The present perfect tense links past actions or events to the present, emphasizing their results or relevance. Unlike the past simple tense, which mentions a specific past time, the present perfect focuses on what happened, not when.
In this guide, you will learn:
- Definition and structure of the present perfect tense
- Rules, common mistakes, and adverbs to use with it
- Differences between present perfect and past simple
- How to use since and for correctly
- Practical examples, exercises, and tips to master it
By the end, you’ll be able to use the present perfect tense confidently in writing and speaking English.
Definition of Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to indicate a link between the present and the past.
- The action happened before now, but the exact time is unspecified.
- We often care more about the result than the action itself.
Tip: If you want to specify when something happened, use the past simple tense.
Uses of Present Perfect Tense

| Use | Example |
| Actions continuing from past to present | I have lived in Bristol since 1984. |
| Actions repeated in an unspecified period | We have visited Portugal several times. |
| Actions completed recently (+just) | I have just finished my work. |
| Actions where the time is unimportant | He has read War and Peace. |
Tip: For repeated or ongoing actions, use since for start points and for for durations.
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
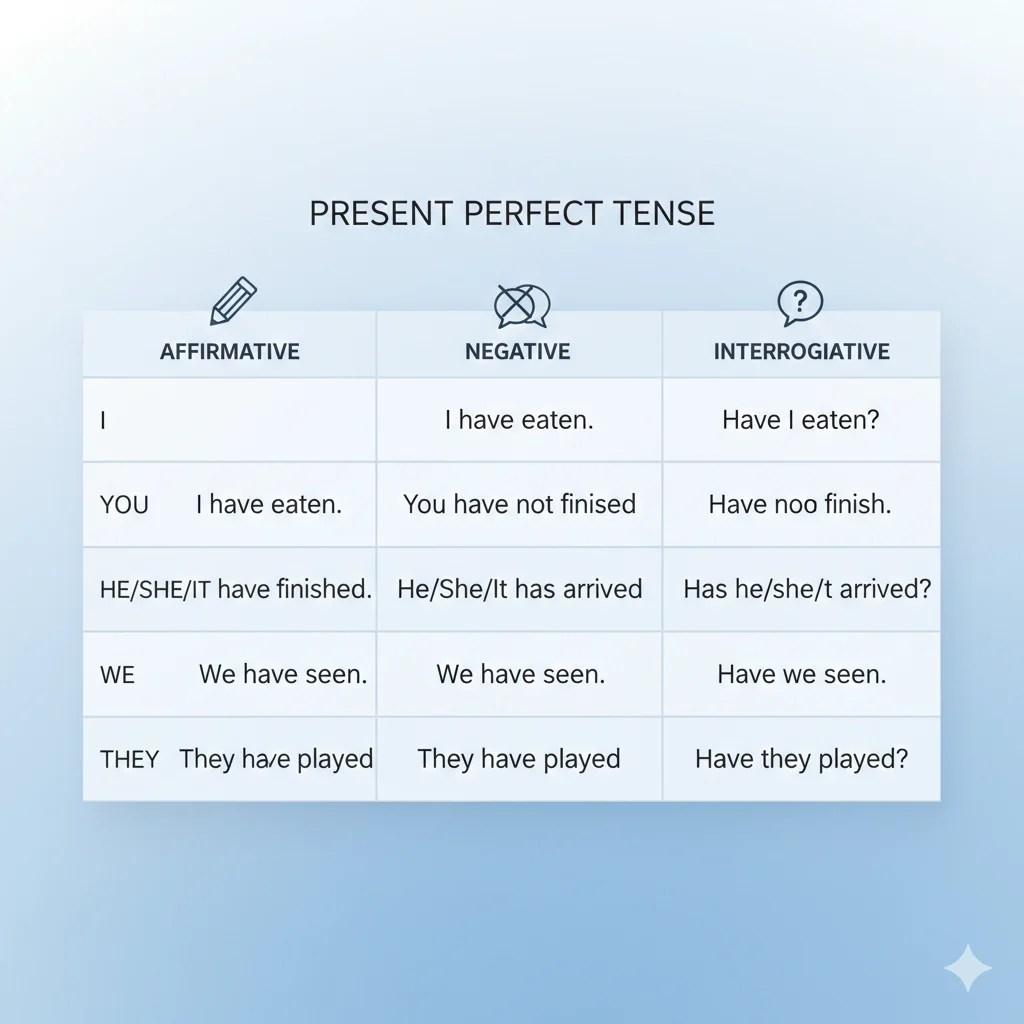
The present perfect is made of:
have/has + past participle
Examples of verb forms (regular and irregular):
| Subject | Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
| I | I have walked | I haven’t walked | Have I walked? |
| You | You have walked | You haven’t walked | Have you walked? |
| He/She/It | He has walked | He hasn’t walked | Has he walked? |
| We | We have walked | We haven’t walked | Have we walked? |
| They | They have walked | They haven’t walked | Have they walked? |
Note: Use has for he, she, it and have for I, you, we, they.
Using Since and For
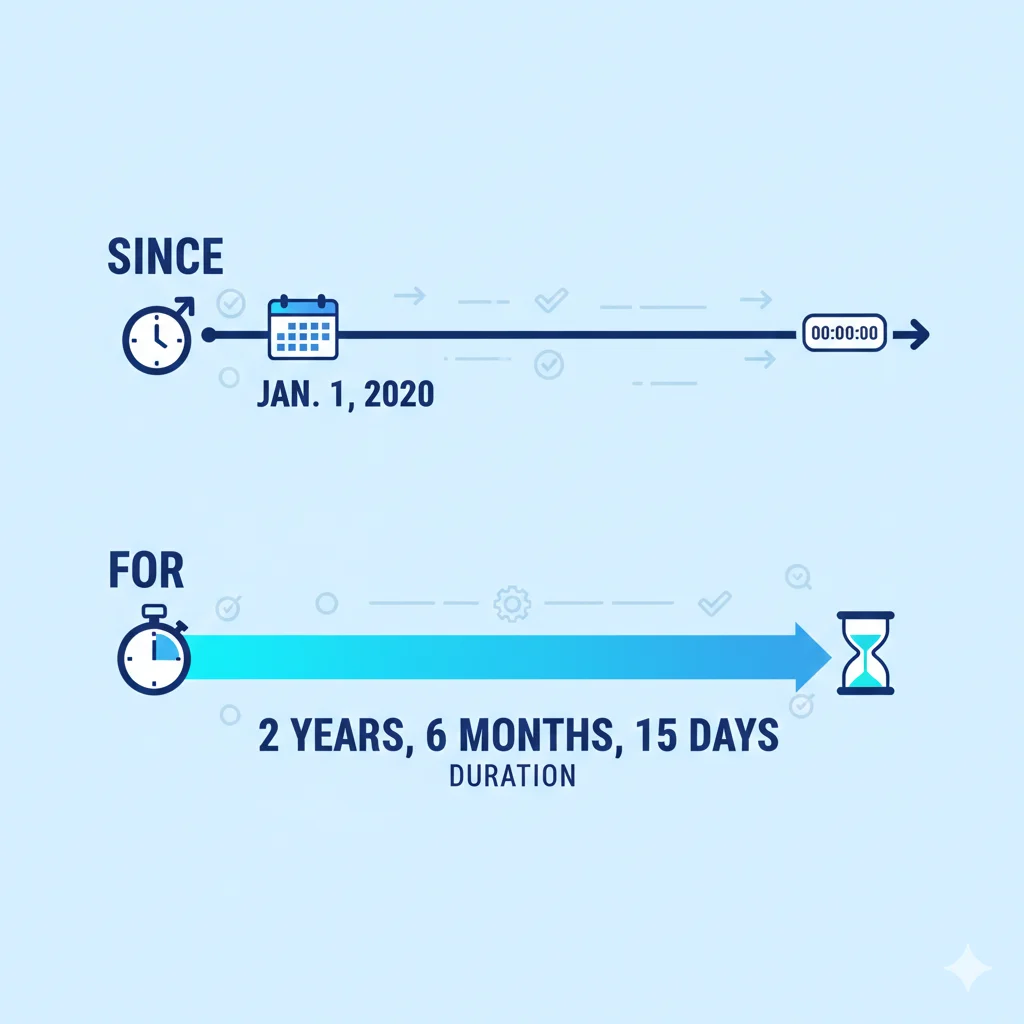
| Word | Use | Example |
| Since | Starting point of an action | I have lived here since 2015. |
| For | Duration of an action | I have lived here for 5 years. |
Common mistakes:
| ❌ Incorrect | ✅ Correct |
| I have lived here since 5 years. | I have lived here for 5 years. |
| She has worked here for Monday. | She has worked here since Monday. |
Present Perfect vs Past Simple

| Feature | Present Perfect | Past Simple |
| Time | Unspecified / Effect on present | Specific past time |
| Focus | Result / Experience | Action happened in the past |
| Example | I have visited London. | I visited London last year. |
| Keywords | already, yet, just, ever, never, since, for | yesterday, last week, in 2010 |
Tip: Use present perfect when you care about results. Use past simple to mention specific times.
Common Adverbs Used
| Adverb | Use | Example |
| Already | Something happened before now | I have already finished my homework. |
| Just | Action happened a short time ago | She has just called you. |
| Yet | Negative/questions, something expected | Have you done your homework yet? |
| Ever | Life experiences (questions) | Have you ever visited Paris? |
| Never | Action hasn’t happened at any time | I have never eaten sushi. |
| Recently / Lately | Actions not long ago | I have recently started a new hobby. |
Placement tip: Most adverbs go between have/has and past participle.
Common Mistakes to Avoid

| Mistake | Correct Form | Tip |
| I finished my homework. | I have finished my homework. | Don’t forget have/has + past participle |
| I have visited London last year. | I visited London last year. | Present perfect = unspecified time; past simple = specific time |
| I already have eaten. | I have already eaten. | Place adverbs between have/has and past participle |
| I have went to the store. | I have gone to the store. | Learn irregular verbs |
Exercises to Practice

- Fill in the blanks:
- I ______ (finish) my homework.
- She ______ (visit) London twice.
- They ______ (not see) that movie yet.
- Correct the mistakes:
- I has eaten breakfast already → ✅ I have eaten breakfast already.
- She have never been to Italy → ✅ She has never been to Italy.
- Short Answer Questions:
- Have you ever tried sushi?
- How long have you studied English?
Tip: Regular practice improves accuracy and fluency.
Tips to Master Present Perfect Tense
- Memorize the structure: have/has + past participle
- Use common adverbs: already, just, yet, ever, never
- Compare with past simple: check if the action is at a specific time
- Practice writing and speaking daily
- Learn irregular verbs: go → gone, see → seen, write → written
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Rules
The present perfect continuous tense describes actions that started in the past and are still continuing or have recently finished, with an emphasis on duration.
Key Rules:
- Formed with has/have + been + verb-ing.
- Often used with time expressions like for, since, lately, recently.
- Shows that the action is ongoing or relevant to the present.
Examples of Usage:
- She has been studying English for two hours.
- I have been working here since 2019.
- They have been waiting for the bus all morning.
Past Perfect Tense Rules
The past perfect tense is used to show an action that happened before another action in the past.
Key Rules:
- Formed with had + past participle.
- Often used with words like before, after, by the time.
- Helps indicate the sequence of past events.
Examples of Usage:
- She had finished her homework before dinner.
- By the time we arrived, they had left.
- He had never seen such a beautiful sunset before that day.
Present Perfect Tense Examples
The present perfect tense connects the past with the present. It shows that an action occurred at an unspecified time or has relevance now.
Examples:
- I have visited London twice.
- She has already eaten breakfast.
- They have completed the project successfully.
Present Perfect Tense Formula
Understanding the formula is essential for beginners:
Positive Sentences:
- Subject + has/have + past participle
Example: She has finished her homework.
Negative Sentences:
- Subject + has/have + not + past participle
Example: I have not seen that movie.
Questions:
- Has/Have + subject + past participle?
Example: Have you finished your work?
Present Perfect Tense Rules Chart
Here’s a simple chart to help you remember the rules:
| Tense | Structure | Usage | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Perfect | has/have + past participle | Action completed at an unspecified time | already, yet, ever, never |
| Present Perfect Continuous | has/have + been + verb-ing | Action started in past, still continuing | for, since, lately |
| Past Perfect | had + past participle | Action completed before another past action | before, after, by the time |
Present Perfect Tense Rules with Examples
Here’s a quick breakdown of rules with examples:
- Use “has” with singular subjects, “have” with plural subjects
- She has written a book.
- They have visited Paris.
- Use for life experiences
- I have traveled to Japan.
- Use for actions that started in the past and continue now
- We have lived here for ten years.
- Use for recent events with results now
- He has lost his keys.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Examples
Here are some examples to see it in action:
- I have been reading this book for two hours.
- She has been learning French since January.
- They have been playing football all afternoon.
- We have been waiting for you since 3 PM.
Present Perfect Tense Rules for Beginners
If you’re just starting, focus on these simple points:
- Form: has/have + past participle.
- Time Reference: No exact time mentioned.
- Use:
- Life experiences: “I have visited Italy.”
- Completed actions with present relevance: “She has finished her work.”
- Actions continuing until now: “We have known each other for years.”
Tip: Beginners should memorize common past participles like done, eaten, gone, seen, written to use this tense confidently.
FAQs About Present Perfect Tense
Q1. When should I use the present perfect tense?
A: For actions at unspecified times, ongoing actions, or life experiences.
Q2. Can I use present perfect with a specific past time?
❌ Incorrect: I have visited Paris in 2019.
✅ Correct: I visited Paris in 2019.
Q3. How is it different from past simple tense?
A: Present perfect = focus on results or relevance
Past simple = focus on specific time
Conclusion
The present perfect tense connects past actions to the present and is essential for natural English.
By learning its structure, adverbs, rules, and common mistakes, and practicing exercises regularly, you can speak and write English confidently.
Start applying the present perfect tense today, and it will soon become second nature!