Have you ever come across the word “evaluate” and wondered what it truly means? Whether in school, at work, or in everyday life, understanding how to evaluate something is an essential skill.
The term might sound formal, but it’s simply about examining, assessing, or judging information, options, or situations carefully before making a decision.
From analyzing data in academics to assessing products before buying, evaluating helps us make informed choices and avoid mistakes.
In this guide, we’ll explore the meaning of evaluate, show how it’s used in different contexts, and provide practical tips to improve your evaluation skills.
You’ll also learn the differences between evaluate, assess, and analyze, along with common mistakes to avoid. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to use evaluate correctly in both writing and conversation.
Definition of Evaluate

The word “evaluate” is commonly used in English to mean examining something carefully to judge its value, quality, or significance. According to the dictionary, to evaluate is “to form an idea of the amount, number, or value of something” or “to assess or judge carefully.” In simpler terms, evaluating means looking closely at details, considering evidence, and making an informed decision.
For example, in academics, a teacher might ask students to evaluate a research paper, meaning they should analyze its strengths, weaknesses, and overall quality before forming an opinion. In business, managers evaluate employee performance by examining achievements, skills, and contributions to make fair decisions about promotions or improvements. Even in everyday life, you evaluate choices—like deciding which smartphone to buy or choosing a restaurant for dinner—by considering different factors.
Synonyms for evaluate include: assess, judge, appraise, analyze, review, and examine. Understanding these synonyms helps expand your vocabulary and ensures you use the word correctly in different contexts. Evaluating is more than just forming an opinion—it involves critical thinking, careful observation, and reasoning.
Etymology and History of Evaluate
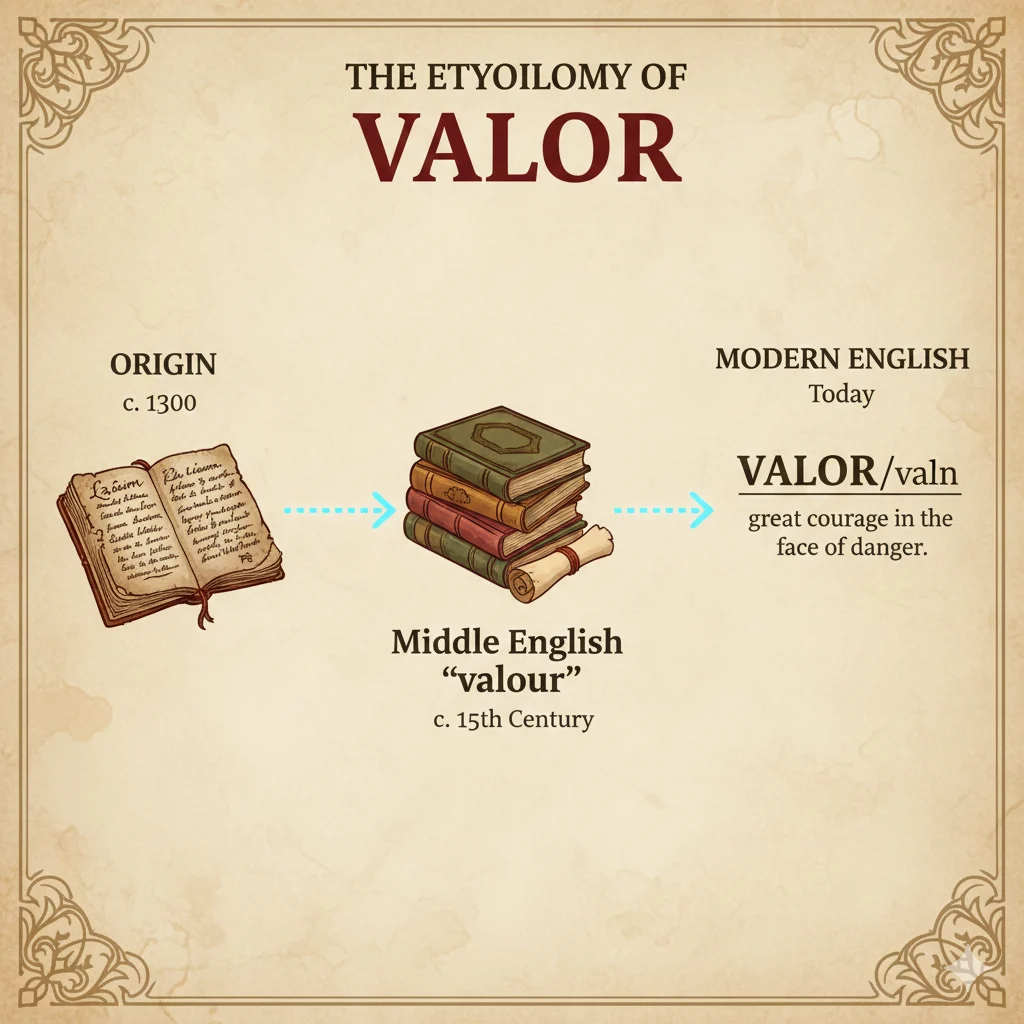
The word “evaluate” has an interesting origin that helps us understand its meaning more deeply. It comes from the Latin word valere, which means “to be worth” or “to have value.” The modern English verb “evaluate” started appearing in the 17th and 18th centuries, originally in contexts related to determining the monetary value of objects. Over time, its use expanded beyond financial contexts to include assessing quality, performance, and significance in a wide range of fields.
By the 19th and 20th centuries, “evaluate” had become a standard term in academics, science, and professional work. Teachers would ask students to evaluate essays, researchers would evaluate experiments, and managers would evaluate projects or employee performance. Today, the word is used in almost every part of life—from evaluating personal decisions to analyzing complex data in business and technology.
Understanding the history of evaluate is helpful because it shows that at its core, the word is about determining value. Whether you are judging a piece of work, a product, or a situation, evaluating always involves careful observation, analysis, and reasoning—skills that have been valued for centuries.
Different Contexts of Evaluate

The word evaluate is versatile and appears in many different contexts, each with its own focus. Understanding these contexts helps you use the word accurately in both writing and conversation.
1. Academic Context:
In schools and universities, students are often asked to evaluate essays, research papers, or experiments. This involves analyzing evidence, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and forming a judgment based on facts. For example, a teacher might say, “Evaluate the effectiveness of the author’s argument,” which requires critical thinking rather than just summarizing.
2. Business and Professional Context:
In the workplace, managers and leaders evaluate employee performance, projects, or strategies. Evaluation here is crucial for decision-making, promotions, or improvements. For instance, a manager might evaluate a marketing campaign by reviewing results, customer feedback, and overall impact on the business.
3. Everyday Life Context:
Even in daily life, we constantly evaluate. From choosing the best product to buy, deciding which route to take while driving, or assessing options before a major life decision, evaluating helps us make informed choices.
4. Technology and Science Context:
In research, data analysis, or software testing, evaluating involves assessing results, accuracy, and effectiveness. For example, scientists evaluate experiment outcomes to draw conclusions or improve methodologies.
By recognizing these contexts, it becomes clear that evaluating is about careful judgment based on evidence, regardless of the situation.
How to Use Evaluate in a Sentence

Using the word evaluate correctly in a sentence is important to communicate your ideas clearly. The term typically involves careful judgment, analysis, or assessment of something. Here are some examples across different contexts to guide you:
1. Academic Context:
- “Students are required to evaluate the sources used in their research papers.”
- “Please evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed solution in this case study.”
2. Business and Professional Context:
- “The manager will evaluate employee performance at the end of the quarter.”
- “We need to evaluate the success of our marketing campaign before launching the next one.”
3. Everyday Life Context:
- “Before buying a new laptop, I always evaluate the features and reviews.”
- “She carefully evaluated her options before choosing a university.”
4. Technology or Science Context:
- “Researchers must evaluate the experiment results to ensure accuracy.”
- “The software team will evaluate the application’s performance before the update is released.”
Tips for Using Evaluate:
- Use it when making informed judgments rather than just stating opinions.
- Pair it with nouns like results, options, performance, data, or evidence for clarity.
By practicing these examples, you can confidently use evaluate in both formal writing and everyday conversations.
Evaluate vs. Similar Words
The word evaluate is often confused with similar terms like assess, analyze, and appraise, but each has its own nuance. Understanding these differences helps you use them correctly.
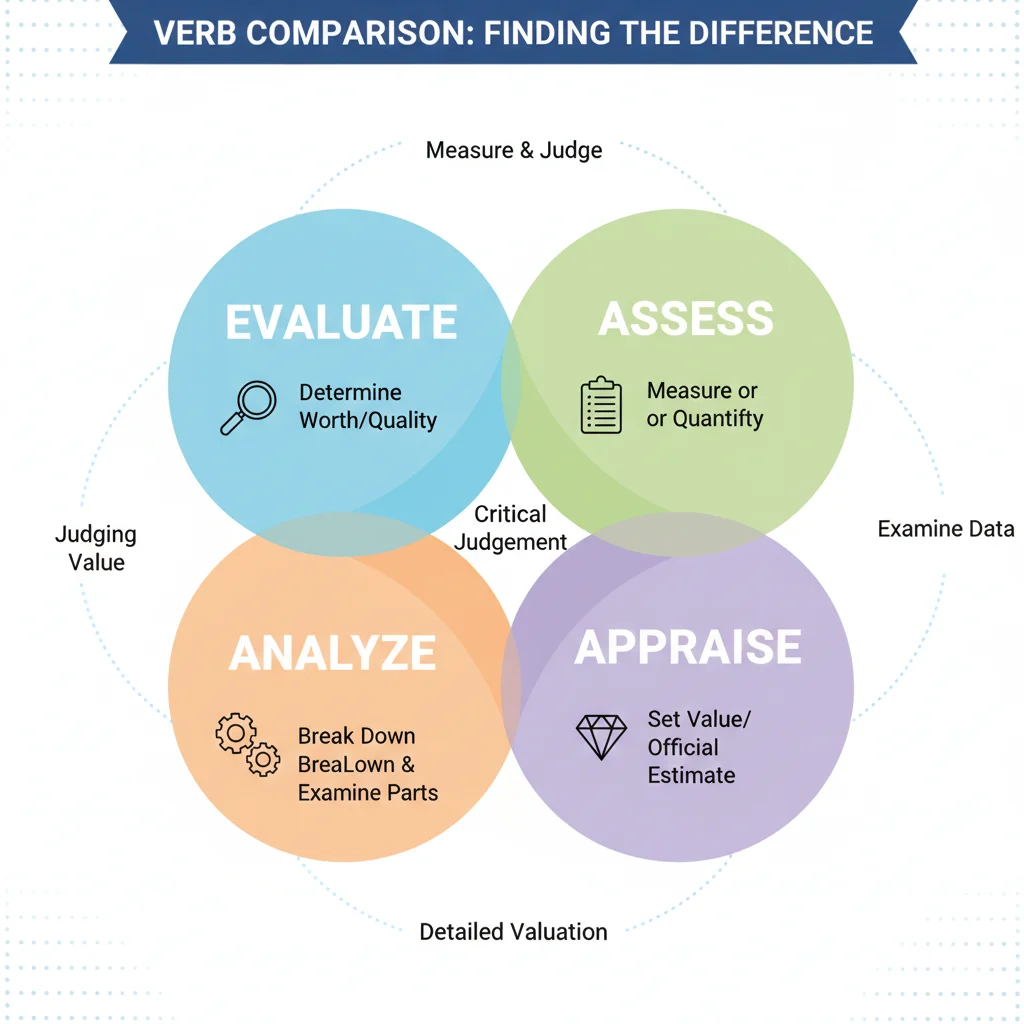
1. Evaluate vs. Assess:
While both involve judgment, assess often focuses on measuring or estimating value, quality, or performance. Evaluate goes a step further by including critical thinking and forming a conclusion.
- Example: “The teacher will assess your test score” vs. “The teacher will evaluate your overall performance in the class.”
2. Evaluate vs. Analyze:
Analyze means to break something down into parts to understand it better, while evaluate involves judging the value or quality of those parts.
- Example: “We will analyze the survey data to find patterns” vs. “We will evaluate the survey results to decide the next steps.”
3. Evaluate vs. Appraise:
Appraise is often used for determining monetary or material value, like real estate or artwork. Evaluate is broader and can be used in academics, business, and life.
- Example: “The jeweler will appraise the diamond” vs. “The committee will evaluate the candidate’s proposal.”
By understanding these distinctions, you can choose the right word based on context, making your writing and speech clearer and more professional.
Why Evaluating is Important

Evaluating is more than just forming an opinion—it is a critical skill that helps you make informed decisions, solve problems, and improve outcomes in all areas of life. Whether in academics, business, or personal situations, the ability to evaluate allows you to think critically, analyze information, and choose wisely.
1. In Academics:
Students who know how to evaluate can analyze research, understand arguments, and provide thoughtful feedback. This skill is crucial for essays, projects, and exams, helping students go beyond memorization to truly understand and assess information.
2. In Business and Professional Life:
Managers and employees use evaluation to assess performance, review projects, and make strategic decisions. Evaluating carefully ensures resources are used efficiently and helps identify areas for improvement, increasing overall success.
3. In Everyday Life:
Evaluation helps in making everyday choices, such as selecting a product, planning a trip, or deciding on a career path. By weighing options and considering evidence, you reduce mistakes and make smarter decisions.
4. In Technology and Research:
Evaluating data, experiments, or software results ensures accuracy and reliability, which is essential for scientific progress and technological innovation.
In short, evaluating is a foundational skill that supports better thinking, smarter decisions, and successful outcomes across all areas of life.
How to Improve Evaluation Skills
Improving your ability to evaluate effectively is a skill that can benefit academics, work, and daily life. It involves critical thinking, careful observation, and making decisions based on evidence rather than assumptions. Here are some practical steps to enhance your evaluation skills:
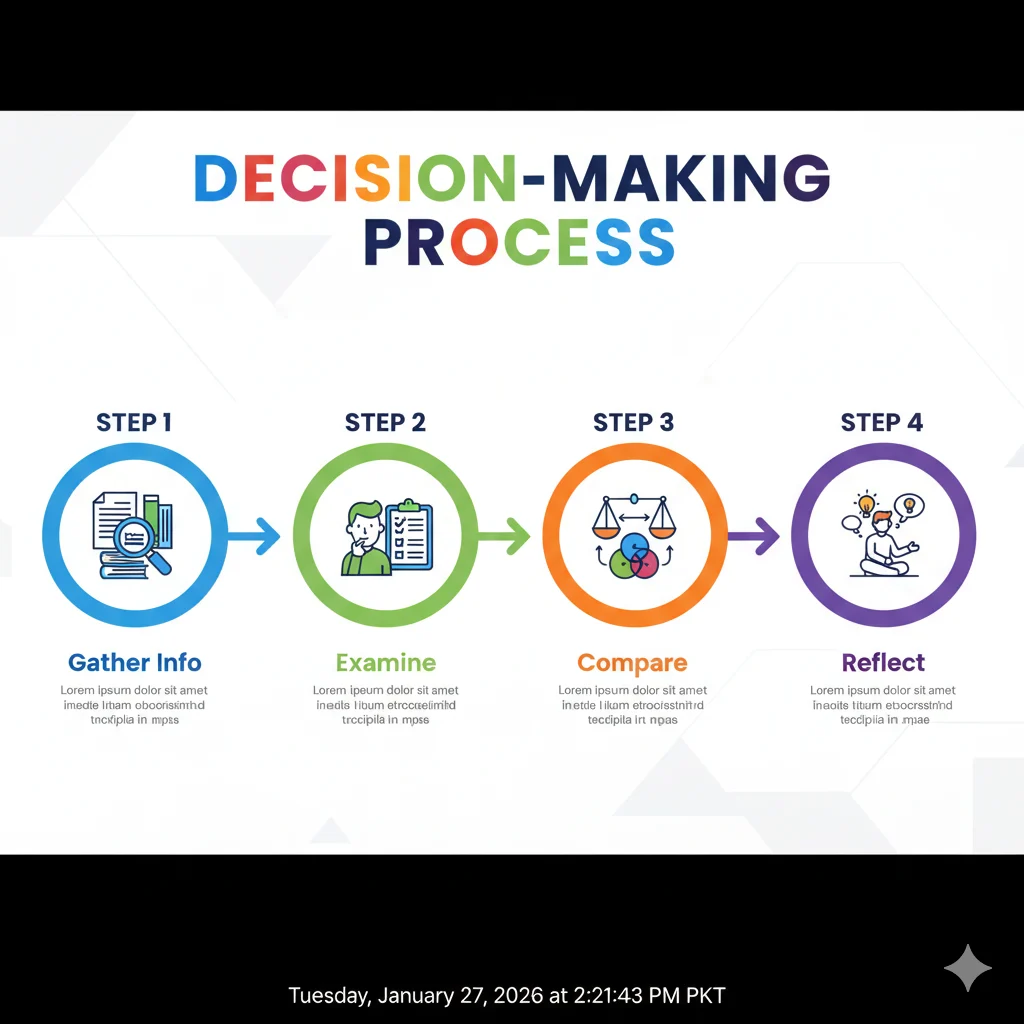
1. Gather Information:
Before evaluating, collect all relevant facts, data, or evidence. Understanding the full picture is essential for making accurate judgments.
2. Examine Details Carefully:
Look beyond the surface. Identify strengths, weaknesses, patterns, and trends. Ask yourself: What works well? What could be improved?
3. Compare Options:
When faced with multiple choices, evaluate each option against consistent criteria. This helps you make fair and informed decisions.
4. Consider Different Perspectives:
Evaluate situations from multiple angles. This reduces bias and allows a balanced judgment.
5. Practice Critical Thinking:
Question assumptions, analyze results, and avoid jumping to conclusions. Critical thinking is key to effective evaluation.
6. Reflect and Learn:
After making a decision, review the outcome. Did your evaluation lead to the best result? Learn from successes and mistakes to improve future evaluations.
By practicing these steps regularly, you can sharpen your evaluation skills, making your decisions more accurate, thoughtful, and effective in every context.
Common Mistakes When Using Evaluate

Even though evaluate is a commonly used word, many people make mistakes when using it in writing or conversation. Being aware of these errors can improve clarity and professionalism.
1. Confusing Evaluate with Assess or Analyze:
As discussed earlier, evaluate involves judgment based on evidence, while assess focuses on measuring, and analyze focuses on breaking things into parts. Using them interchangeably can cause confusion.
- Incorrect: “I will analyze your performance.”
- Correct: “I will evaluate your performance.”
2. Ignoring Evidence:
Evaluation should be based on facts and evidence, not just personal opinion. Skipping research or data can lead to biased or unreliable conclusions.
3. Overgeneralizing:
Making broad statements without detailed examination is a common mistake. Effective evaluation requires specific observations and examples.
4. Misusing in Everyday Conversation:
Some people use evaluate in casual contexts where simpler words like “check” or “look at” might be better. For instance, saying “I’ll evaluate the menu” is better expressed as “I’ll check the menu.”
5. Using Evaluate Only in Formal Contexts:
While it is formal, evaluate can also be used in daily life. Avoid limiting it unnecessarily.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can use evaluate accurately and enhance both your communication and decision-making skills.
Evaluation in Exams and Academic Assignments

In academics, the word evaluate is frequently used in exam questions, essays, and assignments. Understanding how to respond to evaluation-based prompts is crucial for achieving high marks.
When an exam question asks you to evaluate, it expects more than a simple description or explanation. You are required to analyze information, weigh evidence, and form a judgment. For example, a question might ask: “Evaluate the impact of climate change on agriculture.” Here, you must consider both positive and negative effects, provide supporting evidence, and conclude with a reasoned judgment.
Evaluation also differs from describe or explain. While describing only requires stating facts and explaining involves clarifying them, evaluating demands critical thinking. You need to assess the significance, effectiveness, or value of what you are studying.
Tips for evaluating effectively in exams:
- Read instructions carefully to understand the criteria.
- Use evidence and examples to support your points.
- Compare different viewpoints when relevant.
- Conclude with a clear judgment based on analysis.
Mastering evaluation skills not only improves your grades but also develops critical thinking that can be applied in professional and personal contexts.
FAQs About Evaluate
Here are some of the most frequently asked questions about the word evaluate to help you understand its meaning, usage, and context better.
1. What does evaluate mean in school?
In academics, evaluate means to analyze information, examine evidence, and form a judgment. Teachers often ask students to evaluate essays, research, or experiments instead of just summarizing facts.
2. What is the difference between evaluate and assess?
While both involve judgment, assess usually focuses on measuring or estimating value, whereas evaluate involves critical thinking and forming conclusions based on evidence.
3. Can evaluate be used in everyday conversation?
Yes! You can use it when making decisions, like evaluating products, options, or situations. Example: “I need to evaluate which phone to buy before making a choice.”
4. How do you evaluate a situation effectively?
To evaluate effectively:
- Gather all relevant information
- Consider the pros and cons
- Analyze details critically
- Form a reasoned judgment based on evidence
5. How is evaluate used in professional settings?
In business or work, evaluating often involves reviewing performance, projects, or strategies to make informed decisions, improve outcomes, and ensure efficiency.
These FAQs make it easier to understand and apply evaluate correctly in academics, business, and daily life.
Quick Tips for Everyday Evaluation
Evaluating doesn’t have to be complicated. By practicing a few simple strategies, you can make better decisions in your daily life. Here are some quick tips for everyday evaluation:
1. Define Your Goal:
Before evaluating anything, ask yourself, “What am I trying to decide or achieve?” Having a clear purpose makes the evaluation more focused and effective.
2. Gather Relevant Information:
Collect facts, reviews, and opinions before making a decision. For example, if buying a product, check features, ratings, and prices.
3. Compare Options:
List the advantages and disadvantages of each choice. This helps you see which option meets your goals best.
4. Consider Consequences:
Think about the short-term and long-term outcomes of each option. This prevents impulsive or poorly informed decisions.
5. Stay Objective:
Try not to let emotions or biases influence your judgment. Focus on evidence and logic to make a fair evaluation.
6. Reflect After Decisions:
After making a choice, review the results. Did your evaluation lead to the best outcome? Use this reflection to improve future evaluations.
By using these tips, you can evaluate situations quickly and accurately, making your everyday decisions smarter, more confident, and reliable.
Conclusion
Understanding what evaluate means is essential for academics, professional life, and everyday decision-making.
So, what does evaluate mean? To evaluate is to carefully examine, analyze, and judge something based on evidence and reasoning. It is a vital skill used in education, work, and everyday life. By understanding how to evaluate properly, you can make smarter decisions, communicate clearly, and think more critically.
Mastering evaluation is not just about using the right word—it’s about developing a mindset that values careful thinking and informed judgment.