The past tense of sneak, which is sneaked, is a key component of English grammar that describes actions that happened in the past.
If you’re a student, language learner, writer, or grammar enthusiast, understanding how to use sneaked correctly can enhance your writing and communication skills.
This article will guide you through the definition, structure, and usage of sneaked as the past tense of the verb sneak, along with practical examples and tips to avoid common mistakes.
We’ll break down verb conjugation, sentence formation, and even provide exercises and quizzes to help you practice.
By the end, you’ll confidently know how to use sneaked in everyday sentences and avoid pitfalls.
Let’s dive into the world of sneaked tense and make grammar fun and approachable!
What Is the Sneaked Tense?

The sneaked tense refers to the past tense form of the verb sneak, which means to move stealthily or secretly. It’s used to describe actions that occurred in the past, like sneaking into a room or avoiding detection. Sneaked is the regular past tense form, but you might also encounter snuck, an irregular form commonly used in informal contexts. For this article, we’ll focus on sneaked as the standard form in formal writing. Understanding sneaked helps you narrate past events clearly, making it essential for storytelling or describing sneaky actions.
How to Recognize Sneaked Tense?
To recognize sneaked, look for:
- Action in the past: The verb describes something that already happened (e.g., “She sneaked into the party”).
- Regular verb ending: Sneaked follows the standard “-ed” ending for regular verbs.
- Context clues: Words like “yesterday,” “last night,” or “ago” often signal past tense.
- Subject-verb agreement: Sneaked works with all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
Structure of Sentence
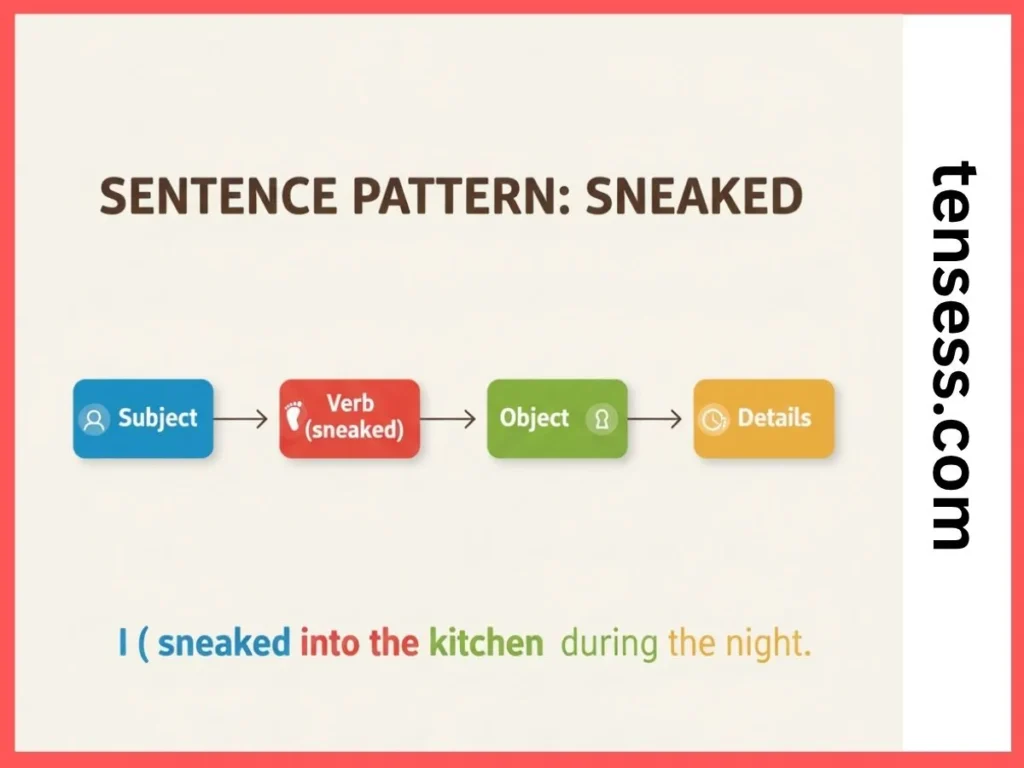
The sentence structure for sneaked tense follows a simple pattern:
- Subject + sneaked + object (optional) + additional details.
- Example: “I sneaked into the kitchen to grab a cookie.”
- It can also include adverbs or time phrases to clarify when the action happened (e.g., “They sneaked quietly last night”).
Formation

The sneaked tense is formed by adding -ed to the base verb sneak. This makes it a regular verb in past tense. No auxiliary verbs are needed for simple past tense sentences, but in certain cases (e.g., past perfect), helping verbs like had are used.
Verbs
The verb sneak belongs to the category of regular verbs when using sneaked. However, the alternative form snuck is an irregular verb used in informal English. For clarity, we’ll stick with sneaked for standard writing.
Helping Verbs
In simple past tense, sneaked doesn’t require helping verbs. However, in past perfect or past continuous forms:
- Had is used for past perfect (e.g., “She had sneaked out before dawn”).
- Was/were is used for past continuous (e.g., “They were sneaking around the house”).
Explanation of Some Verbs with Reference to Sneaked
Some verbs similar to sneak in meaning include creep, slip, and tiptoe. Like sneaked, these verbs often describe stealthy movement:
- Creeped: “She creeped past the guard” (similar to sneaked in past tense).
- Slipped: “He slipped into the room unnoticed.”
- Tiptoed: “They tiptoed around the sleeping dog.”
These verbs share a sneaky, quiet action but differ slightly in tone or context.
Table of Some Regular or Irregular Verbs in Sneaked Tense
| Base Verb | Past Tense | Regular/Irregular |
| Sneak | Sneaked | Regular |
| Creep | Creeped | Regular |
| Slip | Slipped | Regular |
| Tiptoe | Tiptoed | Regular |
| Run | Ran | Irregular |
| Hide | Hid | Irregular |
| Go | Went | Irregular |
| Take | Took | Irregular |
Simple Sentence Examples
- I sneaked into the movie theater yesterday.
- She sneaked a peek at the gift.
- He sneaked out of class early.
- We sneaked through the back door.
- They sneaked around the garden at night.
- You sneaked into the meeting unnoticed.
- It sneaked past the cat quietly.
- The kids sneaked into the attic.
- John sneaked a candy from the jar.
- The dog sneaked under the fence.
Negative Sentence Examples
- I didn’t sneak into the party.
- She didn’t sneak out last night.
- He didn’t sneak past the guard.
- We didn’t sneak into the room.
- They didn’t sneak around the house.
- You didn’t sneak a cookie from the jar.
- It didn’t sneak through the gate.
- The kids didn’t sneak upstairs.
- John didn’t sneak into the office.
- The cat didn’t sneak outside.
Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Did I sneak into the kitchen?
- Did she sneak out of the house?
- Did he sneak past the teacher?
- Did we sneak into the concert?
- Did they sneak around the park?
- Did you sneak a look at the answers?
- Did it sneak through the window?
- Did the kids sneak into the basement?
- Did John sneak into the meeting?
- Did the dog sneak into the yard?
Negative and Interrogative Sentence Examples
- Didn’t I sneak into the room quietly?
- Didn’t she sneak out before dinner?
- Didn’t he sneak past the security?
- Didn’t we sneak into the theater?
- Didn’t they sneak around the corner?
- Didn’t you sneak a peek at the book?
- Didn’t it sneak under the table?
- Didn’t the kids sneak upstairs?
- Didn’t John sneak into the party?
- Didn’t the cat sneak outside?
How to Conjugate Sneaked Tense
Sneaked is a regular verb, so its conjugation is straightforward:
- Start with the base verb: sneak.
- Add -ed to form the past tense: sneaked.
- Use with all subjects (I, you, he, she, it, we, they).
- No changes for singular or plural subjects.
- For negative sentences, add did not before sneak.
- For questions, use did + subject + sneak.
- In past perfect, use had sneaked.
- In past continuous, use was/were sneaking.
- Ensure time phrases match past tense (e.g., “yesterday”).
- Practice with different sentence types for fluency.
Conjugation Table for Sneaked Tense
| Subject | Simple Past | Negative | Interrogative |
| I | Sneaked | Didn’t sneak | Did I sneak? |
| You | Sneaked | Didn’t sneak | Did you sneak? |
| He/She/It | Sneaked | Didn’t sneak | Did he/she/it sneak? |
| We | Sneaked | Didn’t sneak | Did we sneak? |
| They | Sneaked | Didn’t sneak | Did they sneak? |
Spelling Changes or Irregularities
- Sneaked is regular, so it simply adds -ed to sneak.
- Snuck is an irregular form used in informal English but should be avoided in formal writing.
- No spelling changes occur with sneaked for any subject.
- Be cautious with pronunciation: sneaked rhymes with “leaked,” not “snuck.”
Sentence Examples with Different Subjects
- I sneaked into the library to study.
- You sneaked a snack from the fridge.
- He sneaked past the sleeping guard.
- She sneaked a glance at her phone.
- It sneaked through the open door.
- We sneaked into the concert for free.
- They sneaked around the campsite.
- The cat sneaked onto the counter.
- John and I sneaked out at midnight.
- The kids sneaked into the treehouse.
- My dog sneaked under the gate.
- You all sneaked into the party.
- She sneaked a cookie before dinner.
- He sneaked into the office early.
- They sneaked past the teacher.
Common Mistakes with Sneaked Tense
- Using snuck in formal writing (e.g., “He snuck out” instead of “He sneaked out”).
- Forgetting did in negative sentences (e.g., “She not sneaked” instead of “She didn’t sneak”).
- Omitting did in questions (e.g., “Sneaked she?” instead of “Did she sneak?”).
- Confusing sneaked with present tense sneak (e.g., “Yesterday, I sneak”).
- Misplacing time phrases (e.g., “I sneaked tomorrow”).
- Incorrect subject-verb agreement in questions (e.g., “Did they sneaks?”).
- Using sneaked in future tense contexts (e.g., “I will sneaked”).
- Mixing sneaked with snuck in the same text.
- Overusing had unnecessarily (e.g., “I had sneaked yesterday” instead of “I sneaked yesterday”).
- Mispronouncing sneaked as “snuck.”
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
- Use sneaked in formal writing; reserve snuck for casual speech.
- Always include did not for negatives and did for questions.
- Double-check time phrases to ensure they indicate the past.
- Practice conjugating sneak with all subjects.
- Read your sentences aloud to catch errors.
- Avoid mixing sneaked and snuck in one piece.
- Use grammar checkers to spot incorrect verb forms.
- Review sentence structure for clarity.
- Practice with exercises to reinforce correct usage.
- Consult reliable grammar resources for doubts.
Related Verbs and Synonyms for Sneaked
- Synonyms: Creep, slip, tiptoe, skulk, slink.
- Related verbs:
- Creep: “She creeped past the door” vs. “She sneaked past the door” (similar stealth).
- Slip: “He slipped into the room” vs. “He sneaked into the room” (less emphasis on stealth).
- Tiptoe: “They tiptoed upstairs” vs. “They sneaked upstairs” (tiptoe emphasizes quiet steps).
- Sentence comparisons:
- “She sneaked into the party” (implies secrecy) vs. “She slipped into the party” (implies quick entry).
- “He creeped around the house” (slow and cautious) vs. “He sneaked around the house” (stealthy intent).
Tips to Practice Using Sneaked Tense
- Write 10 sentences using sneaked with different subjects.
- Create a short story about a sneaky adventure.
- Practice negative and interrogative forms daily.
- Read books and highlight past tense verbs like sneaked.
- Use flashcards to memorize sneak vs. sneaked.
- Try speaking sentences aloud with sneaked.
- Complete grammar exercises online.
- Ask a friend to quiz you on sneaked usage.
- Watch movies and note past tense verbs in dialogue.
- Use a grammar app to check your sentences.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the past tense of sneak?
It’s sneaked in formal writing, though snuck is used informally. - Is snuck correct?
Snuck is acceptable in casual contexts but not in formal writing. - How do I use sneaked in a sentence?
Example: “She sneaked into the room quietly.” - What’s the difference between sneaked and snuck?
Sneaked is regular; snuck is irregular and informal. - Can sneaked be used with all subjects?
Yes, it works with I, you, he, she, it, we, they. - How do I form a negative sentence with sneaked?
Use didn’t sneak (e.g., “I didn’t sneak out”). - What are synonyms for sneak?
Creep, slip, tiptoe, skulk, slink. - Is sneaked used in past perfect tense?
Yes, with had (e.g., “She had sneaked out”). - How do I avoid confusing sneaked and snuck?
Stick to sneaked in formal writing and check context. - Where can I practice sneaked tense?
Try grammar apps, exercises, or writing prompts.
Exercises
- Write 5 sentences using sneaked in simple past.
- Convert 3 sentences to negative form using didn’t sneak.
- Create 3 interrogative sentences with did and sneak.
- Combine negative and interrogative forms in 2 sentences.
- Write a paragraph using sneaked at least 3 times.
- Replace sneaked with a synonym in 3 sentences.
- Identify sneaked in a short story you read.
- Practice saying 5 sneaked sentences aloud.
- Rewrite a sentence using had sneaked.
- Create a dialogue with sneaked in 3 lines.
Quizzes
- What is the past tense of sneak? (Answer: Sneaked)
- Is snuck formal or informal? (Answer: Informal)
- Correct or incorrect: “I sneaked yesterday”? (Answer: Correct)
- Fix this: “She not sneaked out.” (Answer: She didn’t sneak out.)
- What’s the interrogative form of “He sneaked”? (Answer: Did he sneak?)
- Choose the synonym: creep, run, jump. (Answer: Creep)
- True or false: Sneaked needs a helping verb in simple past. (Answer: False)
- Fill in: They ___ into the room. (Answer: Sneaked)
- Correct or incorrect: “I will sneak yesterday”? (Answer: Incorrect)
- What’s the past perfect form of sneak? (Answer: Had sneaked)
True or False
- Sneaked is the past tense of sneak. (True)
- Snuck is always incorrect. (False)
- Sneaked requires had in simple past. (False)
- You can say “Did she sneak?” for interrogative. (True)
- Sneaked changes spelling for different subjects. (False)
- Creep is a synonym for sneak. (True)
- “I sneaked tomorrow” is correct. (False)
- Sneaked is a regular verb. (True)
- Negative form uses didn’t sneak. (True)
- Slink is unrelated to sneak. (False)
Conclusion
Mastering the sneaked tense is a simple yet powerful way to improve your English grammar.
By understanding its formation, sentence structure, and common pitfalls, you can confidently use sneaked in writing and conversation.
If you’re sneaking a peek at a gift or describing a stealthy adventure, this verb adds precision to your past-tense narratives.
Practice with the examples, exercises, and quizzes provided to reinforce your skills.
Try writing your own sentences or use a grammar checker to polish your work.
Keep exploring verb conjugation and related verbs like creep or slip to expand your vocabulary.
Share your progress in the comments or challenge yourself with our quizzes to become a sneaked tense pro!