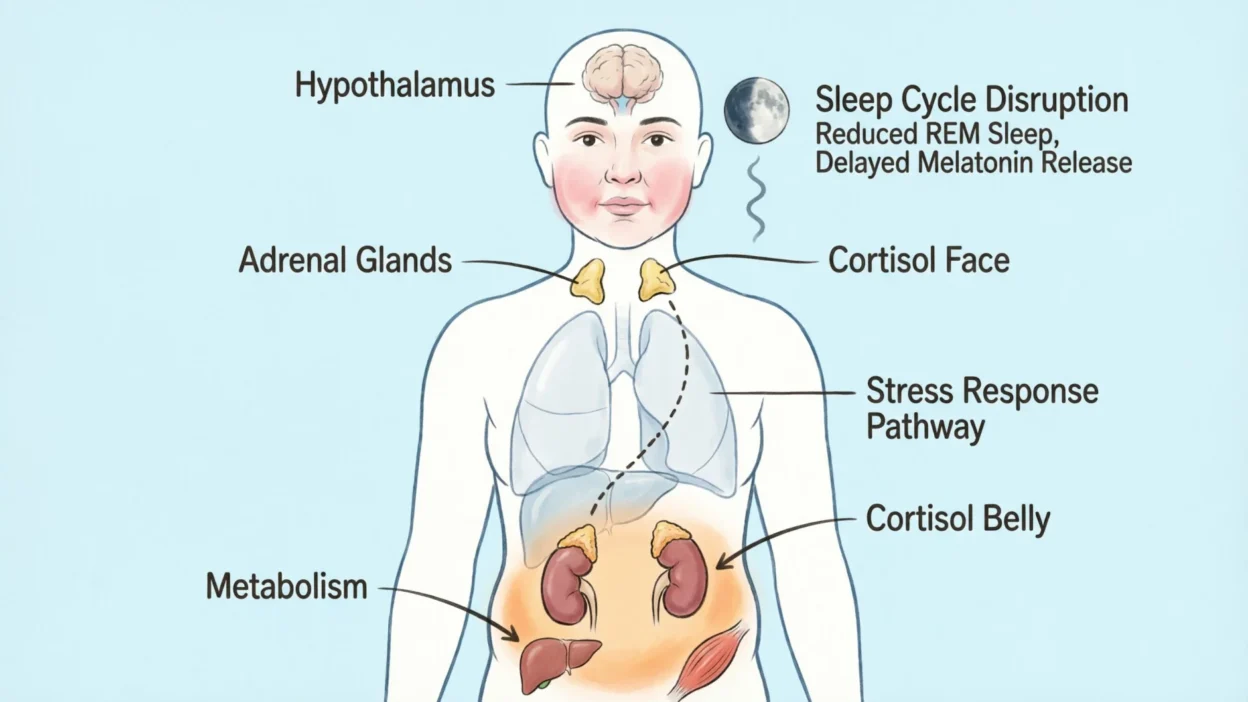
Definition: Cortisol is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps regulate stress response, metabolism, immune function, and energy levels. Often called the stress hormone, cortisol plays a key role in maintaining balance in the body. Understanding what cortisol is, what causes high cortisol, and how to lower cortisol levels can help improve overall health.
Cortisol is one of the most important hormones in the human body, yet many people misunderstand its role. Known as the stress hormone, cortisol does much more than respond to stress it regulates metabolism, inflammation, blood sugar levels, sleep cycles, and immune function.
When cortisol levels are balanced, they help maintain energy, focus, and emotional stability. However, high cortisol levels caused by chronic stress, poor sleep, or lifestyle habits can lead to weight gain, anxiety, fatigue, and other health issues.
Medical research from reputable health institutions shows that understanding cortisol function and recognizing cortisol symptoms early can support better long-term health outcomes.
If you want to know how to tell if cortisol is high, what foods trigger cortisol spikes, or how to lower cortisol naturally, this complete guide covers everything you need to know. By learning how to balance cortisol levels effectively, you can improve both mental and physical well-being.
What Is Cortisol? (Cortisol Pronunciation & Basic Understanding)
Cortisol (pronounced KOR-tih-sol) is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands located above the kidneys. Understanding what is cortisol is essential because it influences many vital systems.
The main cortisol function includes:
- Regulating metabolism and energy use
- Controlling inflammation
- Supporting immune system function
- Managing blood sugar levels
- Helping the body respond to stress
Cortisol naturally follows a daily rhythm highest in the morning and lowest at night.
Cortisol Function How Cortisol Works in the Body
The cortisol function goes beyond stress management. It helps maintain homeostasis by:
- Increasing glucose availability for energy
- Supporting brain alertness during challenges
- Regulating inflammation
- Maintaining blood pressure
During a cortisol spike, the body activates the fight-or-flight response, preparing you to react quickly.
Cortisol and the Stress Response
When you experience stress, the brain signals the adrenal glands to release cortisol. Short-term cortisol spikes are helpful, improving focus and energy.
However, chronic stress leads to:
- High cortisol levels
- Poor sleep
- Increased fat storage (especially cortisol belly)
Understanding what causes high cortisol is important for prevention.
What Causes High Cortisol?
Common causes include:
- Chronic psychological stress
- Lack of sleep
- Excess caffeine intake
- Overtraining in exercise
- Certain medications
- Medical conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome
Cortisol triggering foods like excessive sugar or ultra-processed foods may also contribute indirectly by destabilizing blood sugar.
Effects of High Cortisol Levels (High Cortisol Symptoms)
High cortisol symptoms can vary but often include:
- Weight gain (especially cortisol belly)
- Puffy or round “cortisol face”
- Anxiety or mood swings
- High blood pressure
- Sleep disturbances
- Brain fog
Symptoms of high cortisol levels in females may also include hormonal imbalance, irregular cycles, and increased acne.
Effects of Low Cortisol Levels
Low cortisol may cause:
- Chronic fatigue
- Low blood pressure
- Weak stress response
- Muscle weakness
Medical evaluation may be needed to determine underlying causes.
Cortisol and Sleep
Healthy cortisol levels follow a circadian rhythm:
- High in the morning to wake you up
- Lower at night to support sleep
High cortisol at night often leads to insomnia and poor recovery.
Cortisol and Weight Gain (Cortisol Belly & Cortisol Face)
Long-term elevated cortisol promotes:
- Abdominal fat storage (cortisol belly)
- Facial puffiness (cortisol face)
- Increased appetite and cravings
Managing stress and stabilizing blood sugar can reduce these effects.
Cortisol and Mental Health
High cortisol affects brain areas responsible for mood and memory. Chronic elevation may contribute to:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Poor concentration
Learning how to reduce cortisol can improve emotional balance.
How to Lower Cortisol Naturally
If you’re asking, “How do I lower my cortisol levels?”, evidence-based strategies include:
- Regular moderate exercise
- Meditation or mindfulness
- Balanced nutrition
- Quality sleep routines
- Social connection
These help lower cortisol levels safely.
How to Balance Cortisol Levels Long-Term
Ways to balance cortisol levels:
- Maintain consistent sleep schedule
- Reduce chronic stress exposure
- Avoid overtraining
- Stay hydrated
- Practice relaxation techniques
What Foods Are High in Cortisol Levels? (Diet & Cortisol Detox Diet)
Foods don’t contain cortisol itself, but certain foods trigger cortisol spikes:
- Refined sugars
- Highly processed foods
- Excess caffeine
- Alcohol
A cortisol detox diet focuses on:
- Whole foods
- Healthy fats
- Protein-rich meals
- Magnesium-rich foods
Cortisol Detox Myth vs Reality
A “cortisol detox” isn’t about cleansing toxins but supporting natural hormone balance through lifestyle improvements.
What Supplements Lower Cortisol?
Some supplements to reduce cortisol may include:
- Magnesium
- Ashwagandha
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Rhodiola
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting cortisol treatment with supplements.
Cortisol Test How to Tell If Cortisol Is High
Doctors may recommend a cortisol test if symptoms appear.
Testing methods include:
- Blood test
- Saliva test
- Urine test
These help confirm high cortisol levels or adrenal issues.
Cortisol Treatment When to See a Doctor
Seek medical guidance if you experience:
- Persistent high cortisol symptoms
- Severe fatigue or weight changes
- Sleep problems or mood disturbances
Professional cortisol treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medication, or further evaluation.
Daily Habits That Affect Cortisol Levels
Positive habits:
- Morning sunlight exposure
- Balanced meals
- Stress reduction
Negative habits:
- Overworking
- Poor sleep hygiene
- Excess stimulants
Summary & Key Takeaways
Cortisol is a vital hormone responsible for stress response, metabolism, and immune regulation.
Balanced cortisol levels support energy, sleep, and mental health, while high cortisol can cause weight gain, mood issues, and fatigue.
Understanding what causes high cortisol, recognizing cortisol symptoms, and learning how to lower cortisol naturally can improve long-term health.
Through healthy lifestyle choices, stress management, proper diet, and medical support when necessary, you can maintain balanced hormone function and overall wellness.