The present simple tense is one of the most fundamental tenses in English, used to express habits, general truths, routines, and facts that are always or generally true.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, mastering the present simple tense is essential for clear communication.
This tense is often the first one taught to English learners due to its straightforward structure and wide applicability. In this article, we’ll explore the present simple tense, its structure, conjugation rules, and common mistakes.
With practical verb tense examples, conjugation tables, and exercises, you’ll gain confidence in using this tense correctly.
Let’s dive into how to use the present simple tense in everyday sentences and avoid pitfalls along the way!
What Is the Present Simple Tense?

The present simple tense describes actions that happen regularly, facts that are always true, or states that exist now. It’s used for:
- Habits: She walks to school every day.
- General truths: The sun rises in the east.
- Schedules: The train leaves at 7 PM.
- States: I like chocolate.
This tense is timeless, making it perfect for expressing routines or universal facts.
How to Recognize the Present Simple Tense?
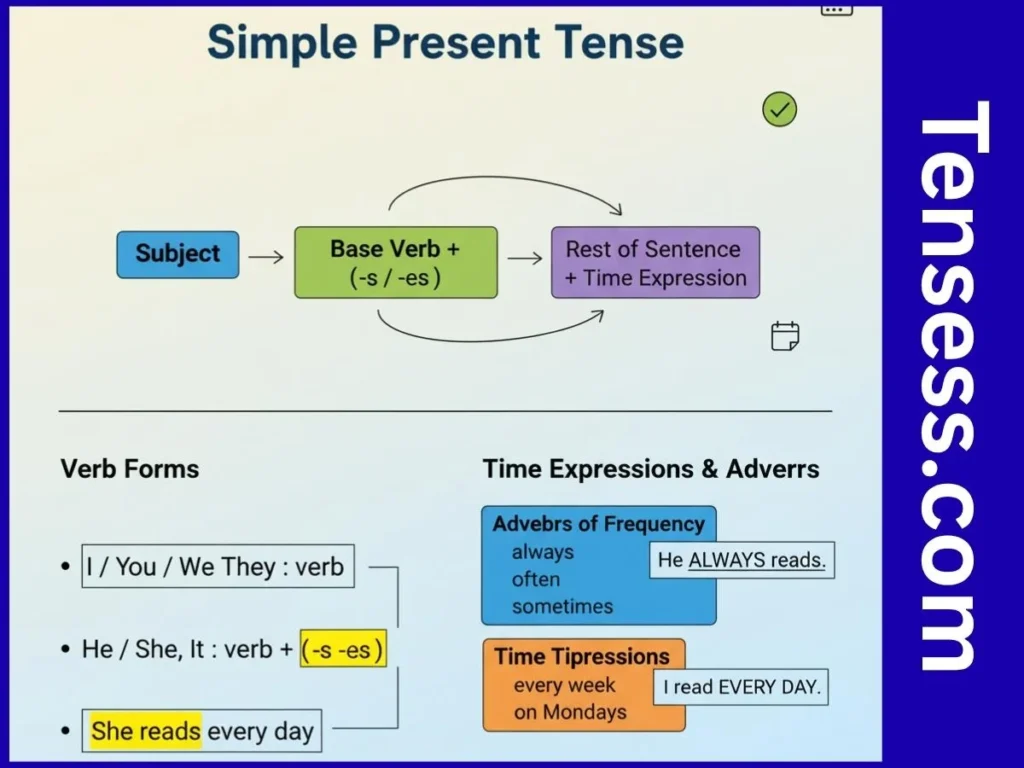
To identify the present simple tense, look for:
- Subject + base verb (add -s or -es for third-person singular subjects like he, she, it).
- Adverbs of frequency like always, often, never, sometimes.
- Time expressions such as every day, on Mondays, usually.
Example: They play football every weekend. The verb play and the time expression every weekend signal the present simple tense.
Structure of a Sentence
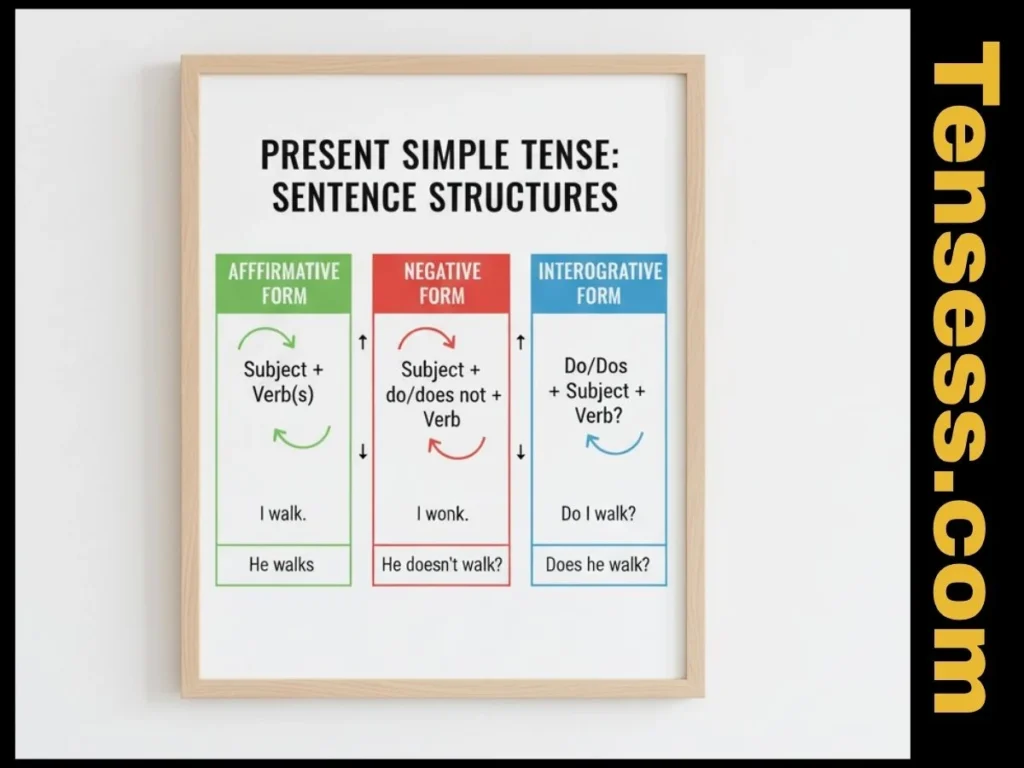
The present simple tense follows this structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + base verb (-s or -es for he, she, it).
- I walk, She walks.
- Negative: Subject + do/does + not + base verb.
- I don’t walk, She doesn’t walk.
- Interrogative: Do/Does + subject + base verb?
- Do I walk?, Does she walk?
Formation
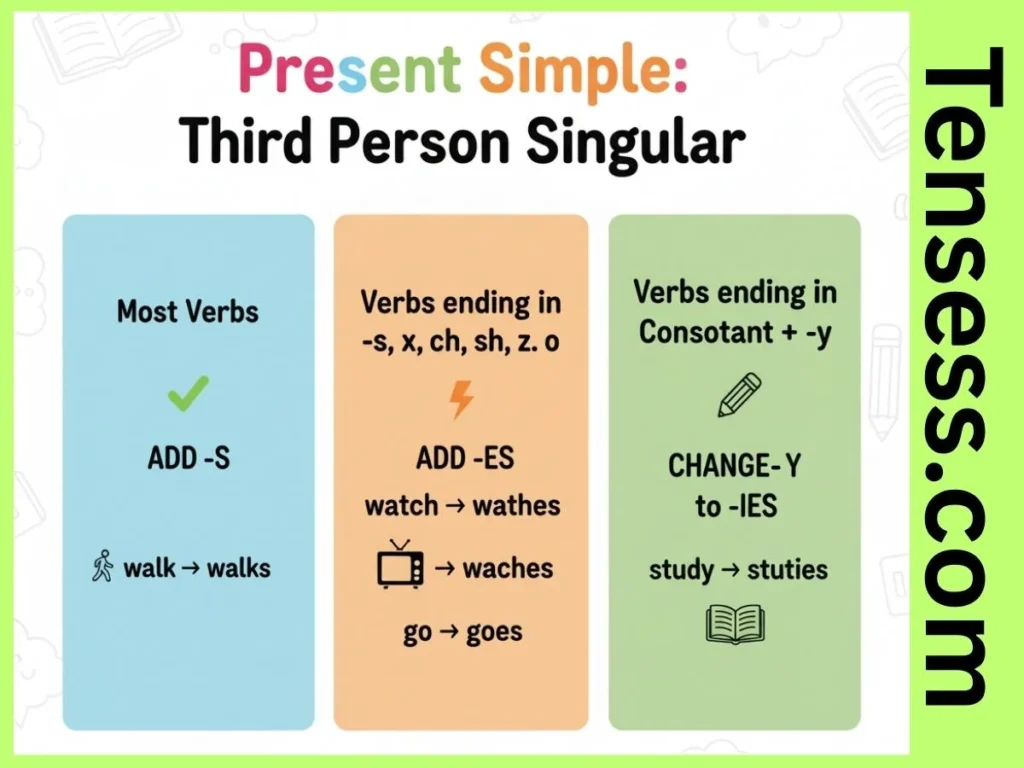
To form the present simple tense:
- Use the base verb for I, you, we, they (e.g., run, eat).
- Add -s or -es for he, she, it:
- -s: walk → walks.
- -es: For verbs ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z (e.g., watch → watches).
- Consonant + -y → -ies (e.g., study → studies).
Verbs
In the present simple tense, verbs are either regular or irregular. Most verbs follow the standard rules (add -s or -es), but some, like have, are irregular (he has, not he haves).
Helping Verbs
The present simple tense uses do and does as helping verbs:
- Do: For I, you, we, they in questions and negatives (Do you like?, I don’t like).
- Does: For he, she, it (Does she like?, She doesn’t like).
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Present Simple Tense
- Go: She goes to the park. The verb go becomes goes for she.
- Have: He has a dog. Irregular, uses has for third-person singular.
- Study: He studies English. Changes -y to -ies after a consonant.
- Watch: She watches TV. Adds -es due to ending in -ch.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Present Simple Tense
| Base Verb | I/You/We/They | He/She/It |
| Walk | Walk | Walks |
| Run | Run | Runs |
| Study | Study | Studies |
| Watch | Watch | Watches |
| Go | Go | Goes |
| Have | Have | Has |
| Do | Do | Does |
| Say | Say | Says |
| Play | Play | Plays |
| Eat | Eat | Eats |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I read books every evening.
- You play tennis on weekends.
- We visit our grandparents often.
- They work in a big office.
- He drives to work daily.
- She sings beautifully.
- It rains a lot in April.
- The dog barks at strangers.
- John studies math every night.
- The children draw pictures in class.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I don’t read newspapers.
- You don’t play soccer.
- We don’t visit museums often.
- They don’t work on Sundays.
- He doesn’t drive a car.
- She doesn’t sing in public.
- It doesn’t rain in summer.
- The cat doesn’t bark.
- Mary doesn’t study French.
- The kids don’t draw at home.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Do I read enough?
- Do you play chess?
- Do we visit often?
- Do they work here?
- Does he drive fast?
- Does she sing well?
- Does it rain much?
- Does the dog bark loudly?
- Does John study hard?
- Do the children draw daily?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Don’t I read enough?
- Don’t you play soccer?
- Don’t we visit often?
- Don’t they work late?
- Doesn’t he drive carefully?
- Doesn’t she sing anymore?
- Doesn’t it rain here?
- Doesn’t the dog bark at night?
- Doesn’t John study enough?
- Don’t the kids draw well?
How to Conjugate Present Simple Tense
- Use the base verb for I, you, we, they.
- Add -s for he, she, it for most verbs.
- Add -es for verbs ending in -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z.
- Change -y to -ies for verbs ending in consonant + -y.
- Use do for negatives/questions with I, you, we, they.
- Use does for negatives/questions with he, she, it.
- Irregular verbs like have → has.
- Keep the base verb for plural subjects.
- Ensure subject-verb agreement.
- Practice with real-life sentences.
Conjugation Table (for All Subjects)
| Subject | Verb: Walk | Verb: Study | Verb: Have |
| I | Walk | Study | Have |
| You | Walk | Study | Have |
| He | Walks | Studies | Has |
| She | Walks | Studies | Has |
| It | Walks | Studies | Has |
| We | Walk | Study | Have |
| They | Walk | Study | Have |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- -s, -sh, -ch, -x, -z: Add -es (kiss → kisses).
- Consonant + -y: Change to -ies (study → studies).
- Vowel + -y: Add -s (play → plays).
- Irregular verbs: have → has, go → goes, do → does.
- Avoid adding -s to irregular verbs like have.
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I love to read novels.
- You run every morning.
- He works in a bank.
- She cooks delicious meals.
- It snows in winter.
- We travel every summer.
- They play soccer weekly.
- John studies at night.
- The cat sleeps all day.
- The children laugh loudly.
Common Mistakes with Present Simple Tense
- Forgetting -s for he, she, it: She walk → She walks.
- Using does with I, you, we, they: I does → I do.
- Adding -s to irregular verbs: He haves → He has.
- Omitting do/does in questions: She like? → Does she like?
- Using don’t with he, she, it: She don’t → She doesn’t.
- Mixing tenses: She walks and ate → She walks and eats.
- Incorrect spelling: He studys → He studies.
- Overusing adverbs: She always never walks → She never walks.
- Subject-verb disagreement: They walks → They walk.
- Misplacing not: She not walks → She doesn’t walk.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Always check for -s with he, she, it.
- Use does only for he, she, it.
- Memorize irregular verbs like have/has.
- Practice forming questions with do/does.
- Use doesn’t for he, she, it negatives.
- Keep tense consistent in sentences.
- Review spelling rules for -ies and -es.
- Use one adverb of frequency per sentence.
- Ensure subject and verb agree in number.
- Write practice sentences daily.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Present Simple Tense
- Go: Synonyms: travel, move. Comparison: She goes to school vs. She travels to school.
- Have: Synonyms: possess, own. He has a car vs. He owns a car.
- Do: Synonyms: perform, execute. I do my homework vs. I perform my tasks.
- Like: Synonyms: enjoy, love. She likes coffee vs. She loves coffee.
- Work: Synonyms: function, operate. It works well vs. It operates well.
Tips to Practice Using Present Simple Tense
- Write a daily routine using present simple.
- Describe habits of friends or family.
- Use flashcards for irregular verbs.
- Practice with online grammar quizzes.
- Speak about general facts aloud.
- Create negative and question sentences.
- Read simple English texts and spot the tense.
- Use apps like Duolingo for practice.
- Write 10 sentences daily with different subjects.
- Join language exchange groups.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the present simple tense? It describes habits, facts, and routines.
- When do we use -s or -es? For he, she, it subjects.
- What are helping verbs in this tense? Do and does.
- How do I form negatives? Use don’t or doesn’t + base verb.
- What’s an example of a general truth? The earth rotates.
- Are there irregular verbs? Yes, like have → has.
- How do I form questions? Do/Does + subject + base verb.
- What adverbs are common? Always, often, never.
- Can I use it for schedules? Yes, e.g., The bus leaves at 8.
- How do I practice? Write daily sentences and take quizzes.
Exercises
- Fill in: I ___ (walk) to school.
- Make negative: She sings loudly.
- Form a question: They play soccer.
- Correct: He don’t like tea.
- Add -s or -es: She ___ (watch) TV.
- Write a sentence with have.
- Use study in a negative sentence.
- Form a question with go.
- Correct: They walks daily.
- Write a sentence with run.
Quizzes
- True/False: She walks is present simple. (True)
- Choose: He ___ to school. (a) go (b) goes (Answer: b)
- Fill: They ___ (not/play) chess.
- Correct: I does my homework.
- Question: ___ she sing? (a) Do (b) Does (Answer: b)
- Choose: She ___ TV. (a) watch (b) watches (Answer: b)
- Fill: It ___ (rain) often.
- Correct: He studys math.
- Question: ___ they work? (a) Do (b) Does (Answer: a)
- True/False: I don’t walks is correct. (False)
True/False
- He walks is present simple. (True)
- She don’t walk is correct. (False)
- Do you like? is a question. (True)
- They studies is correct. (False)
- The sun rises is a fact. (True)
- I does is correct. (False)
- She watches uses -es. (True)
- We go is present simple. (True)
- He haves is correct. (False)
- Does it rain? is a question. (True)
Conclusion
The present simple tense is a cornerstone of English grammar, perfect for expressing habits, facts, and routines.
By understanding its structure, conjugation rules, and common pitfalls, you can use it confidently in writing and speaking.
Practice with the verb tense examples, exercises, and quizzes provided to reinforce your skills.
If you’re a student or a language learner, mastering this tense opens doors to clearer communication.
Try writing 10 sentences today using the present simple tense, or use a grammar checker to polish your work.
Keep practicing, and soon this tense will feel second nature! Share your progress in the comments or join a language community to keep learning.



