The present perfect tense is a vital part of English grammar, connecting past actions to the present moment.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering this tense can elevate your communication skills.
It’s used to describe experiences, completed actions with present relevance, or changes over time.
In this beginner-friendly guide, we’ll break down the present perfect tense, its structure, usage, and examples.
With clear explanations, tables, and practice tips, you’ll gain confidence in using this tense correctly.
Let’s dive into verb tense examples and explore how to use the present perfect tense effectively!
What Is the Present Perfect Tense?
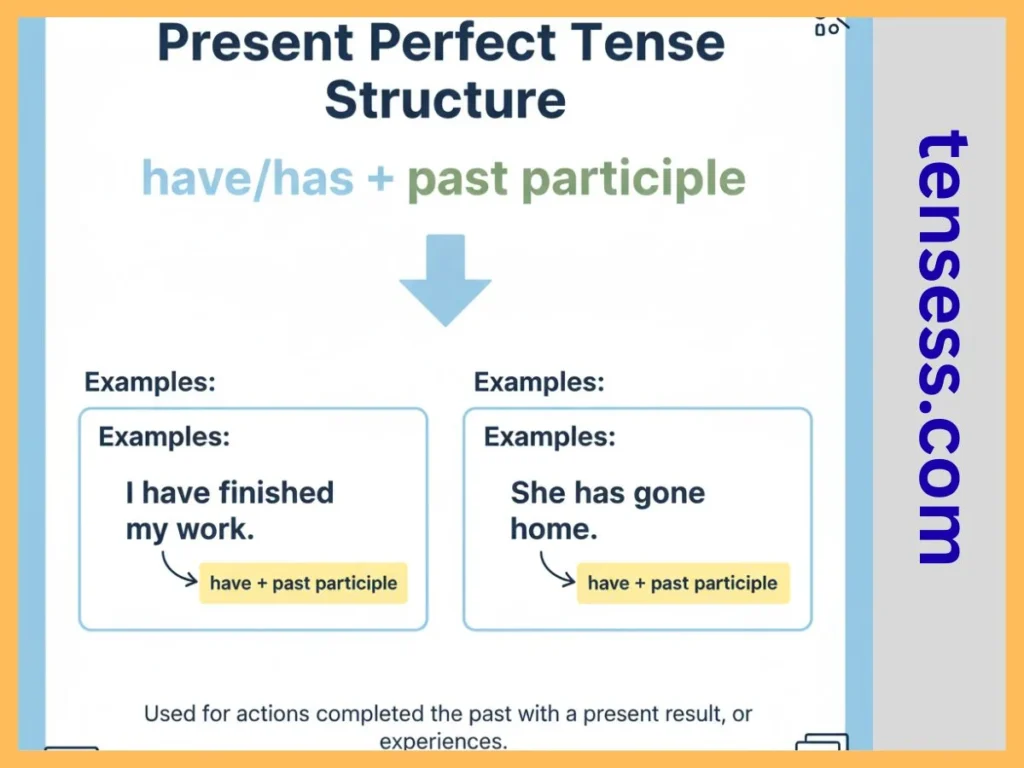
The present perfect tense describes actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past or actions that still have relevance today. It’s formed with have/has + past participle of the main verb. For example, “I have just finished writing this sentence.” It emphasizes the result or experience, not the exact timing. This tense is perfect for talking about life experiences, recent accomplishments, or ongoing situations.
How to Recognize the Present Perfect Tense?
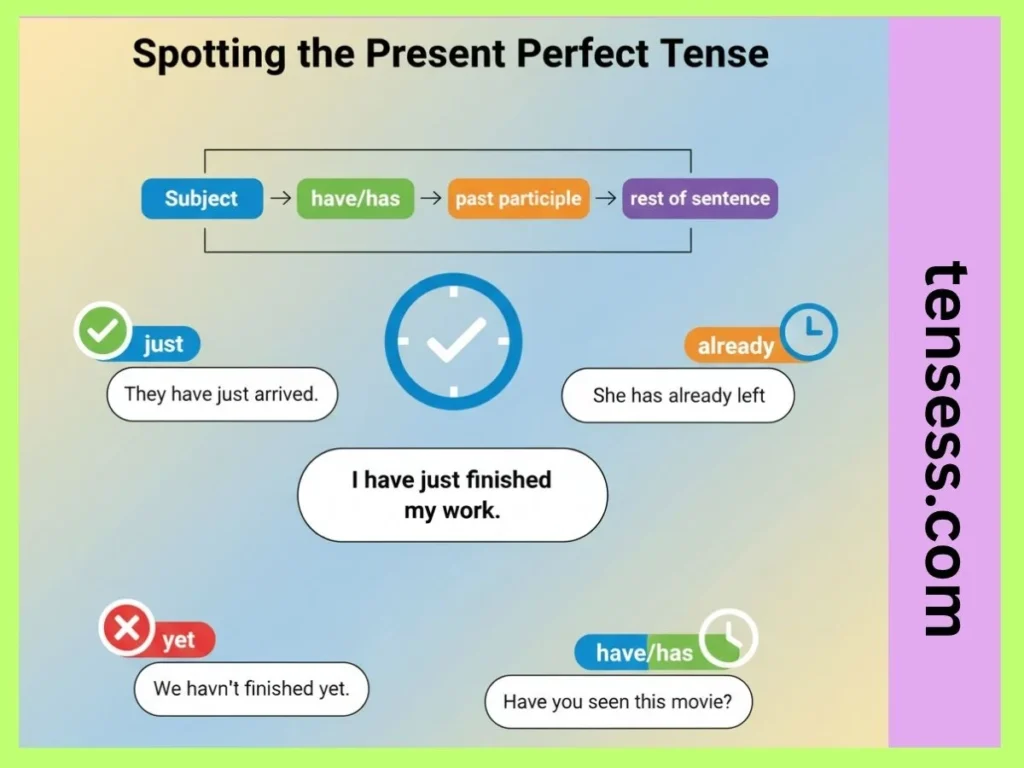
You can spot the present perfect tense by looking for:
- The auxiliary verbs have or has.
- A past participle (e.g., walked, eaten, gone).
- Time expressions like just, already, yet, ever, never, or since.
For example, “She has already left” signals the present perfect tense because it combines has with the past participle left and uses already.
Structure of Sentence
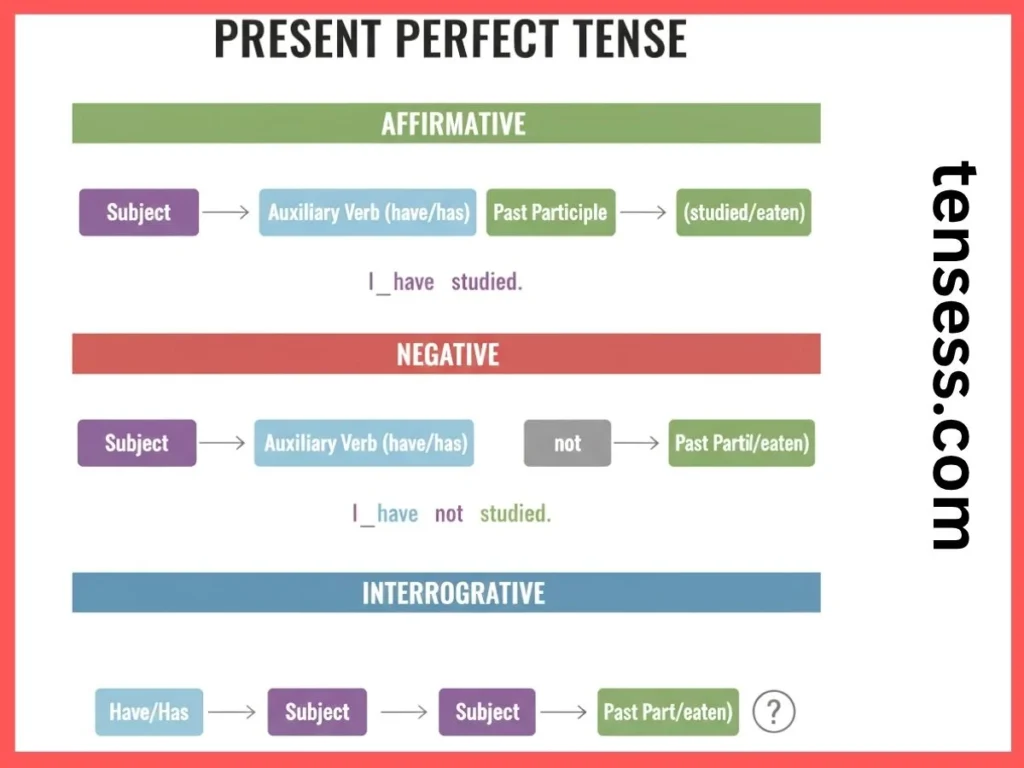
The present perfect tense follows this structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + have/has + past participle (e.g., I have studied).
- Negative: Subject + have/has + not + past participle (e.g., I have not studied).
- Interrogative: Have/Has + subject + past participle? (e.g., Have you studied?).
Formation

To form the present perfect tense:
- Use have for subjects like I, you, we, they.
- Use has for he, she, it.
- Add the past participle of the main verb (regular verbs: verb + -ed; irregular verbs vary, e.g., go → gone).
Verbs
The present perfect tense works with both regular verbs (e.g., walked, played) and irregular verbs (e.g., eaten, gone). The past participle is key, and irregular verbs require memorization.
Helping Verbs
The helping verbs have and has are essential in the present perfect tense. They indicate the tense and agree with the subject:
- Have: Used with I, you, we, they.
- Has: Used with he, she, it.
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Present Perfect Tense
- Go: The past participle is gone. Example: “She has gone to Paris.”
- Eat: The past participle is eaten. Example: “We have eaten lunch.”
- Write: The past participle is written. Example: “He has written a book.”
These verbs show how the present perfect tense highlights completed actions with present relevance.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Present Perfect Tense
| Base Verb | Past Participle | Example Sentence |
| Walk | Walked | I have walked to the park. |
| Eat | Eaten | She has eaten sushi. |
| Go | Gone | They have gone on vacation. |
| Write | Written | He has written a letter. |
| See | Seen | We have seen that movie. |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I have finished my homework.
- She has visited London twice.
- They have played soccer all day.
- He has written three emails.
- We have seen the new museum.
- You have learned a new language.
- It has rained all morning.
- The kids have eaten all the cookies.
- I have lost my keys.
- He has traveled to Japan.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I have not finished my project.
- She has not visited Paris.
- They have not played chess today.
- He has not written the report.
- We have not seen that show.
- You have not learned this rule.
- It has not rained this week.
- The kids have not eaten breakfast.
- I have not lost my phone.
- He has not traveled abroad.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Have you finished your work?
- Has she visited Italy?
- Have they played tennis?
- Has he written a novel?
- Have we seen this film?
- Have you learned Spanish?
- Has it rained today?
- Have the kids eaten lunch?
- Have I lost my wallet?
- Has he traveled to Asia?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Haven’t you finished yet?
- Hasn’t she visited Rome?
- Haven’t they played today?
- Hasn’t he written anything?
- Haven’t we seen this before?
- Haven’t you learned this?
- Hasn’t it rained lately?
- Haven’t the kids eaten yet?
- Haven’t I lost my keys?
- Hasn’t he traveled recently?
How to Conjugate Present Perfect Tense
To conjugate the present perfect tense:
- Identify the subject (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- Use have for I, you, we, they; has for he, she, it.
- Add the past participle of the verb.
- For regular verbs, add -ed (e.g., walk → walked).
- For irregular verbs, use the correct form (e.g., go → gone).
- Ensure subject-verb agreement.
- Use time expressions like just or already for clarity.
- Check for spelling changes in irregular verbs.
- Practice with different subjects.
- Review your sentences for accuracy.
Conjugation Table (for All Subjects)
| Subject | Auxiliary | Verb (Go) | Example Sentence |
| I | have | gone | I have gone to the store. |
| You | have | gone | You have gone to school. |
| He/She/It | has | gone | She has gone to work. |
| We | have | gone | We have gone hiking. |
| They | have | gone | They have gone to Paris. |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- Regular verbs: Add -ed (e.g., play → played).
- Irregular verbs: Memorize forms like go → gone, eat → eaten, see → seen.
- Verbs ending in -y after a consonant: Change y to i and add -ed (e.g., study → studied).
- One-syllable verbs ending in consonant-vowel-consonant: Double the consonant and add -ed (e.g., stop → stopped).
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I have just finished writing this blog.
- You have learned a lot today.
- He has traveled to five countries.
- She has eaten sushi before.
- It has stopped raining.
- We have seen that movie twice.
- They have played soccer all week.
- I have written three articles.
- You have visited the museum.
- He has gone to the gym.
- She has studied for hours.
- We have lost our tickets.
- They have finished their homework.
- I have read that book.
- You have tried this recipe.
Common Mistakes with Present Perfect Tense
- Using present perfect for specific past times (e.g., “I have gone yesterday” → Wrong).
- Forgetting has for third-person singular subjects.
- Using the wrong past participle (e.g., “I have went” → Wrong).
- Omitting have/has in sentences.
- Confusing present perfect with simple past.
- Incorrectly forming irregular past participles.
- Misusing time expressions like yesterday with present perfect.
- Overusing just or already unnecessarily.
- Incorrect subject-verb agreement (e.g., “She have gone” → Wrong).
- Mixing tenses in one sentence.
How to Avoid These Mistakes
- Use simple past for specific times (e.g., “I went yesterday”).
- Always use has for he/she/it.
- Memorize irregular past participles (e.g., go → gone).
- Double-check inclusion of have/has.
- Understand present perfect is for unspecified times or present relevance.
- Refer to a verb conjugation chart for irregular verbs.
- Avoid time expressions like yesterday with this tense.
- Use just/already only when relevant.
- Ensure subject-verb agreement.
- Practice with varied examples.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Present Perfect Tense
- Go: Synonyms include travel, move. Example: “I have gone” vs. “I have traveled.”
- Eat: Synonyms include consume, dine. Example: “She has eaten” vs. “She has dined.”
- See: Synonyms include watch, view. Example: “We have seen” vs. “We have watched.”
- Write: Synonyms include compose, draft. Example: “He has written” vs. “He has composed.”
- Finish: Synonyms include complete, end. Example: “I have finished” vs. “I have completed.”
Sentence Comparisons
- I have gone to Paris. → I have traveled to Paris.
- She has eaten lunch. → She has consumed lunch.
- We have seen the film. → We have watched the film.
- He has written a letter. → He has composed a letter.
- They have finished the task. → They have completed the task.
Tips to Practice Using Present Perfect Tense
- Write 10 sentences using different verbs.
- Use flashcards to memorize irregular past participles.
- Practice with a partner, sharing life experiences.
- Read books and highlight present perfect examples.
- Use apps like Duolingo for grammar exercises.
- Create a journal using the present perfect tense.
- Watch English movies and note tense usage.
- Take online quizzes on verb conjugation.
- Speak about recent accomplishments using this tense.
- Review your sentences with a grammar checker.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the present perfect tense used for? It shows past actions with present relevance.
- How is it different from simple past? Simple past is for specific times; present perfect is for unspecified times.
- Can I use “yesterday” with present perfect? No, use simple past for specific times.
- What are common time expressions? Just, already, yet, ever, never, since.
- How do I form the past participle? Add -ed for regular verbs; memorize irregular forms.
- Is “has” or “have” used for “you”? Use “have” for “you.”
- Can I use present perfect for future actions? No, use future tense for that.
- Why is “I have went” wrong? The correct past participle is “gone.”
- How do I practice this tense? Write sentences and use grammar apps.
- What’s an example of present perfect? “I have just finished this blog.”
Exercises
- Write 5 present perfect sentences about your day.
- Convert 5 simple past sentences to present perfect.
- Create 3 negative present perfect sentences.
- Form 3 interrogative present perfect sentences.
- Use have and has with different subjects.
- Identify the tense in 5 example sentences.
- Correct 3 incorrect present perfect sentences.
- Write a paragraph using only present perfect.
- List 5 irregular past participles.
- Practice with a friend using present perfect verbs.
Quizzes
- What is the past participle of “go”? (Answer: gone)
- Which is correct: “She has went” or “She has gone”? (Answer: She has gone)
- What auxiliary verb is used with “he”? (Answer: has)
- Is “I have eaten yesterday” correct? (Answer: No)
- What tense is “They have played”? (Answer: Present perfect)
- What’s the negative form of “I have seen”? (Answer: I have not seen)
- Which time expression fits present perfect? (Answer: Just)
- What’s the past participle of “write”? (Answer: Written)
- Is “Have you finished?” interrogative? (Answer: Yes)
- Correct this: “He have lost his keys.” (Answer: He has lost his keys.)
True or False
- Present perfect uses “have” or “has.” (True)
- You can use “yesterday” with present perfect. (False)
- The past participle of “eat” is “eaten.” (True)
- “She have gone” is correct. (False)
- Present perfect shows past actions with present relevance. (True)
- “I have seen” is simple past. (False)
- Irregular verbs always end in -ed. (False)
- “Has” is used for “they.” (False)
- Time expressions like “just” fit present perfect. (True)
- “I have wrote” is correct. (False)
Conclusion
The present perfect tense is a powerful tool for connecting past actions to the present, making your English more dynamic and precise.
By mastering its structure—have/has + past participle—and practicing with real-life examples, you can confidently use this tense in writing and conversation.
Avoid common mistakes, like using specific time expressions, and focus on irregular verbs to perfect your skills.
Try writing sentences, taking quizzes, or using a grammar checker to reinforce your learning.
Ready to level up your grammar? Start practicing the present perfect tense today and share your sentences in the comments below!



