The present continuous tense, also known as the present progressive tense, is a vital part of English grammar.
It describes actions happening right now, temporary activities, or future plans.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering this tense will enhance your communication skills.
This beginner-friendly guide breaks down the present continuous tense with easy explanations, real-life verb tense examples, and practical tips. By the end, you’ll understand how to form, recognize, and use this tense confidently.
Let’s dive into the present continuous tense and explore its structure, usage, and common pitfalls to help you speak and write with clarity.
What Is the Present Continuous Tense?

The present continuous tense describes actions occurring at the moment of speaking, temporary situations, or planned future events. For example, “I am writing this article” shows an action happening now. It’s also used for changing situations, like “The weather is getting colder.” This tense adds energy and immediacy to sentences, making it essential for dynamic communication. Understanding how to use the present continuous tense correctly helps you express ongoing actions clearly.
How to Recognize the Present Continuous Tense?
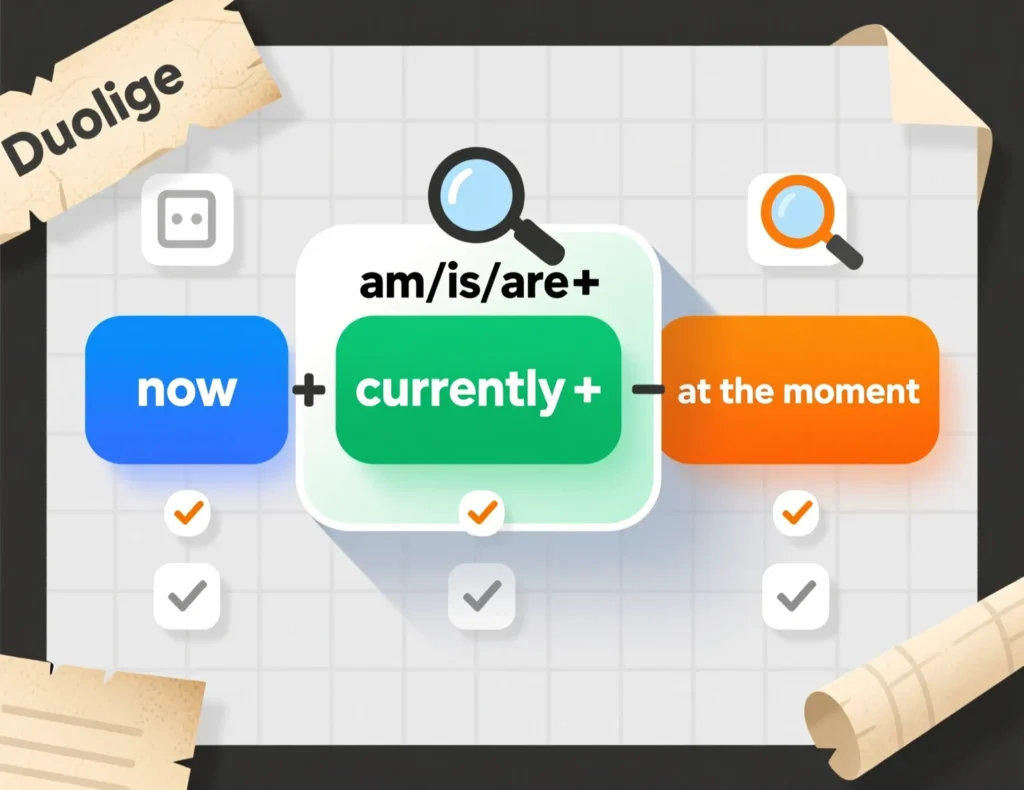
You can spot the present continuous tense by looking for the structure: subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing. For instance, in “She is singing,” “is” is the helping verb, and “singing” is the main verb with the -ing ending. This tense often appears with time expressions like “now,” “at the moment,” or “currently.” Recognizing these clues helps you identify the tense in conversations or texts.
Structure of a Sentence
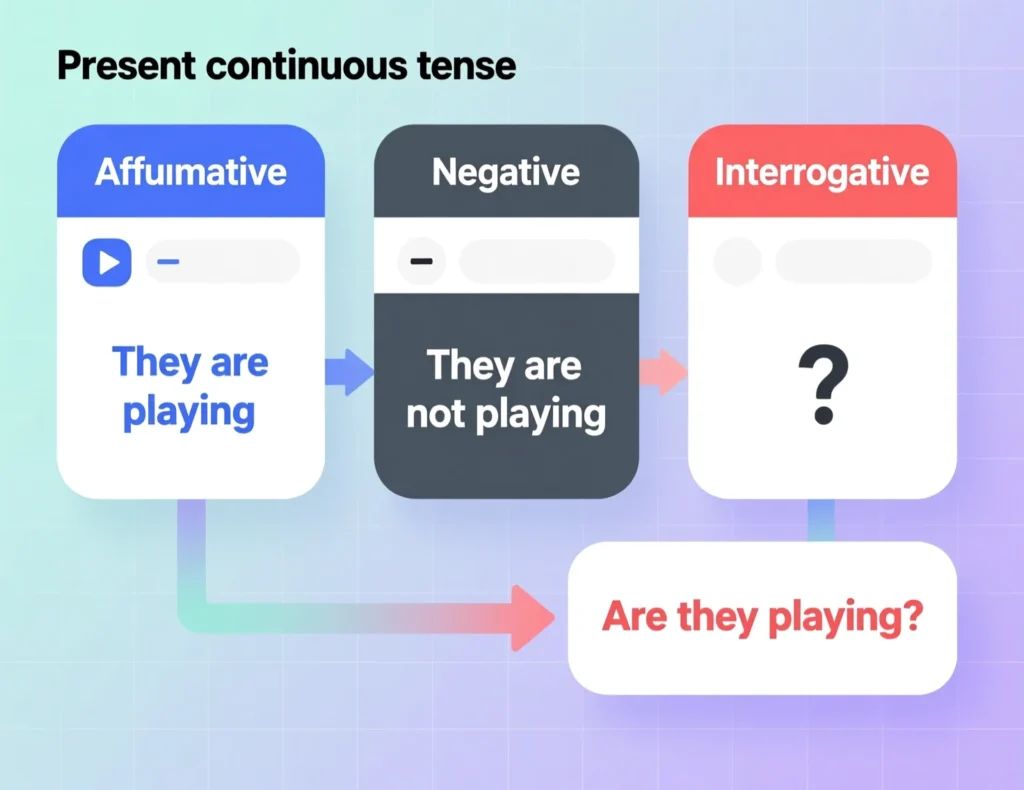
The present continuous tense follows a clear pattern:
- Affirmative: Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing (e.g., “They are playing football.”)
- Negative: Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + -ing (e.g., “They are not playing football.”)
- Interrogative: Am/Is/Are + subject + verb + -ing? (e.g., “Are they playing football?”)
This structure ensures clarity when forming sentences in this tense.
Formation
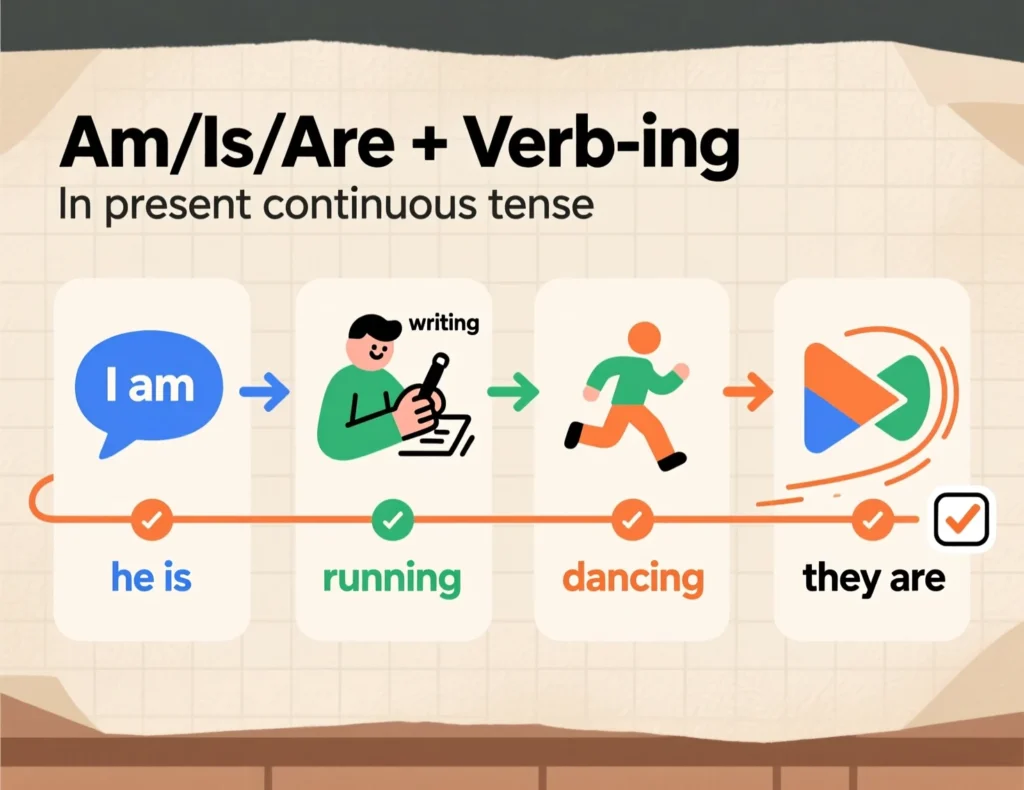
To form the present continuous tense, combine the appropriate form of the verb “to be” (am, is, or are) with the main verb ending in -ing. For example:
- I am reading.
- She is dancing.
- They are studying.
The choice of am, is, or are depends on the subject, and the -ing ending transforms the verb to show ongoing action.
Verbs
The present continuous tense works with most verbs, especially action verbs like “run,” “write,” or “sing.” However, some verbs, called stative verbs (e.g., “know,” “love,” “believe”), are rarely used in this tense because they describe states, not actions. For example, you’d say “I know the answer,” not “I am knowing the answer.”
Helping Verbs
The helping verbs in the present continuous tense are am, is, and are. These forms of “to be” indicate the subject and tense. For example:
- I am (first person singular)
- He/She/It is (third person singular)
- We/You/They are (plural or second person)
These helping verbs are essential for proper verb conjugation.
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Present Continuous Tense
Certain verbs shine in the present continuous tense:
- Run: “He is running in the park” shows an action happening now.
- Study: “They are studying for exams” indicates a temporary activity.
- Plan: “We are planning a trip” suggests a future intention.
Stative verbs like “want” or “need” are less common in this tense, as they describe fixed states.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Present Continuous Tense
| Base Verb | Present Continuous Form | Example Sentence |
| Run | Running | She is running. |
| Write | Writing | I am writing. |
| Swim | Swimming | They are swimming. |
| Take | Taking | He is taking notes. |
| Sit | Sitting | We are sitting. |
| Come | Coming | She is coming. |
| Eat | Eating | They are eating. |
| Dance | Dancing | He is dancing. |
| Read | Reading | I am reading. |
| Play | Playing | We are playing. |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I am reading a book.
- She is dancing in the studio.
- They are playing soccer.
- He is writing a letter.
- We are studying grammar.
- You are singing beautifully.
- It is raining outside.
- John is cooking dinner.
- The kids are laughing loudly.
- I am walking to school.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I am not reading a book.
- She is not dancing today.
- They are not playing soccer.
- He is not writing a letter.
- We are not studying now.
- You are not singing well.
- It is not raining anymore.
- John is not cooking tonight.
- The kids are not laughing now.
- I am not walking to school.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Am I reading correctly?
- Is she dancing in the studio?
- Are they playing soccer?
- Is he writing a letter?
- Are we studying enough?
- Are you singing now?
- Is it raining outside?
- Is John cooking dinner?
- Are the kids laughing?
- Am I walking too fast?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Am I not reading fast enough?
- Is she not dancing today?
- Are they not playing well?
- Is he not writing clearly?
- Are we not studying hard?
- Are you not singing loudly?
- Is it not raining now?
- Is John not cooking tonight?
- Are the kids not laughing?
- Am I not walking properly?
How to Conjugate Present Continuous Tense
Conjugating the present continuous tense is straightforward:
- Identify the subject (I, you, he, etc.).
- Choose the correct form of “to be” (am, is, are).
- Add the main verb with an -ing ending.
- For negatives, insert “not” after the helping verb.
- For questions, invert the subject and helping verb.
- Ensure the verb is an action verb, not a stative verb.
- Use time expressions like “now” for clarity.
- Check for spelling changes (e.g., “run” to “running”).
- Practice with different subjects for fluency.
- Review your sentence for accuracy.
Conjugation Table for All Subjects
| Subject | Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
| I | I am running | I am not running | Am I running? |
| You | You are running | You are not running | Are you running? |
| He/She/It | He is running | He is not running | Is he running? |
| We | We are running | We are not running | Are we running? |
| They | They are running | They are not running | Are they running? |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
Some verbs require spelling adjustments in the present continuous tense:
- Verbs ending in -e drop the “e” (e.g., write → writing).
- Verbs ending in a consonant after a stressed vowel double the consonant (e.g., run → running).
- Verbs ending in -ie change to -y (e.g., lie → lying).
- Irregular verbs like “go” (going) follow standard -ing rules.
These changes ensure proper verb conjugation.
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I am learning English.
- You are reading a novel.
- He is painting the house.
- She is running in the park.
- It is snowing outside.
- We are watching a movie.
- They are dancing at the party.
- John is cooking dinner.
- The dogs are barking loudly.
- You are writing a letter.
- I am singing a song.
- She is studying for exams.
- They are playing games.
- He is swimming in the pool.
- We are planning a trip.
Common Mistakes with Present Continuous Tense
- Using stative verbs (e.g., “I am knowing” → “I know”).
- Forgetting the helping verb (e.g., “She running” → “She is running”).
- Omitting -ing (e.g., “They are play” → “They are playing”).
- Incorrect subject-verb agreement (e.g., “I is running” → “I am running”).
- Misusing for permanent states (e.g., “I am living here forever” → “I live here”).
- Wrong word order in questions (e.g., “She is running?” → “Is she running?”).
- Spelling errors (e.g., “writting” → “writing”).
- Overusing the tense for future plans without context.
- Confusing with present simple (e.g., “I am reading every day” → “I read every day”).
- Ignoring time expressions like “now” or “currently.”
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Use action verbs, not stative verbs, in this tense.
- Always include am, is, or are.
- Double-check the -ing ending.
- Match the helping verb to the subject.
- Reserve the tense for temporary or ongoing actions.
- Practice question formation with inversion.
- Review spelling rules for -ing forms.
- Clarify future plans with time expressions.
- Differentiate between present continuous and present simple.
- Proofread sentences for accuracy.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Present Continuous Tense
Verbs like “run,” “work,” and “play” are commonly used in the present continuous tense. Synonyms or related terms include:
- Work (synonym: labor) → “She is working” vs. “She is laboring.”
- Talk (synonym: speak) → “They are talking” vs. “They are speaking.”
- Move (synonym: shift) → “He is moving” vs. “He is shifting.”
Verbs confused with this tense include stative verbs like “know” or “like.”
Sentence Comparisons
- Work: “I am working now” (temporary) vs. “I work every day” (habit).
- Talk: “She is talking loudly” (now) vs. “She talks a lot” (general).
- Run: “They are running fast” (now) vs. “They run daily” (routine).
- Study: “He is studying tonight” vs. “He studies every evening.”
- Play: “We are playing soccer” vs. “We play soccer weekly.”
- Sing: “You are singing well” vs. “You sing beautifully.”
- Write: “I am writing a letter” vs. “I write letters often.”
- Dance: “She is dancing now” vs. “She dances professionally.”
- Read: “They are reading books” vs. “They read every night.”
- Eat: “He is eating lunch” vs. “He eats lunch at noon.”
Tips to Practice Using Present Continuous Tense
- Write 5 sentences daily using different subjects.
- Describe what people around you are doing.
- Use time expressions like “now” or “currently.”
- Practice forming negative sentences.
- Create questions and answer them aloud.
- Read books and highlight present continuous examples.
- Watch English videos and note the tense.
- Use grammar apps to practice.
- Speak with friends using the tense.
- Keep a journal of ongoing activities.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the present continuous tense? It describes actions happening now or temporarily.
- Can stative verbs be used? Rarely, as they describe states, not actions.
- How do I form questions? Invert the subject and helping verb (e.g., Is she running?).
- What’s the difference with present simple? Present continuous is for now; present simple is for habits.
- Can it show future plans? Yes, with time expressions (e.g., “I am meeting her tomorrow”).
- Why use -ing? It indicates ongoing action.
- How to avoid spelling errors? Follow -ing spelling rules.
- Is “am not” correct? Yes, for first-person singular negatives.
- Can I use contractions? Yes, like “I’m” or “she’s.”
- How to practice? Write, speak, and read daily.
Exercises
- Write 5 present continuous sentences about your day.
- Convert 5 present simple sentences to present continuous.
- Form 3 negative sentences.
- Create 3 interrogative sentences.
- Describe a photo using the tense.
- Rewrite a paragraph using only present continuous.
- Identify the tense in a short story.
- Practice with a friend, describing actions.
- Use 5 different verbs in sentences.
- Check your sentences with a grammar tool.
Quizzes
- What is the correct form: “She ___ (run) now”? is running
- Is “I am knowing” correct? No, use “I know.”
- Form a question: “They/play/soccer”? Are they playing soccer?
- Negative form of “He is eating”? He is not eating.
- Spell the -ing form of “write”? Writing
- Is “We are liking” correct? No, use “We like.”
- Conjugate “dance” for “they”? They are dancing.
- Use “study” in a sentence. I am studying now.
- Fix: “I is running.” I am running.
- Spot the error: “She are singing.” She is singing.
True or False
- The present continuous tense uses am/is/are. True
- Stative verbs are common in this tense. False
- “I am run” is correct. False
- Questions start with am/is/are. True
- It can describe future plans. True
- “Running” is spelled “runing.” False
- “They are playing” is present continuous. True
- “I like” is present continuous. False
- Negatives use “not” after the helping verb. True
- “She is writeing” is correct. False
Conclusion
The present continuous tense is a powerful tool for describing actions happening now, temporary situations, or future plans.
By mastering its structure—subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing—you can communicate with precision and clarity.
This guide has covered verb conjugation, examples, common mistakes, and practice tips to help you use the tense confidently.
Whether you’re a student, writer, or language learner, practicing the present continuous tense will improve your English skills.
Try writing sentences, describing your day, or using a grammar checker to refine your work. Share your sentences in the comments or test your skills with our quizzes! Keep practicing, and you’ll master this tense in no time.



