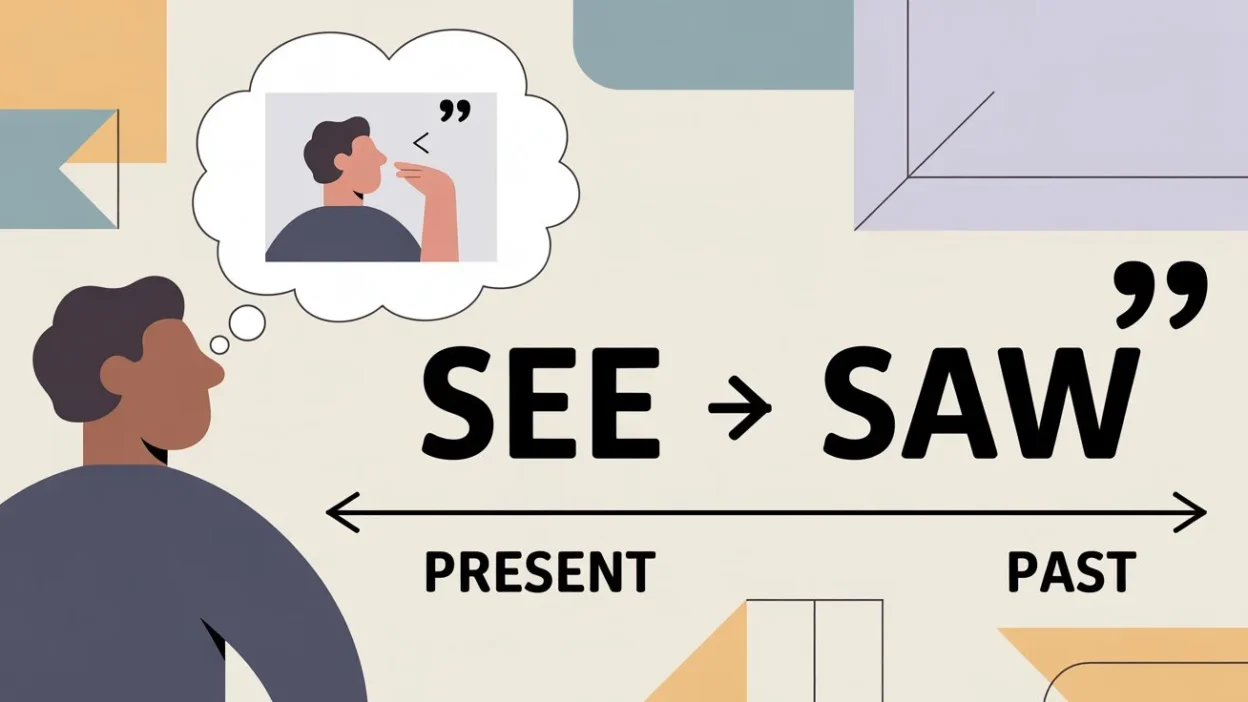
If you’re describing a movie you watched or a place you visited, the verb saw helps you communicate actions that happened in the past.
This article is your go-to guide for understanding how to use saw correctly, with clear explanations, real-life examples, and practical tips.
We’ll break down the past simple tense, its structure, conjugation, and common mistakes to avoid.
By the end, you’ll feel confident using saw in your conversations and writing.
Let’s dive into the world of the past tense of see and explore how this irregular verb shapes your sentences!
What Is the “Saw” Tense?
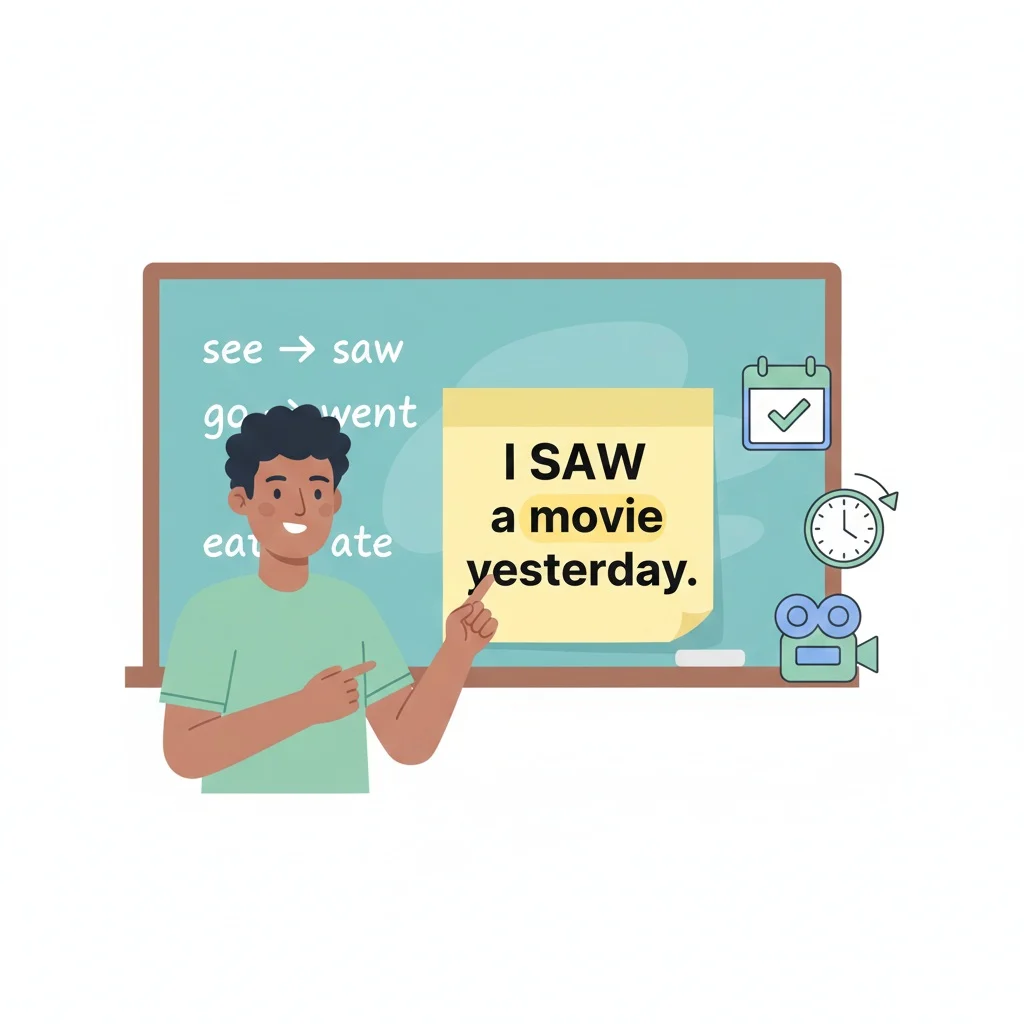
. Unlike regular verbs that add “-ed” (e.g., walked), see transforms into saw without following a predictable pattern. It’s used in the past simple tense to indicate completed actions, such as “I saw a bird yesterday.” This tense doesn’t require helping verbs like “have” or “had” in simple sentences, making it straightforward for beginners. Understanding saw is key for storytelling, describing past events, or sharing experiences.
How to Recognize the “Saw” Tense?

.” For example:
- “She saw a concert last night” indicates a specific past event.
- No helping verbs (e.g., was, were) are needed in simple sentences, unlike other tenses like the past continuous (was seeing).
Check for saw paired with subjects like I, you, he, she, it, we, or they, and ensure no additional verb forms like “seen” (used with “have” in perfect tenses) are present.
Structure of a Sentence

The past simple tense with saw follows this structure:
Subject + saw + object (optional) + time expression (optional).
- Example: “I saw a movie yesterday.”
- Subject: I, you, he, she, it, we, they.
- Verb: Saw (no variation across subjects).
- Object: What was seen (e.g., a movie, a bird).
- Time expression: When it happened (e.g., yesterday, last summer).
This structure is consistent for affirmative sentences. Negative and interrogative forms may include helping verbs like “did.”
Formation
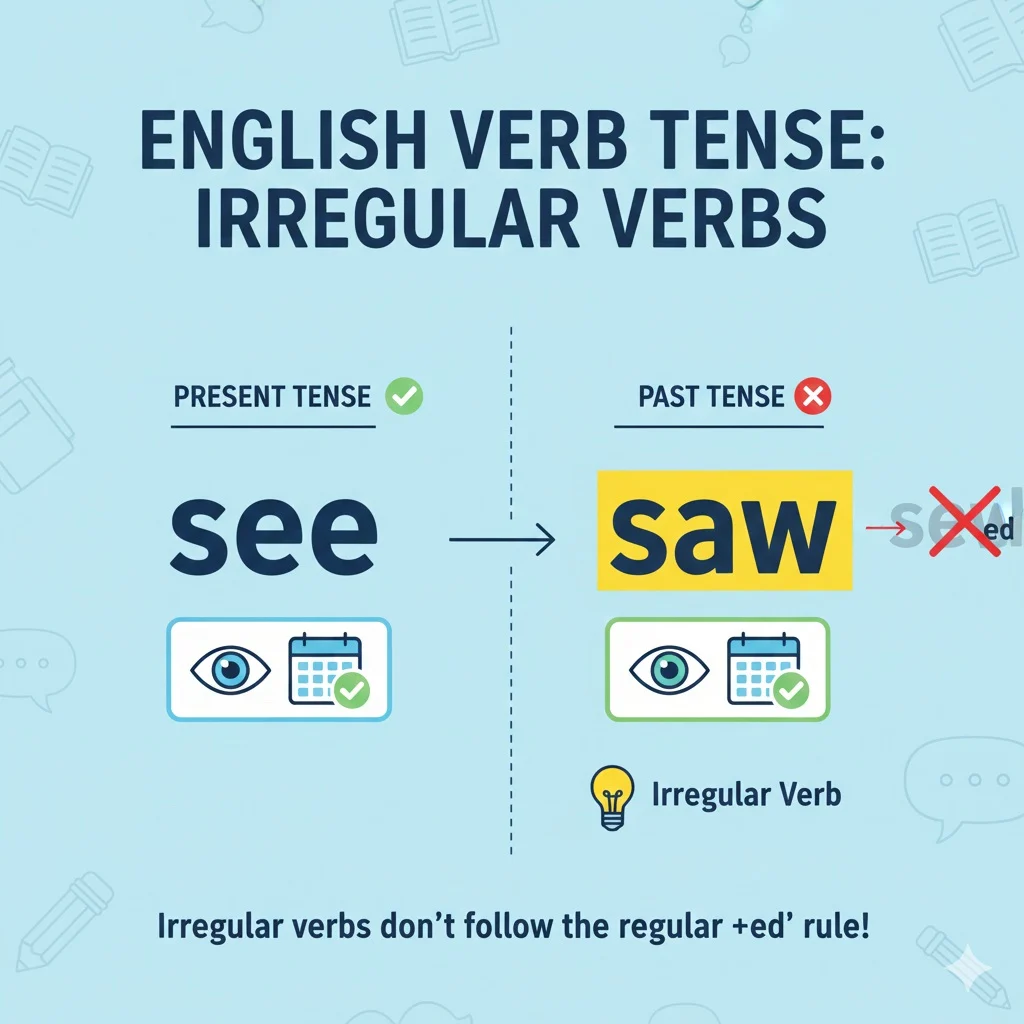
. Unlike regular verbs, see doesn’t follow the “-ed” rule because it’s irregular. For example:
- Present: “I see a dog.”
- Past: “I saw a dog.”
No helping verbs are needed in affirmative sentences, but negatives and questions use “did” (see examples below).
Verbs
The verb see is unique because it’s irregular, meaning its past form (saw) doesn’t follow standard rules. Other verbs in the past simple tense can be regular (e.g., walked, talked) or irregular (e.g., went, ran). Saw is used consistently across all subjects, making it simple to apply once you recognize its irregularity.
Helping Verbs
In the past simple tense, saw typically doesn’t require helping verbs in affirmative sentences. However:
- Negative sentences: Use “did not” (didn’t) + base verb “see.” Example: “I didn’t see the show.”
- Interrogative sentences: Use “Did + subject + see?” Example: “Did you see the game?”
The helping verb “did” is crucial for forming negatives and questions.
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to “Saw”
Irregular verbs like see share similarities with others in the past simple tense. Here’s how saw compares:
- Go → Went: “I went to the park and saw a squirrel.”
- Take → Took: “She took a photo when she saw the sunset.”
- Know → Knew: “He knew the answer after he saw the clue.”
These verbs, like saw, change unpredictably in the past tense, requiring memorization.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in “Past Simple Tense”
| Base Verb | Past Simple | Regular/Irregular |
| See | Saw | Irregular |
| Walk | Walked | Regular |
| Go | Went | Irregular |
| Take | Took | Irregular |
| Look | Looked | Regular |
| Run | Ran | Irregular |
| Talk | Talked | Regular |
| Write | Wrote | Irregular |
| Read | Read | Irregular |
| Play | Played | Regular |
Simple Sentence Examples
Here are 10 past tense of see examples with different subjects:
- I saw a beautiful sunset yesterday.
- You saw the new museum last week.
- He saw a deer in the forest.
- She saw her friend at the mall.
- It (the cat) saw a bird outside.
- We saw a great movie last night.
- They saw the parade in town.
- John saw the accident on the road.
- The kids saw a clown at the fair.
- My parents saw the Eiffel Tower in 2019.
Negative Sentence Examples
Use “didn’t + see” for negatives:
- I didn’t see the email you sent.
- You didn’t see the warning sign.
- He didn’t see the game last night.
- She didn’t see the mistake in her work.
- It didn’t see the toy in the corner.
- We didn’t see the concert due to traffic.
- They didn’t see the new exhibit.
- Sarah didn’t see the dog run away.
- The tourists didn’t see the monument.
- My brother didn’t see the fireworks.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
Use “Did + subject + see” for questions:
- Did I see you at the party?
- Did you see the shooting star?
- Did he see the new car?
- Did she see the painting in the gallery?
- Did it see the shadow move?
- Did we see that actor in person?
- Did they see the beach at sunrise?
- Did John see the email I sent?
- Did the kids see the magic show?
- Did your parents see the old castle?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
Combine “Didn’t + subject + see” for negative questions:
- Didn’t I see you at the store?
- Didn’t you see the sign on the road?
- Didn’t he see the movie everyone loved?
- Didn’t she see the error in the report?
- Didn’t it see the bird fly away?
- Didn’t we see that play last year?
- Didn’t they see the festival downtown?
- Didn’t Mary see the email I sent?
- Didn’t the students see the science exhibit?
- Didn’t your friends see the new park?
How to Conjugate “Saw” Tense
The past tense of see is saw for all subjects, making conjugation simple:
- I saw
- You saw
- He saw
- She saw
- It saw
- We saw
- They saw
- John saw
- The team saw
- My friends saw
No changes occur based on the subject, unlike some verbs that vary (e.g., was/were).
Conjugation Table
| Subject | Conjugation |
| I | Saw |
| You (singular) | Saw |
| He/She/It | Saw |
| We | Saw |
| You (plural) | Saw |
| They | Saw |
| John | Saw |
| The team | Saw |
| My friends | Saw |
| The dog | Saw |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
The verb see is irregular, so its past form (saw) doesn’t follow the “-ed” rule of regular verbs. There are no spelling changes for saw across subjects, but learners often confuse it with seen, which is used in perfect tenses (e.g., “I have seen”). Always use saw for past simple tense and seen with helping verbs like “have” or “had.”
Offer 10–15 Sentence Examples
Here are 15 past tense of see examples with varied subjects:
- I saw a rainbow after the rain.
- You saw the football match on TV.
- He saw a rare bird in the park.
- She saw her teacher at the store.
- It (the dog) saw its reflection in the mirror.
- We saw a fantastic play last weekend.
- They saw the new bridge opening.
- Lisa saw a shooting star last night.
- The children saw a lion at the zoo.
- My friend saw the latest Marvel movie.
- John saw an old friend at the airport.
- The tourists saw the ancient ruins.
- You (plural) saw the festival fireworks.
- The cat saw a mouse in the kitchen.
- My parents saw a concert in London.
Common Mistakes with “Saw” Tense
Here are 10 frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Using “seen” instead of “saw”: “I seen a movie” is incorrect. Use “I saw a movie” or “I have seen a movie.”
- Forgetting “did” in negatives: “I not saw” is wrong. Use “I didn’t see.”
- Incorrect question structure: “Saw you the game?” is wrong. Use “Did you see the game?”
- Mixing tenses: “I saw a movie and I see it again” is confusing. Use “I saw a movie and I’ll see it again.”
- Using “saw” with “have”: “I have saw” is incorrect. Use “I have seen.”
- Omitting time markers: “I saw a movie” is vague without context. Add “yesterday” or similar.
- Overusing “saw”: Repeating “saw” in a paragraph can sound repetitive. Use synonyms like “noticed.”
- Confusing subjects: “They saw” and “He saw” are correct, but “They saws” is wrong.
- Misusing in continuous tense: “I was saw” is incorrect. Use “I was seeing.”
- Ignoring irregularity: Expecting “seed” or “seeed” as past tense is wrong. Memorize saw.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for “Saw”
Synonyms for see in the past tense include:
- Noticed: “I noticed a change” vs. “I saw a change.”
- Observed: “She observed the stars” vs. “She saw the stars.”
- Watched: “He watched the game” vs. “He saw the game.”
- Looked: “They looked at the painting” vs. “They saw the painting.”
Comparison:
- “I saw the accident” (general observation).
- “I watched the accident” (focused, prolonged observation).
Confused verbs:
- Seen: Used with “have/had” (e.g., “I have seen it”).
- Look: Implies intentional action, unlike see.
Tips to Practice Using “Saw” Tense
- Write a diary entry using saw to describe yesterday’s events.
- Narrate a movie you watched using saw in 5 sentences.
- Practice negative sentences: “I didn’t see that show.”
- Ask friends questions: “Did you see the new café?”
- Use flashcards to memorize see → saw.
- Read books and highlight saw in past-tense sentences.
- Create a story using saw with different subjects.
- Practice quizzes (see below) to test your knowledge.
- Speak aloud: Describe what you saw last weekend.
- Use a grammar checker to verify correct usage of saw.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past tense of see?
It’s saw for the past simple tense. - When do I use “saw” vs. “seen”?
Use saw for past simple (e.g., “I saw it”). Use seen with “have/had” (e.g., “I have seen it”). - Does “saw” change with subjects?
No, saw is the same for I, you, he, she, it, we, they. - Can “saw” be used in questions?
Yes, with “did” (e.g., “Did you see it?”). - Is “see” a regular verb?
No, it’s irregular (see → saw → seen). - What’s a synonym for “saw”?
Noticed, observed, or watched. - How do I make a negative sentence with “saw”?
Use “didn’t + see” (e.g., “I didn’t see it”). - Can “saw” be used in continuous tense?
No, use “was/were seeing” for continuous. - How do I practice “saw”?
Write sentences, take quizzes, or narrate past events. - What’s a common mistake with “saw”?
Confusing it with “seen” without “have/had.”
Exercises
- Write 5 sentences using saw with different subjects.
- Convert: “I see a bird” to past tense.
- Make a negative sentence: “She didn’t __ the show.”
- Form a question: “Did they __ the game?”
- Correct: “I seen a movie yesterday.”
- Write a paragraph about a trip using saw.
- Identify the error: “He saws a dog.”
- Use saw with “yesterday” in a sentence.
- Combine saw and noticed in one sentence.
- Rewrite: “We have saw the play” correctly.
Quizzes
Choose the correct answer:
- What is the past tense of see?
a) Seed b) Saw c) Seen - Correct sentence:
a) I sawed a movie b) I saw a movie c) I seen a movie - Negative form:
a) I not saw b) I didn’t see c) I don’t saw - Question form:
a) Saw you it? b) Did you see it? c) Do you saw it? - Synonym for saw:
a) Look b) Noticed c) See - Correct usage:
a) I have saw b) I have seen c) I seeing - Subject agreement:
a) They saws b) They saw c) They seen - Time marker:
a) I saw it tomorrow b) I saw it yesterday c) I see it yesterday - Irregular verb:
a) Walk b) See c) Talk - Correct negative question:
a) Didn’t you see it? b) Not you saw it? c) Didn’t you saw it?
True or False
- Saw is the past tense of see. (True)
- Saw is used with “have” in past simple. (False)
- “Did you see it?” is correct. (True)
- “I seen it” is correct for past simple. (False)
- Saw changes with subjects like “was/were.” (False)
- “I didn’t see it” is a negative sentence. (True)
- See is a regular verb. (False)
- “Noticed” can replace saw in some sentences. (True)
- “I was saw” is correct for past continuous. (False)
- Saw is used for completed past actions. (True)
Conclusion
Mastering the past tense of see (saw) is a key step for students, language learners, and writers aiming to communicate clearly about past events.
This irregular verb is simple to use once you understand its structure, conjugation, and common pitfalls.
By practicing with real-life examples, quizzes, and exercises, you can confidently use saw in conversations and writing.
Avoid mistakes like confusing saw with seen, and try synonyms like noticed or watched to diversify your vocabulary.
Start practicing today—write a few sentences using saw, share them with friends, or use a grammar checker to polish your skills.
Keep exploring verb tense examples to strengthen your English grammar!