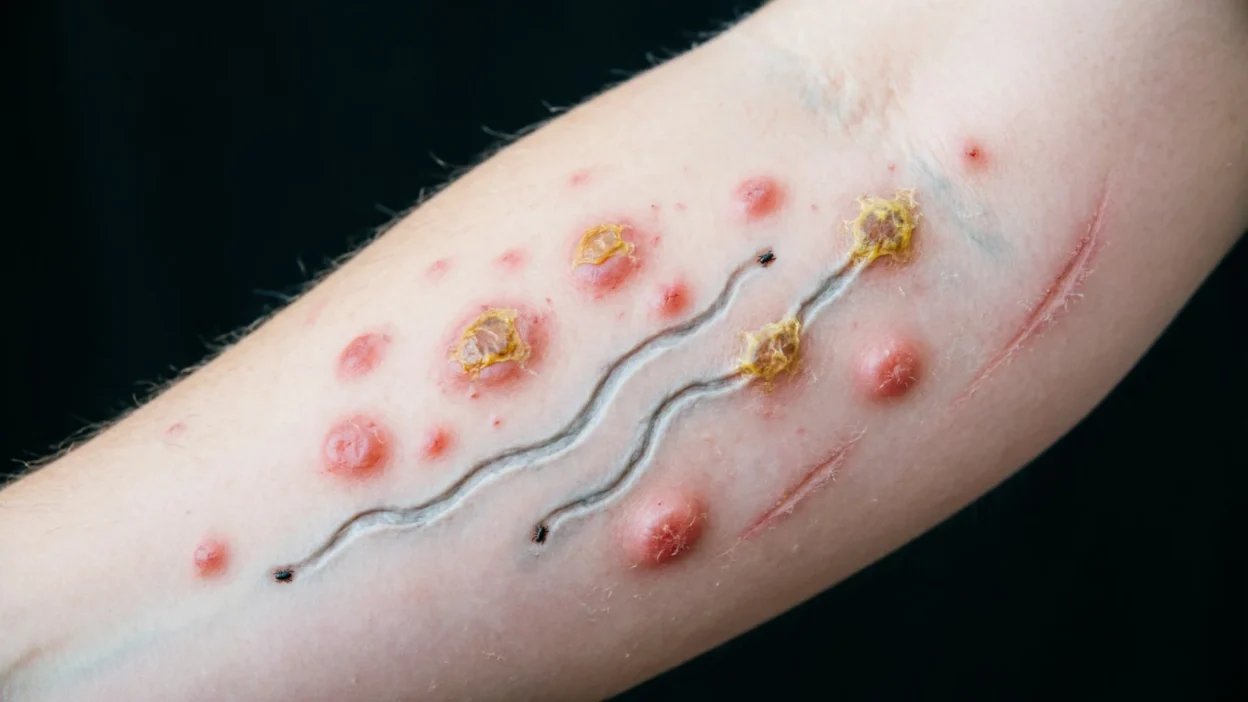
Definition : Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by tiny mites. It appears as small red bumps, burrow lines, and intense itching, often worse at night. Early detection helps prevent spreading and allows prompt treatment.
Scabies is a common skin infestation caused by microscopic mites called Sarcoptes scabiei. Understanding what scabies looks like is essential for early recognition and treatment.
The condition typically causes clusters of small red bumps, burrow tracks, and intense itching, especially at night, which can easily be mistaken for other skin conditions. Identifying early scabies helps prevent its spread to family members or close contacts.
How do you get scabies? Scabies spreads through prolonged skin-to-skin contact or sharing infested clothing, towels, or bedding. While anyone can be affected, children, older people adults, and those living in crowded environments are at higher risk.
This guide covers scabies symptoms, scabies rash pictures, early scabies burrows, treatment options, and prevention tips, helping readers safely understand how to identify scabies, what to do if infected, and how to protect themselves. Always consult a doctor, as scabies treatment must be guided by a healthcare professional.
What is Scabies?
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by the tiny mite Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow into the skin to lay eggs, which triggers itching, inflammation, and rash formation. People often wonder, what are scabies and how do they affect the body. The condition is highly contagious and can spread through direct skin contact or shared items like towels and bedding.
Symptoms generally appear 2–6 weeks after exposure in first-time infestations, while those previously infected may notice symptoms within days. Misidentifying scabies as eczema, allergic rashes, or insect bites can delay proper treatment. Understanding what causes scabies and recognizing early signs allows for prompt scabies treatment and prevents further spread.
What Does Scabies Look Like on Skin?
Scabies can be identified by several key features:
- Tiny red or pink bumps that often appear in clusters.
- Burrow lines, which are thin, wavy tracks showing where mites have tunneled under the skin.
- Blister-like spots or crusted areas in severe infestations.
What does scabies look like to the human eye? You may see small bumps, burrows, or sores caused by scratching. Common areas include fingers, wrists, elbows, waistline, under breasts, and genitals. In children, the scalp, face, and palms can also be affected. Recognizing these signs helps distinguish scabies from other skin conditions, ensuring early medical attention and proper scabies medication.
Early Signs of Scabies
Early scabies can be subtle, making recognition crucial. Common early indicators include:
- Intense nighttime itching
- Small red or pink bumps forming clusters
- Early scabies burrows, visible as thin raised lines, often between fingers, wrists, and waistline
- Mild skin irritation or redness
Early detection answers questions like, how does scabies first look? and how do I tell if I have scabies? Prompt recognition allows for faster treatment and reduces the chance of spreading to family members.
Scabies Rash vs Other Skin Conditions
Scabies rash can resemble other conditions, so it’s important to know the differences:
- Eczema: Dry, scaly patches, rarely with burrows.
- Allergic rashes: Appear suddenly, resolve quickly when allergens are removed.
- Bed bug bites: Linear clusters on exposed areas; do not form burrows.
- Acne: Typically localized to face, chest, or back, not burrowed.
Identifying the scabies rash correctly ensures proper scabies treatment and prevents misdiagnosis.
Where Does Scabies Usually Appear?
Scabies tends to target warm, thin-skinned areas. Common locations include:
- Between fingers and on wrists
- Waistline and lower abdomen
- Under breasts and genitals
- Feet and ankles
- Scalp and face in infants or children
Knowing where scabies appears is essential for how to identify scabies early and distinguish it from other rashes.
What Do Scabies Burrows Look Like?
Burrows are thin, gray or white, S-shaped lines created by mites under the skin. These are most visible on fingers, wrists, waist, and under breasts.
Early scabies burrows are subtle but a clear indicator of infestation. Burrows are a hallmark sign that differentiates scabies from eczema or mosquito bites.
Scabies Symptoms Beyond the Rash
Other scabies symptoms include:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- Scratching-induced sores or crusts
- Risk of secondary bacterial infections
- In severe cases, crusted scabies may develop, with thickened scaly patches
Recognizing these symptoms helps answer, what are three symptoms of scabies? and ensures timely medical care.
How Scabies Looks in Different Skin Tones
- Light skin: Red or pink bumps, burrow lines visible
- Dark skin: Brown, purple, or darker red bumps; burrows may be less obvious
- Children: Scalp, face, and palms may also show bumps
Visual variation is important for accurately answering what does scabies look like on humans across different skin tones.
How Doctors Diagnose Scabies
Doctors diagnose scabies through:
- Visual examination of bumps, burrows, and rashes
- Skin scraping under a microscope to detect mites or eggs
- Dermoscopy for magnified visualization
Accurate diagnosis ensures correct scabies treatment, avoiding delays or complications like crusted scabies.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Treatment options include:
- Prescription creams: Permethrin, crotamiton
- Oral medications: Ivermectin for severe or crusted cases
- Household contact treatment to prevent reinfestation
Home care is essential: wash bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water. Following these steps can get rid of scabies in 24 hours in mild cases, while more severe infestations require scabies medication prescribed by a doctor.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical care if:
- Severe or persistent itching
- Rapidly spreading rash
- Signs of infection from scratching
- Symptoms not improving after initial treatment
- Infants, older people, or immunocompromised are affected
Professional care is essential for early scabies recognition and proper management.
Prevention Tips
Prevent scabies by:
- Avoiding skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals
- Washing bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water
- Treating all household contacts simultaneously
- Avoiding shared personal items
These steps reduce risk and help get rid of scabies quickly, while preventing reinfestation.
FAQs About Scabies
How do I tell if I have scabies? Look for red bumps, burrow lines, and nighttime itching.
How does scabies first look? Small red bumps and subtle burrows, often between fingers or wrists.
What are three symptoms of scabies? Itching, burrows, and red bumps.
How to cure scabies fast? Use prescription creams or oral medication under medical supervision.
What does crusted scabies look like? Thick, scaly patches, often highly contagious.
What does scabies look like on a dog? Dogs can get a different type of scabies mite causing itching; human scabies does not typically infect pets.
Conclusion
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by microscopic mites. Recognizing what scabies looks like—from tiny red bumps, early scabies burrows, and scabies rash to severe crusted scabies—is crucial for early treatment.
Proper scabies treatment with prescription creams, oral medications, and hygiene measures can get rid of scabies in 24 hours in mild cases.
Early recognition and how to identify scabies prevent spreading to family members and reduce complications.
By following prevention tips and consulting a healthcare professional, scabies can be effectively treated, protecting both you and your household.