I saw a bird” vs. “I looked at the sky.”
- Eat (ate) vs. Drink (drank): “I ate dinner” vs. “I drank water.”
- Write (wrote) vs. Draw (drew): “She wrote a story” vs. “She drew a picture.”
- Run (ran) vs. Walk (walked): “He ran fast” vs. “He walked slowly.”
Tips to Practice Using Past Tense
- Write a short story about your day yesterday.
- Describe a past vacation using 10 past tense verbs.
- Practice negative sentences (e.g., “I did not go to school”).
- Form questions like “Did you eat breakfast?”
- Memorize 10 irregular verbs daily.
- Use flashcards for irregular verb forms.
- Speak about past events with a friend.
- Read books and highlight past tense verbs.
- Complete online past tense quizzes.
- Check your writing with a grammar tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past tense? It describes completed actions (e.g., “I walked”).
- How do I form the past tense? Add -ed for regular verbs or use irregular forms.
- What’s the difference between regular and irregular verbs? Regular verbs add -ed; irregular verbs change uniquely.
- When is did used? In negative and interrogative sentences.
- Can all verbs use the past tense? Yes, all verbs have a past form.
- What are common past tense mistakes? Using -ed on irregular verbs.
- How do I conjugate irregular verbs? Memorize their unique forms (e.g., “go” → “went”).
- Are there spelling rules for regular verbs? Yes, like changing y to i (e.g., “study” → “studied”).
- How can I practice the past tense? Write, speak, and use quizzes.
- What’s an example of a past tense sentence? “She read a book.”
Exercises
- Convert “I eat” to past tense. (Answer: I ate.)
- Write a negative sentence with “play.” (Answer: I did not play.)
- Form a question with “see.” (Answer: Did you see?)
- Change “study” to past tense. (Answer: Studied.)
- Write a sentence with “go” in past tense. (Answer: I went home.)
- Make “run” negative. (Answer: I did not run.)
- Form a question with “write.” (Answer: Did she write?)
- Convert “sing” to past tense. (Answer: Sang.)
- Write a sentence with “read” in past tense. (Answer: He read a book.)
- Make “walk” interrogative. (Answer: Did you walk?)
Quizzes
- What is the past tense of “go”? (Answer: Went.)
- Is “walked” regular or irregular? (Answer: Regular.)
- What’s the negative of “I saw”? (Answer: I did not see.)
- Form a question with “eat.” (Answer: Did you eat?)
- What’s the past tense of “study”? (Answer: Studied.)
- Is “sang” correct for “sing”? (Answer: Yes.)
- What’s the past tense of “write”? (Answer: Wrote.)
- Form a negative with “run.” (Answer: I did not run.)
- What’s the past tense of “see”? (Answer: Saw.)
- Is “read” (/rɛd/) correct for past tense? (Answer: Yes.)
True or False
- The past tense describes future actions. (False)
- Regular verbs add -ed in past tense. (True)
- “Went” is the past tense of “go.” (True)
- “I did not went” is correct. (False)
- “Did you see?” is a past tense question. (True)
- Irregular verbs follow the -ed rule. (False)
- “Studied” is the past tense of “study.” (True)
- “I eated” is correct. (False)
- “Did” is used in negative past tense sentences. (True)
- The past tense can use time words like “yesterday.” (True)
Conclusion
The past tense is a powerful tool for sharing stories, describing experiences, and communicating clearly.
By understanding its structure, conjugation rules, and common pitfalls, you can use it confidently in writing and conversation.
Whether you’re a student, language learner, or writer, practicing the past tense with real-life examples and exercises will boost your grammar skills.
Try writing a short paragraph about a past event, or use a grammar checker to refine your sentences.
With the tips, tables, and examples in this article, you’re well-equipped to master the past tense.
Keep practicing, and soon you’ll be using past tense verbs like a pro! Share your own past tense sentences in the comments or try our quizzes to test your skills.